# SOPs FIR Langen
EDDF, EDDG, EDDK, EDDL, EDDR, EDDS, EDFH, EDFM, EDLN, EDLP, EDLV, EDLW, EDTL, ETAD, ETAR, ETHF, ETHN, ETNG, ETNN, ETOU, ETSB
# EDDF - Frankfurt/Main Airport
# EDDF - Overview
Frankfurt/Main airport is one of the largest airports in Europe and the world. Together with London Heathrow, it is also the busiest airport on the VATSIM network.
**All stations at Frankfurt require a Tier 1 endorsement ([mentoring session necessary](https://training.vatsim-germany.org/ "Training Request Thread")).** DEL and GND positions require the EDDF\_GNDDEL endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher. TWR requires the EDDF\_TWR endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. All APP/DEP positions require the EDDF\_APP endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
**Training:** Controllers with the S1 rating can staff TWR positions during their training (active EDDF\_TWR solo endorsement required). Controllers with the S2 rating can staff APP/DEP positions during their training (active EDDF\_APP solo endorsement required).
### Frankfurt/Main ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **DEP-ATIS**
| ADDF
| EDDF\_D\_ATIS
| 118.730
| --
| --
|
| **ARR-ATIS**
| AADF
| EDDF\_A\_ATIS
| 118.030
| --
| --
|
| **Delivery**
| DFC
| EDDF\_DEL
| 122.035
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| Coordinator
| --
| EDDF\_CO\_DEL
| --
| event position, monitors 122.035
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **Apron**
|
| **Center Apron**
| DFGC
| EDDF\_C\_GND
| 121.855
| primary
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **West Apron**
| DFGW
| EDDF\_W\_GND
| 121.755
| secondary
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| East Apron
| DFGE
| EDDF\_E\_GND
| 121.955
| tertiary
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
South Apron
| DFGS
| EDDF\_S\_GND
| 121.655
| not yet used in reality
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| Deicing
| DFGI
| EDDF\_ICE\_GND
| 121.985
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **Tower / Ground**
|
| **Center Tower**
| DFTC
| EDDF\_C\_TWR
| 118.780
| primary
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_TWR](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **West Tower**
| DFTW
| EDDF\_W\_TWR
| 124.855
| secondary
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_TWR](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| North Tower
| DFTN
| EDDF\_N\_TWR
| 136.500
| tertiary
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_TWR](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| South Tower
| DFTS
| EDDF\_S\_TWR
| 119.905
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_TWR](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| Supervisor
| --
| EDDF\_CO\_TWR
| --
| event position, airport-wide flow control and decision making
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_TWR](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)")
|
| Ground
| DFG
| EDDF\_GND
| 121.805
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **Arrival / Departure**
|
| **North Approach**
(Pickup)
| DFAN
| EDDF\_N\_APP
| 120.805
| primary arrival
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)")
|
| South Approach
(Pickup)
| DFAS
| EDDF\_S\_APP
| 125.355
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **North Arrival**
(Feeder)
| DFANT
| EDDF\_H\_APP
| 127.280
| primary feeder
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| South Arrival
(Feeder)
| DFAST
| EDDF\_L\_APP
| 118.505
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| North Departure
| DFDN
| EDDF\_N\_DEP
| 120.155
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **South Departure**
| DFDS
| EDDF\_S\_DEP
| 136.130
| primary departure
| Tier 1: [EDDF\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
### CTR Frankfurt/Main
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-03/eddf.jpg)
*Frankfurt/Main D-CTR - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
### Airport Capacity
| **Outbound EDDF** | **Inbound EDDF** |
|---|
| **RWY 18** | 40 / hr
every 2 min
+ 10 extra movement | **alternating** | 35 - 40 / hr |
| **RWY 25C / 25L** | 25 / hr
every 3 min
+ 5 extra movement | **parallel independent** | 50 - 60 / hr |
| **RWY 07C / 07R** | 40 / hr
every 2 min
+ 10 extra movement | **single runway** | 25 - 30 / hr |
| **Sector Arrival South (DFAS)**: 8 - 10 aircraft at the same time |
| **Sector Arrival North (DFAN)**: 10 - 12 aircraft at the same time |
- **RWY 25:** 10 - 12 active startup approvals at the same time
- **RWY 18/07:** up to 15 active startup approvals at the same time
# EDDF - Delivery
Frankfurt Delivery is responsible for enroute and startup clearances for all departing IFR aircraft. VFR aircraft have to call Delivery for departure information. Information about VFR squawk codes at EDDF can be found in the Tower chapter. For all departures (IFR and VFR) Frankfurt Delivery is the first station to contact.
**Startup:** Startup will normally be given when the pilot is ready for pusback and startup and not together with the IFR clearance. When startup clearance cannot be given immediately or the pilot is not ready for startup within the next 5 minutes during high traffic situations, the pilot needs to stay on Delivery frequency until he receives startup clearance. If an expected startup time (TSAT) exists, the pilot should be informed about it. This procedure might be necessary during events with a lot of outbound traffic.
**Maximim active Startup Approvals** at the same time (status SUG until DEP) per runway (use the vSID startup counter):
**RWY 25:** 10 - 12
**RWY 07/18:** 15
Depending on the traffic situation, only for a short time more startup approvals shall be used.
With startup Delivery transfers the aircraft to the responsible Apron station depending on the current stand.
**Events:** For events Delivery has a very important role regarding the efficient traffic flow at the airport and runways. Check the usage of slots as well as the Event Coordinator article for more information. During events startup should only be issued when the outbound is ready for pushback within the next 5 minutes. Otherwise clearance can already be given and the pilot needs to report ready for startup on Delivery frequency.
### SID Assignment
The runway used for departure and the corresponding SID are based on the first waypoint of a flight plan. Outbounds to the north (MARUN, OBOKA, TOBAK) will use runway 25C/07C by default. Departures to the east, south and west (SULUS, CINDY, ANEKI, SOBRA, ULKIG) will get runway 18 for departure. There is only one exception of that during 07 operations, where outbounds to the east (SULUS / KOMIB) will also use runway 07C.
**South Apron:** Aircraft parked in the southern part of the airport can be told to prepare both runways (25C/07C and 07R/25L), final decision will be by Tower later on during taxi depending on inbound traffic. This should be noted in the remark section (e.g. "25C/25L"). During low traffic situation, runway 25L/07R can be issued directly.
The default SID designator for each runway and waypoint can be seen in the table below.
| **Waypoint** | **RWY 25C** | **RWY 18** | **RWY 07C** |
| **ANEKI** | - | L | - |
| **CINDY** | - | S | - |
| **KOMIB** | - | - | D |
| **OBOKA** | M / G | - | E / D |
| **MARUN** | M / F | - | E / D |
| **SOBRA** | - | L | - |
| **SULUS** | - | S | D |
| **TOBAK** | M / F | - | D |
| **ULKIG** | - | L | - |
*[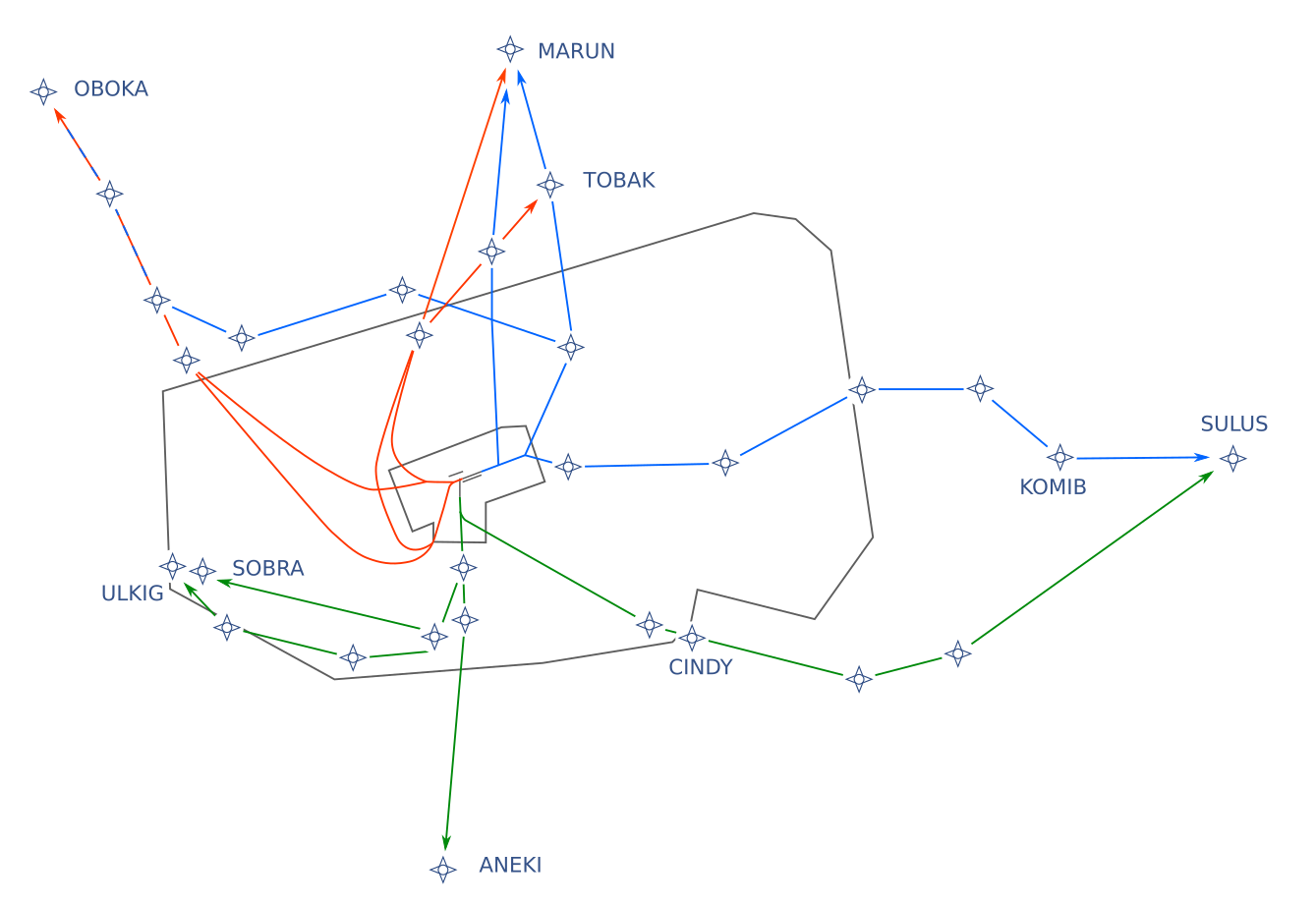](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/eddf-sid-waypoints.png)Location of waypoints that are available for flights out of Frankfurt*
For a quick overview the **[Quicksheet for EDDF](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/xKbC3HDGMj4Ae2E)** includes all assignment rules.
The Quicksheet includes all useful SIDs outbound EDDF, with the ones for standard operation set in bold font. For deviation from these rules, **coordination between** **Delivery and the Tower** controllers is required, as he is responsible for the departure sequences. Be advised that non-standard SIDs can create dependencies to other arrivals and departures. **Exemption:** Departures in brackets can be cleared **without prior coordination** when filed or requested by a pilot.
For almost all SIDs, **no** coordination with APP is required as the routes are designed in a way that they don't affect the inbounds. Only the Non-RNAV-SIDs (Q/C/B) as well as R/T SIDs from runway 18 need prior coordination with APP
Especially during high workload for TWR default SIDs have to be used. If necessary the pilot's filed route has to be amended by Delivery (often a complete new route is required).
Additonally you can use the **[SOP-Quicksheet for EDDF](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/rJCQS6FLB9fwk6s)** as a reference (this is by no means the entire SOP but covers the most important procedures)
### Departure Routes
#### Runway 25C/25L
**M/H/W/K-Departures:** Runway 25C/25L is primarily used for northbound flights. All aircraft except 2-engine Heavies are always assigned the M/H-Departures (so called "Südumfliegung") by default. After departure they lead with a left turn towards the south before turning to the north. This is for two reasons: Noise abatement for cities directly west of the airport and to avoid conflicts with 25R missed approaches. If the above mentioned aircraft types are not able to fly this departure route (e.g. they cannot comply with the climb restriction), they need to use the F and G-Departures.
W and K departures have exactly the same flight path as M/H departures but they require special equipment (RNP + fixed radius). Therefore they will only be assigned when filed in the flight plan or requested by the pilot. Coordination with TWR / APP is not necessary because of the identical flight path.
**F/G-Departures:** Heavies with 2 engines will get a departure route with Designator F/G and turn directly north after take-off (deviations due to weather possible). Non-standard departures towards the south that use runway 25C/25L (e.g. to save taxi time) will also use Designator F (e.g. CINDY\_F).
**N/P-Departures:** Night Departures with Designator N shall be used for all 3- and 4-engined Heavy and Super aircraft between 2200-0700LT. Single- and Twin-Props may use Designator P to SOBRA instead of runway 18.
**Low Visibility Operations:** During LVO all departing traffic that is able to fullfill the climb restriction (including two engined heavies) out of runway 25C/25L should get the M/H SIDs due to restrictions with approaching traffic.
#### Runway 07C/07R
**E/D-Departures:** Runway 07C/07R is used for north- and eastbound flights. Light and Medium aircraft are assigned a departure with Designator E, if available. Heavy and Super aircraft are assigned a departure with Designator D. Non-standard departures to the south from runway 07C (e.g. due to tailwind on runway 18) will also use Designator E/D (e.g. ANEKI\_E).
Between 2200-0700 LT all flights towards the north and east should get Designator D due to noise abatement.
**SULUS-Departures:** During 07 operations departures to the east (SULUS, KOMIB) are sent only via runway 07C/07R and not via runway 18.
**X/Y-Departures:** Designator X and Y are only available for departures to the south and west and for aircraft with special equipment (RNP + fixed radius). They should not be used.
#### Runway 18
In standard configuration runway 18 is used for outbound flights to the south (ANEKI, CINDY), west (SOBRA, ULKIG) and east (SULUS, KOMIB). SIDs with Designator S and L should be used according to the table above. S is always the shorter routing, while L is the one used if someone cannot comply with the restrictions on the S route (exception: ULKIG#L shall be preferred). SOBRA#U can be used when filed while all other SIDs with designator R and T shall not be used. During 07 operations runway 18 is not used for flights to SULUS / KOMIB.
During 25 operations, aircraft parked in the west or south can use non-standard departures from runway 18 to save taxi time (OBOKA\_S, MARUN\_S, TOBAK\_S). During 07 operations, runway 18 instead of runway 07 shall **NOT** be assigned due to conflicts with inbound traffic.
### Datalink Clearance (PDC/DCL)
At Frankfurt Airport we offer Datalink Clearance to the pilots throughout the **[Hoppie System](https://www.hoppie.nl/acars/)** and the Topsky Plugin. The airport code EDDF should be used (already preselected).
An example of the DCL message the pilot will receive can be seen below. **Startup option in the DCL window need to be set to "YES" when startup should be approved via Datalink.** By default every outbound has to call Delivery for startup.
Other DCL messages can be enabled within the Topsky CPDLC settings file manually.
CLD 2042 220117 EDDF PDC 026 SAS461L CLRD TO EKCH OFF 25C VIA MARUN7M SQUAWK 2037 ADT MDI NEXT FREQ 122.035 ATIS H REPORT READY ON 122.035
### Additional Information
#### vSID Rules/Areas
The following alias commands (.command**<space><enter>**) can be used to toogle vSID rules/areas.
| **Alias** | **vSID Command** | **Description** |
| **.south** | .vsid area eddf south | all northbound outbounds parking in the south will get runway 25L/07R for departure
|
| **.east25** | .vsid area eddf east25 | all outbounds parking east of N5 will get runway 25C for departure
|
| **.west18** | .vsid area eddf west18 | all outbounds parking west of N11 will get runway 18 for departure
|
| **.gat18** | .vsid area eddf gat18 | all outbounds parking at the new GAT will get runway 18 for departure
|
| **.sulus18** | .vsid rule eddf sulus18
| all SULUS outbounds via runway 18 instead of runway 07C/07R
|
| **.allnorth** | .vsid rule eddf allnorth | all outbounds to the north will get F/G departures out of runway 25C
|
| **.night** | .vsid night eddf | **disable** night SIDs (enabled by default)
|
| **.lvp** | .vsid lvp eddf | no F/G departures out of runway 25C
|
#### Old SIDs
Over time several SIDs have been replaced. New controllers might not know the old ones that a pilot with an older AIRAC cycle could have in his database. If someone only has an outdated AIRAC cycle, the old SIDs could be used instead of a vectored departure. You will find the current equivalents in the table below.
| **Old Waypoint** | **Current Waypoint** | **Route to use in case of old AIRAC** |
|---|
| **BIBTI** | OBOKA | **BIBTI #M/#G or #E/#D SID** |
| **DKB** | CINDY | **DKB #S SID** for CINDY Z74 HAREM T104 DKB |
| **NOMBO** | CINDY | **NOMBO #S SID** for CINDY Z74 LAMPU DCT NOMBO |
| **RATIM** | CINDY | **RATIM #S SID** for CINDY L603 RATIM (Prop only) |
| **ROTEN** | CINDY | **ROTEN #S SID - ROTEN #T STAR** (DEST EDDN only) |
| **AKONI** | CINDY | **AKONI #S SID** for CINDY SID |
#### SID Restrictions
Due to a lot of different route planning tools, some non valid routes out of Frankfurt exist. To ensure an efficient operation within the upper and lower airspace several restrictions should be met if workload permits. To solve the issue, usually **a completely new route has to be filed!** Therefore **[grd.aero-nav.com](https://grd.aero-nav.com)** can be used. All restrictions can be found in the table below.
| **Waypoint** | **Restriction** | **Remark** |
| **ANEKI** | **not** for DEST EDDM + EDMM FIR | reroute via CINDY |
| **CINDY / KOMIB** | EDDN only: CINDY mandatory during 25 ops,
KOMIB mandatory during 07 ops | reroute if wrong waypoint in FPL |
| **CINDY** | via CINDY \[...\] **T104** \[...\] DEST EDDM, EDDN only | reroute for other DEST required |
| **CINDY** | via CINDY **L603** \[...\] Prop only, max. FL230 | reroute for non prop |
| **TOBAK** | **not** via TOBAK Z10 \[...\] | reroute via MARUN |
| **MTR / TAU / FKS** | NON-RNAV only, max. FL90 | reroute for RNAV capable aircraft (e.g. A320, B738) |
# EDDF - Apron/Ground
Frankfurt **Apron** can be split into 4 stations as shown in the table and images below. Additionally, there exists a **Ground** station which will always be taken over by Tower though if not staffed.
If more than one of these stations is staffed, Delivery needs to be staffed first. If just one Apron is online, this Apron takes over all other Apron stations, but not Frankfurt Ground.
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
|
| **Center Apron**
| DFGC
| EDDF\_C\_GND
| 121.855
| **primary**
|
| **East Apron**
| DFGE
| EDDF\_E\_GND
| 121.955
| **secondary**
|
| **West Apron**
| DFGW
| EDDF\_W\_GND
| 121.755
| will be taken over be DFGC if not staffed
|
| **South Apron**
| DFGS
| EDDF\_S\_GND
| 121.655
| will be taken over by DFGE if not staffed
not yet operational in the real world
|
| Deicing
| DFGI
| EDDF\_ICE\_GND
| 121.985
| deicing operations only
|
| Ground
| DFG
| EDDF\_GND
| 121.805
| will be taken over bei DFTS if not staffed
|
[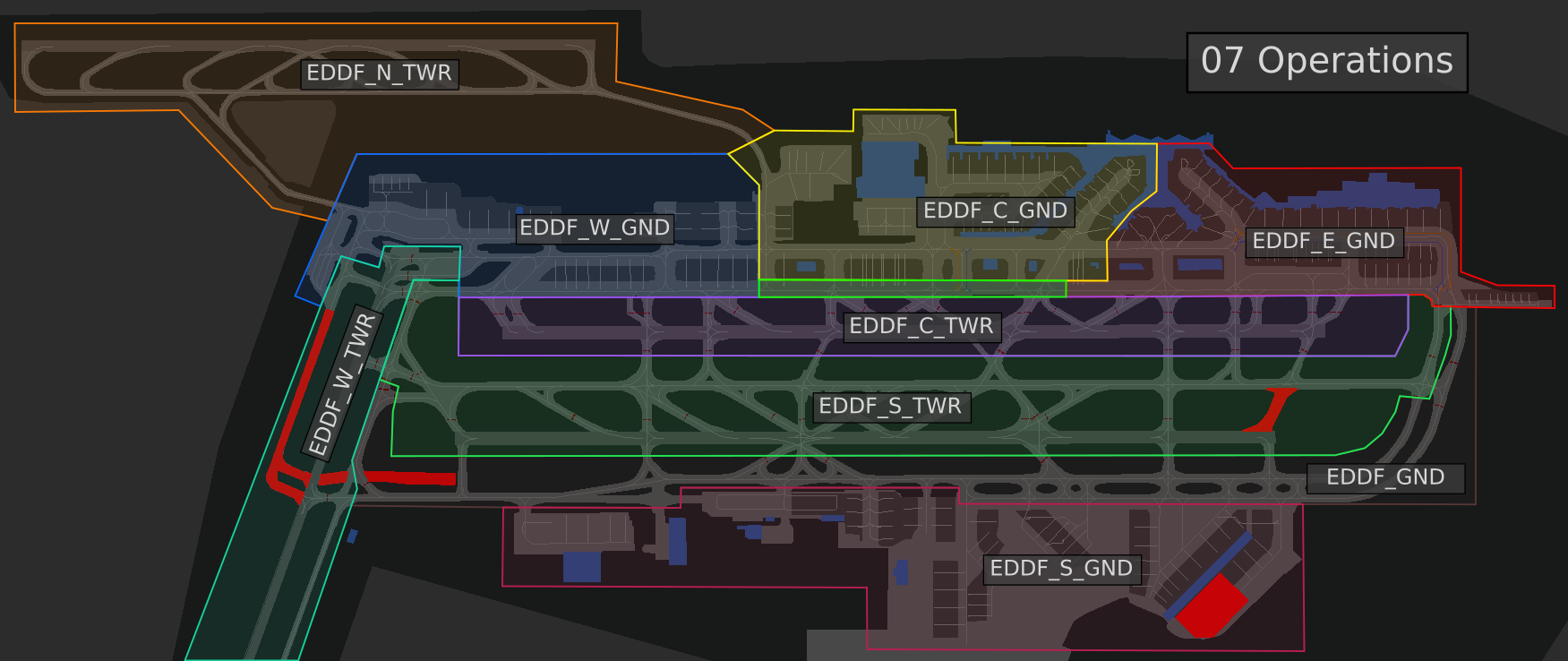](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/eddf-aor-twr-07.png)*AoR for 07 operations*
[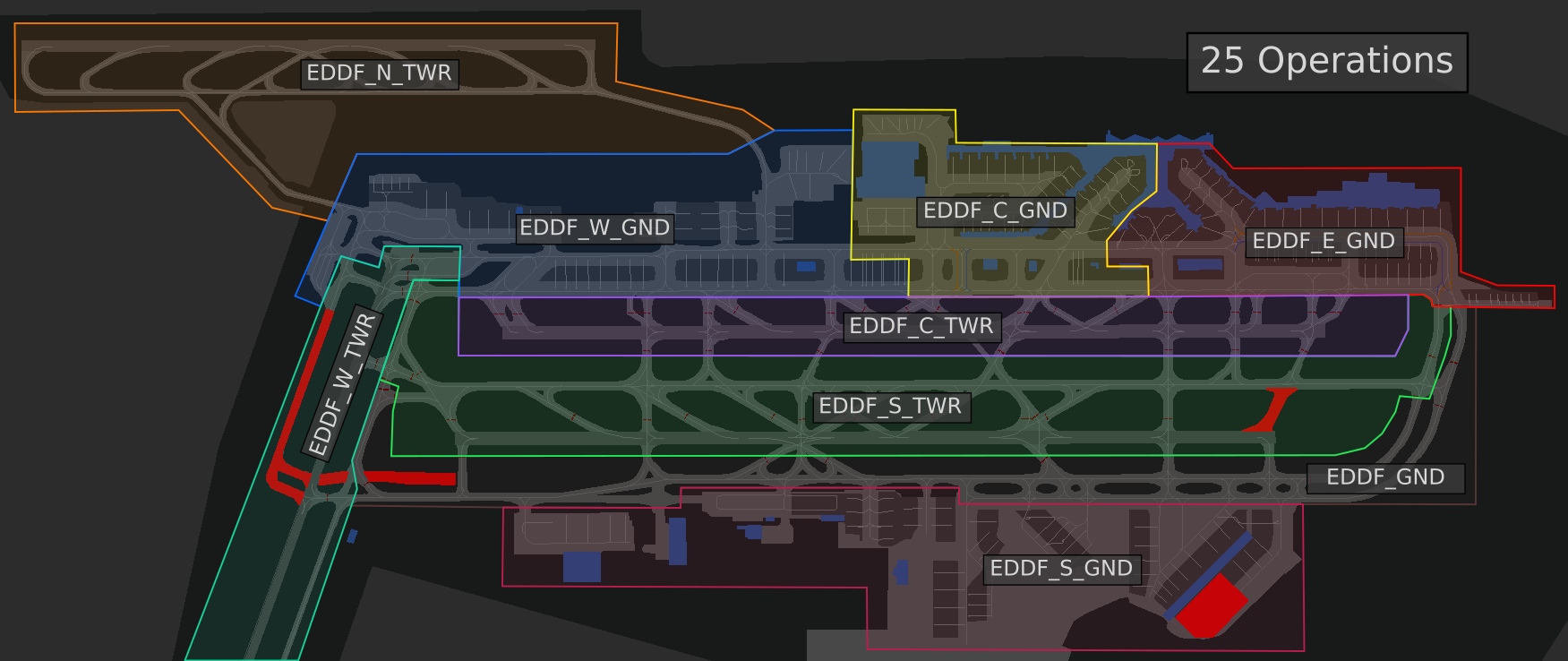](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/eddf-aor-twr-25.png)*AoR for 25 operations*
### General Procedures
#### Taxiway Usage
Taxiway L is always used in the direction towards the holding point of the center runway, depending on runway in use. Taxiway N is used the other way (see image). During 07 operations taxiway N west of N11 is also used towards the west, which shall be used for runway 18 outbounds (L, N14, N).
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/edff-eddf-n-l.png)*Usage of Taxiways N and L*
#### Taxiway Restrictions
All relevant restrictions can be found in the Euroscope Ground Radar (Functions -> Maps -> Restrictions). For B747, A380, A346 and B77W, charts can also be found [here](https://chartfox.org/EDDF#EDDF_90779). The auto gate assignment will take care of that, so if a stand is auto assigned, the aircraft is allowed to taxi on the taxiway to get there.
#### Taxiway Links
Links connect taxiways N7 and N8 at different locations to enable the best traffic flow. If N7 and N8 are used within the same instruction, **Links 3, 4 or 5** shall be used whenever applicable. These Links should be used with care because some pilots might not find/know them (Links are difficult to find as there are no signs, just visible at the charts). More images are available [here](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/airports-langen-fir-edgg/page/general "Taxiway Links at Frankfurt Airport").
**Link 1** does not exist in real life anymore, and can not be found on any charts! Link 3 or N8 - N - N7 should be used instead.
[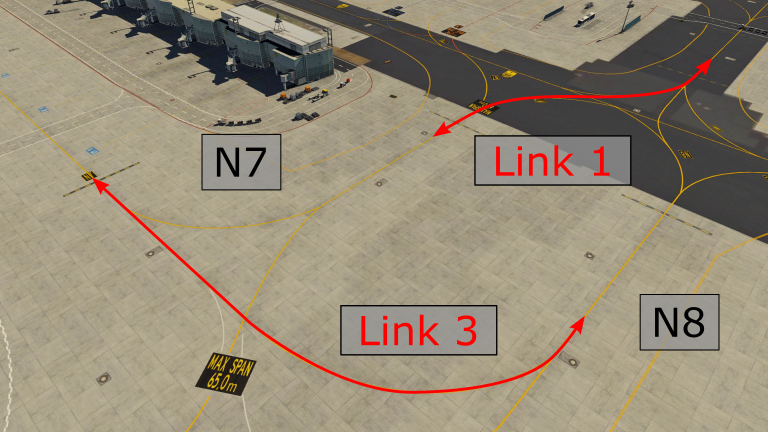](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/eddf-link1-link3-outside.png)*Usage of Link 1 and Link 3 between N7 and N8*
#### Colored Lines
Colored lines (orange and blue) can be used by all aircraft up to code C aircraft (A321/B739). Preplanning is required to use them the most efficient way.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/blueorange.jpg)*N-Blue and N-Orange used at the same time for parallel taxi*
#### Pushback
V134 - V178 (all facing south), as well as positions C2, B10 and A1 are taxi out positions. V143 and V144 are pushback positions! Almost all stands at the new GAT (V702-V721) are pushback positions, only V701 is a taxi out stand.
##### Straight pushbacks
Pushback from positions **V108 - V118** (even numbers) always have to be done straight back. Straight pushback out of **V106** will end behind position V108 facing north, when a GSX profile is used. Otherwise the intersection L/N-East - T is blocked.
> DLH123, pushback approved, straight back, no turn.
[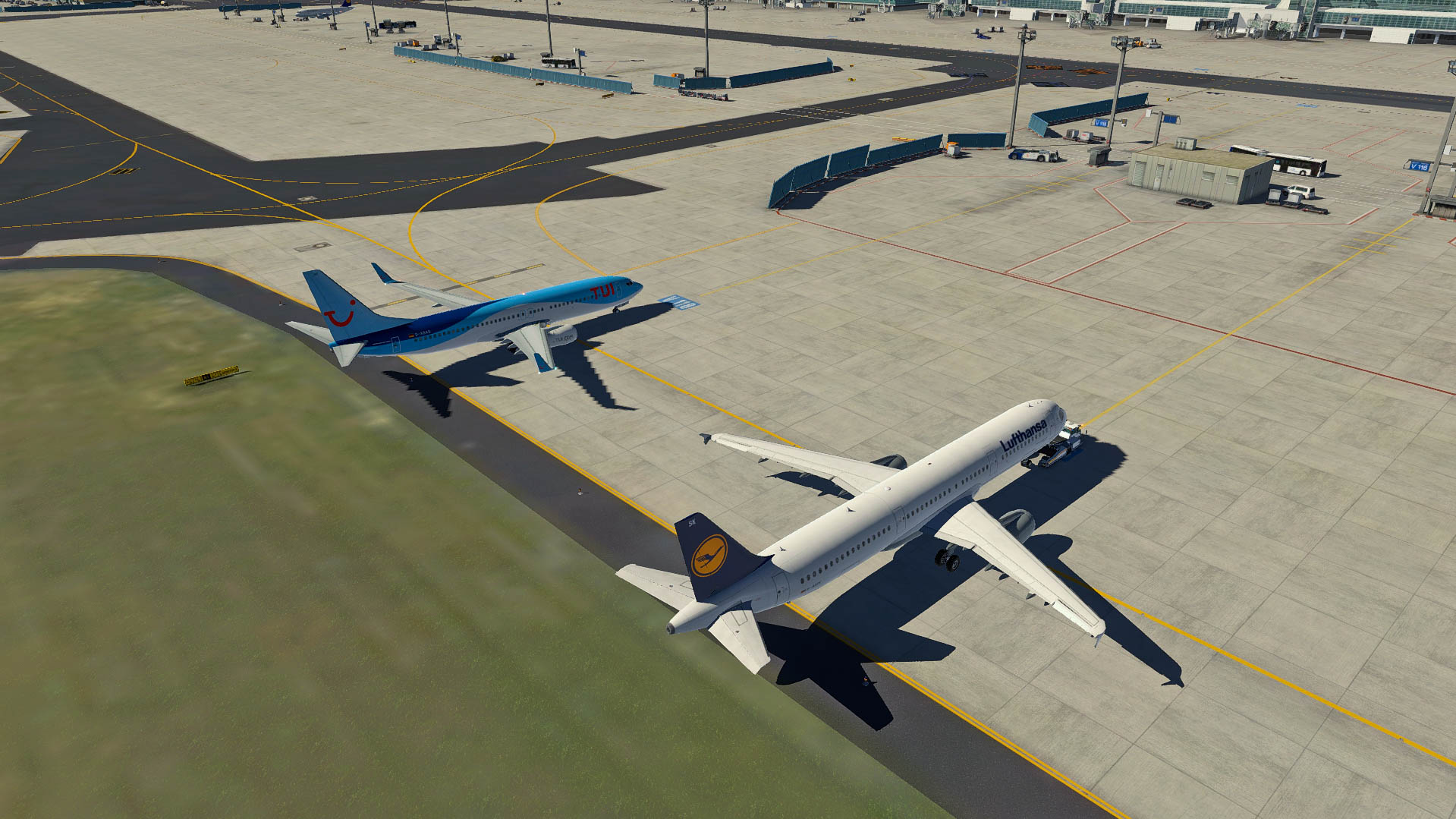](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/eddf-straight-push.jpg)*Straight pushback at positions V108 - V118 without turn*
Straight pushback is also possible from positions V266 - V270 instead of using pushback areas 1 and 2.
In the real world, a straight pushback from V270 will result make a slight curve to end up behind stand V269 facing North. Some GSX profiles may simulate this, so controllers should consider V269 blocked until the straight pushback from V270 has concluded.
##### Pushback Areas
Various areas of Frankfurt's apron utilize predefined pushback areas to which pilots can be instructed to push. Depending on the combination of the stand and the pushback area, a push and pull maneuver may be required which not all pilots are able to comply with; if in doubt, controllers should ask the pilot if they are able to conduct a push and pull maneuver. Additionally, some GSX profiles now only offer presets for these areas at appropriate parking positions so pilots may explicitly request an area if they are given a normal pushback; this should be accommodated when possible, but GSX also allows pilots to manually edit their pushback route, so when a normal pushback makes more sense, the pushback to an area can also be denied.
These areas are always only available for the applicable yellow taxiline; when instructing an aircraft to push onto a colored line, areas may not be used.
As charts don't inform pilots of the possible directions for each area, the **direction shall always be given with the clearance when instructing a pilot to push to an area**.
| **Taxiway**
| **Area**
| **Nose gear abeam stand**
| **Facing**
| **Restriction** |
| N
| 2
| E5 / V111
| *West/East*
|
|
| N-East
| 1
| *nose gear abeam service road between V106 and V107*
| North
|
|
| N3
| 1
| C6 / B44
| South
| max. Code C
|
| 2
| C11 / B45
| South
| max. Code E
|
| N5
| 1
| A15 / B22
| South
| max. Code C
|
| 2
| B25 / A21
| South
| max. Code E
|
| 3
| B26 / A25
| South
|
|
| N7/N8
| 1
| A16
| West
| max. Code C
|
| 2
| A24
| South-West
| max. Code E
|
| 3
| A58A
| West
|
|
| 4
| A30
| West
| max. Code C
|
| 5
| A58B
| East
| max. Code E
|
| 6
| A40
| West
| max. Code E
|
| 7
| A66B
| West
|
|
| 9
(should not be used)
| *short of N*
| South
|
|
| P1
| 1
| F238
| *West/East*
|
|
| 2
| V267
| West
|
|
| S4
| 1
| G6
| North
|
|
| 2
| G12
| North
|
|
| S5
| 1
| H4
| North | max. Code C
|
| 3
| G13
| North
|
|
| S7
| 2
| H12
| North
|
|
| S11/S15
| 6
| V326
| North
|
|
| 7
| *short of S*
| North
|
|
| 1
| K4
| West
| max. Code C
|
| 2
| K10
| West
|
|
| 4
| *short of S11*
| West |
|
| L
| 1
| V94
| West
| max. Code C
|
| 2
| V97
| West
| max. Code C
|
##### Other restrictions
Pushbacks from **position F231** are only possible facing East.
Pushbacks from **positions B23, B28, B42 and B48** have to finish the pushback on taxiway N (or in N4). While the pushback is still in progress, the intersection N - N4 can **not** be used!
#### Gate Assignment
Gates will be assigned by Ground Radar Plugin according to the real world. A-Stands are mainly used for DLH, AUA, TAP, AEE, SWR and UAL (Schengen and Non-Schengen area). Gates A50 to Gates A69 are DLH only. B and C-Stands are used for Star Alliance flights outside the Schengen area. Terminal 2 is mostly used for non-Star Alliance members and low cost operators, that are also located at the V-Positions in front of Terminal 2.
The first apron controller the inbound traffic contacts will always tell them their gate, even if it's under another Apron's responsibility.
> **Frankfurt Apron (West)**: DLH1255, gate A25, taxi via N11, L hold short of N8.
>
> **Frankfurt Apron (West)**: DLH1255, contact Apron on 121.855.
#### Inbounds 25C/07C
Inbound traffic from runway 25C/07C will be handed over from Tower with a hold short of L. This traffic is still blocking the runway after vacating and has to be treated with number one priority.
#### Handoff
Handoff to the next Apron controller will always take place with a hold short instruction of the next intersection close to the border of the area of responsibility (e.g. traffic from Center to West at N with a hold short of N10). Do not label any hold short for the transfer that is defined by the SOP!
#### Traffic Flow
If you have any “potential conflict” that will just generate waiting time for the pilot, please try to solve the problem without assigning a new gate. That will improve your preplanning skills a lot. Always try to work with conditional information as precisely as possible, but do not overload the pilot with useless information!
> **Frankfurt Apron**: DLH123 at L give way to opposite company A320.
>
> **Frankfurt Apron**: DLH456 at N4 number two behind Singapore A350 from right.
>
> **Frankfurt Apron**: DLH789 behind opposite British Airways A319 taxi to holding point runway 18 via N, hold short of N5.
##### Tricks
- keep the traffic flow dynamical and use conditional instructions as often as practicable. Resolve a hold short with a conditional instruction as soon as practicable.
- you may deviate from the default taxi flow (coordination might be required) to enable an efficient flow (e.g. via N3, N, N1 instead of L).
- you may have to adjust the routing to avoid conflicts and holdshorts
- you have to monitor taxiway M and the holding points to see what you can expect entering your sector within the next minutes
### Use of Intersections
**Runway 07C/25C:** Apron will not clear outbound traffic into intersections for runway 25C/07C. All outbounds are instructed to hold short of the intersection and Tower will instruct them to join the intersection that might be the best for the departure sequence.
> **Frankfurt Apron**: DLH123, taxi to runway 25C via N4 and L, hold short of L3.
> **Frankfurt Apron (Center)**: DLH505, taxi to runway 25C via N8 and L, hold short of N4.
>
> **Frankfurt Apron (Center)**: DLH505, contact Apron on 121.955.
>
> **Frankfurt Apron (East)**: DLH505, hallo, continue via L, hold short of L3.
>
> **Frankfurt Apron (East)**: DLH505, contact Tower on 118.780.
> **Frankfurt Apron**: AAL71, taxi to runway 25C via N, N1, hold short of L.
>
> **Frankfurt Apron**: BAW906U, taxi to runway 18 via orange line and N, hold short of N5.
It is important that every handoff takes place as early as possible and has to be free of conflicts. Every potential conflict needs to be solved prior to the handoff. As soon as the outbound traffic is in contact with Tower, it is released by Apron up to L1 and Tower has the possibility to use every further intersection available. Even if the pilot reported to Apron to be able for L6, Tower still can use L3 (or L1) intersection if there is no benefit for the outbound to use an intersection. In that situation with traffic on L under control of Tower, other outbound traffic e.g. joining L via N3 needs to be number 2 behind the traffic on L.
Intersections a pilot is able for should be noted in the remarks. Do not label any hold short for the transfer that is defined by the SOP!
Keep in mind that if you would like to solve a conflict it might be useful to let outbound traffic continue via L even if he would be able for L6.
**Runway 18:** Departures out of runway 18 will always be sent directly to the holding point via N/L. Handoff should take place early, so that Tower still has the chance to take outbounds via N-South. During 25 operations intersection L needs to be coordinated. During 07 Operations N is still preferred for all heavy aircraft (routing via L, N14, N).
During high traffic load (decision rests with apron control) All MEDIUM and LIGHT aircraft departing via runway 18 and parking east of taxiway N3 shall be asked if they are able for departure out of intersection S. If they are, they should taxi to hold short of U2. Frankfurt Ground is responsible for further taxi (see "Transition 1" below).
> **Frankfurt Apron**: DLH123A, advise able to depart from runway 18 intersection S?
### Transition 1
Outbounds via runway 18 intersection S will taxi via the southside of the airport and are transferred from Apron to Ground (if staffed, otherwise Center Tower) short of stopbar U2. Further taxi will be issued via U - S - S11 - R - S28 - S. Explicit crossing of stopbars U2 and U6 is required. This is a standard taxi routing called "Transition 1". It can only be found in the AIP EDDF, there are no markings on the taxiways.
> **Frankfurt Ground:** DLH123A, cross U2 and U6, taxi via transition 1 to holding point S runway 18.
If the pilot seems to be unfamiliar with Transition 1, issue the taxiways as usual. Depending on the inbound traffic for runway 25L/07R (there should be no opposite during taxi) further taxi via M can be used to save time.
### Runway Crossing
The taxiways used for crossing are based on the planned parking position and runway in use (see image below). These taxiways are mandatory and only if a pilot uses the wrong taxiway the Tower controller should deviate from that after coordination with Apron. It is also possible to coordinate a different crossing taxiway (M6, M10, M30, Y, T) or procedure between Tower and Apron for crossing.
**LVO:** During LVO inbound traffic landed on runway 25L/07R will not cross the center runway. All traffic needs to taxi via T or Y, depending on their planned stand.
Tower is not allowed to issue take-off clearances as long as the intersection is blocked by just crossed traffic. That’s why **Tower will issue the initial taxi route after crossing** to the Pilot. This depends on the runway in use and the intersection used (see images).
When traffic crossed the runway it shall be sent to the according apron control as soon as possible, so traffic does not need to stop.
Apron is responsible for separation in the Apron at all times. Tower can issue the crossing clearances without looking at potential conflicts. A lot of planning is required for that.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-07/crossing-07.jpg)
| **Entry** | **Stand** | **Hold short of** |
| **P** | all except those via P1 | N11 |
| **P1** | F231 - F238 and V266 - V270 | W |
| **S4 - S23** | South Parking (S, V3xx, J, K, G) | S4 - S23, according to the stand |
### Stopbars
Stopbars U2 - U8, T2 - T8, Y2 - Y12 and S40 close to the extended centerline are used to avoid conflicts between taxiing and arriving / departing aircraft. They can be seen on the Airport Chart and on the Euroscope Radar. Taxiway U should be used southbound and Taxiway T should be used northbound.
**Stopbars at T and U:** There must not be any traffic between T2 and T4 (RWY 25C) or T6 and T8 (RWY 25L) when there is landing traffic vertically above TWY T or departures out of 07C/07R still below 500ft AGL. The same applies for U2/U4/U6/U8.
However, there is one exception for U: Taxiing traffic with a tail height **not greater than 11,81 m** (all light and medium aircraft except A318 and B737 NG/MAX) may cross all stopbars at U **independenly from arrivals if they are on a precision approach** (ILS / GLS). This helps especially for traffic on Transition 1 (see above)
As a rule of thumb, the crossing clearance at a stopbar for may be given when the inbound is on minimum 4 NM final.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/eddf-t4.jpeg)*Inbounds have to hold short of stopbar T4 (yellow lines on the ground).*
*Name of the stopbar at the red sign on the left.*
**Stopbars at Y:** There must not be any traffic between Y4/Y10 and Y2 (RWY 07C) or Y6/Y12 and S40 (RWY 07R), when there is landing traffic vertically above TWY Y or outbounds runway 25C/25L still below 500ft AGL.
### Specialties during 07 Operations
**Border at N5:** Traffic from Center to East Apron needs to hold short of N5. As soon as the handoff is initiated, this traffic is released and will always be number one (green aircraft). Only hand off aircraft which you do not need to stay there (e.g. if you would like to have your outbound at N5 as number 1 - see image, THY25L).
[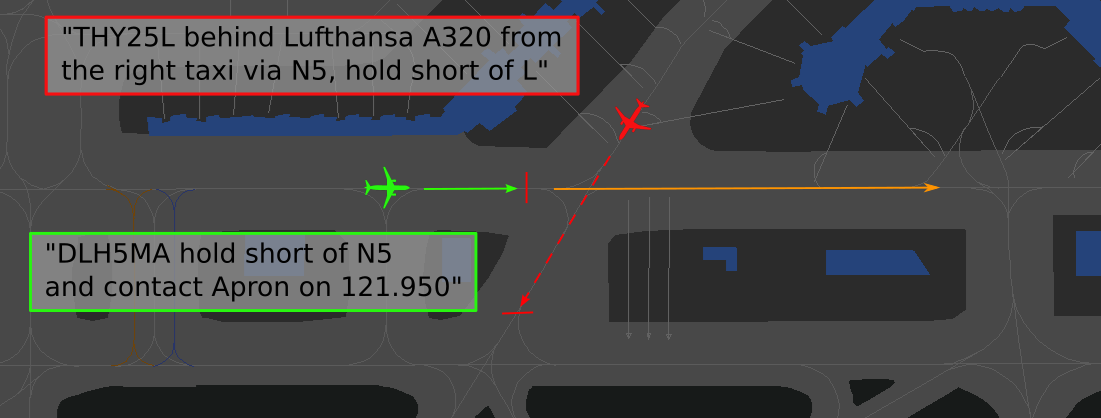](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddf-n5-07.png)
| **Station** | **Station ID** | **Login** | **Frequency** | **Remark** |
| **Center Tower** | DFTC | EDDF\_C\_TWR | 118.780 | **primary station** |
| **West Tower** | DFTW | EDDF\_W\_TWR | 124.855 | **secondary station** |
| **North Tower** | DFTN | EDDF\_N\_TWR | 136.500 | will be taken over by DFTW if not staffed |
| **South Tower** | DFTS | EDDF\_S\_TWR | 119.905 | will be taken over by DFTC if not staffed |
| **Ground** | DFG | EDDF\_GND | 121.805 | will be taken over by DFTS if not staffed |
Ground can also be taken over by West Tower after coordination. However, it cannot be taken over by any Apron station.
If multiple Tower stations are staffed, the responsibility for VFR traffic within the control zone can be coordinated for every single VFR flight or in general. Without coordination, South Tower is responsible for all VFR traffic (inbound VFR traffic from the North will initially call North Tower).
### Runway Usage
Frankfurt Tower is responsible for the direction of operations. 25 operation is preferred up to a tailwind component of 5 kts. Runway 18 is always used up to a tailwind component of 15 knots.
If the [tailwind component](https://sim.tools/ "sim.tools") of runway 18 is greater than 10 knots, this should be broadcasted via ATIS. Then pilots need to report if unable to accept runway 18 on initial call. It might be more efficient to close runway 18 depending on the amount of pilots that report being unable due to the required separation (see separation below).
**Approaches:** By default, the ILS Approach is used for all arrivals, except coordinated otherwise. For runway 25R/07L ILS Y is preferred without tailwind and during CAT I operations.
Inbounds for the GAT and the south apron should be instructed to vacate runway 25L/07R to the south.
### Separation and transfer of communication
#### Departing Traffic
All departures must be separated by at least **3 NM or wake turbulence separation**, whichever is greater. Tower has to ensure initial separation between departures and between departures and missed approaches.
**Departures with the same SID** need to be separated by at least 5 NM at transfer of communication.
**Rule of Thumb for aircraft with same performance:**
A separation of 3 NM can be achieved when the succeeding traffic receives its takeoff clearance as soon as the preceeding traffic is overflying the end of the departure runway. For a separation of 5 NM the proceeding traffic needs to be 2 NM away from the end of the departure runway.
**Same SID, different runways:** Especially between southern departures out of runways 07/25 and 18, Tower has to pay special attention to initial separation.
All departing aircraft out of Frankfurt must be instructed to contact the appropriate Langen Radar frequency after departure. This instruction shall be given when the aircraft is airborne and free of conflict with other departures and / or missed approaches. The transfer should be initiated early enough to avoid the flight leveling off (at +/- 1000 ft AMSL).
As the approach / departure controller shall always cross-couple both real-life departure frequencies, the departure frequency will always be 120.155 for departures towards MARUN, TOBAK, OBOKA and 136.130 for departures towards SULUS, KOMIB, CINDY, ANEKI, SOBRA and ULKIG - regardless of the departure runway / SID.
#### Arriving Traffic
For inbounds, Frankfurt Arrival is responsible for separation until transfer of communication. Frankfurt Tower is responsible for maintaining separation of arriving traffic from transfer of communication until touchdown, if necessary by use of adequate means (e.g. speed control), and during the initial part of a missed approach.
The minimum separation between two aircraft approaching the same runway is **3 NM or wake turbulence separation**, whichever is higher.
However, under certrain circumstances, the radar separation can be reduced to **2.5 NM** according to NfL I-55/11:
- Both aircraft are within a 10 NM final
- Wake turbulence separation is not applicable
- The exit taxiways of the runway can be observed from the control tower visually or by means of surface movement radar (always applicable at VATSIM)
- The runway is dry
The reduced radar separation minimum may also be applied between alternating approaches to the parallel runways (see below). In these cases, neither the line of sight of the exit taxiways nor the runway conditions need to be considered as a precondition.
**Modes of Operation:** Langen Radar has to coordinate with tower whether parallel independent, dependent or alternating (former staggered) mode will be used. The minimum separation between an aircraft on final runway 25L/07R and another aircraft on final runway 25R/07L is measured diagonal head to head.
| **Mode**
| **Minimum separation 25L/07R - 25R/07L**
|
| alternating
| 2.5 NM
|
| dependent
| 1.5 NM
|
| parallel independent
| independent
|
The default mode with only one arrival / feeder controller is **dependent**. Only when two feeders are in use, **independent** operations are possible. Aircraft performing non-precision approaches (RNP, swingovers) are not allowed for dependent and independent operations.
For different seperation examples check the images below.
Separation Examples
| [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-10/eddf-seperation-independant.jpg)
| [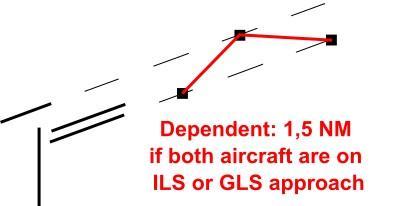](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-04/eddf-seperation-dependant.jpg)
|
| [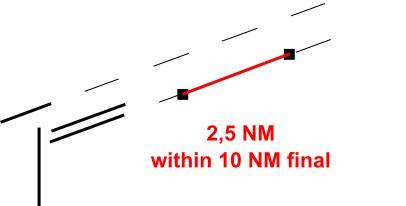](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-10/eddf-seperation-same-rwy.jpg) | [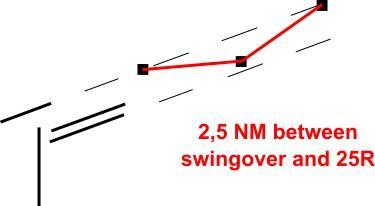](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-04/eddf-separation-swing.jpg) |
| **Runway** | **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 1**
| **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 2**
| **preceding CAT 3**
**succeeding CAT 1/CAT 2/CAT 3**
|
| **07L/25R** | 600m | 1500m | 2400m |
| **07C/25C** | 600m | 1500m | 2400m |
| **07R/25L** | 600m | 1500m | 2400m |
| **18** | N/A | N/A | 2400m |
### Runway Dependencies
The parallel runway systems 25L/25C and 07C/07R cannot be used for (in)dependent parallel approaches or independent parallel departuers. Instead, radar separation or wake turbulence separation must be applied for departures and arrivals.
However, during approaches on the southern or the center runway, the other runway may be used for departures simultaneously (taboo zones for runway 25 have to be considered though, see below).
#### 25 Operations
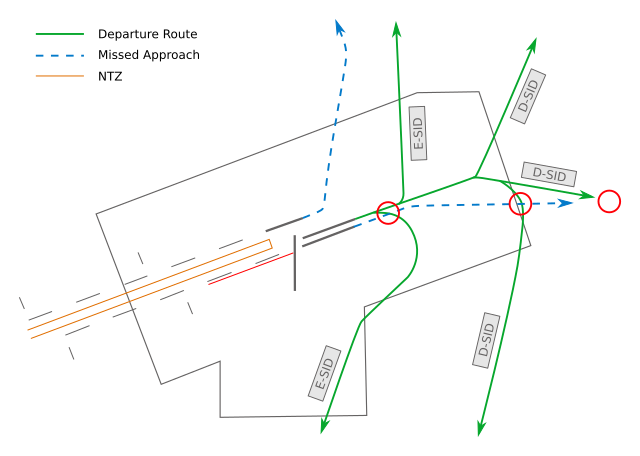
**M/H-Departure and departures to the south (e.g. CINDY#F):** Takeoff clearances for runway 25C/25L can be issued when the following conditions are met:
- **Inbound Traffic:** For departures out of runway 25C, the takeoff roll may only start when there is no inbound for runway 25L between 4 NM final and the threshold. For inbounds and outbounds on the same runway, only runway separation has to be applied.
- 25R missed approaches are completely independent to 25C departures with initial turn to the south
- **Outbound Traffic:** Takeoff clearance may be given once the departure on runway 18 has started its takeoff roll
**F/G-Departure to the north:** Takeoff clearances for runway 25C/25L can be issued when the following conditions are met.
- The takeoff roll may only start when there is no inbound for runway 25R between 4 and 0,5 NM final
- (Independent to arrivals on runway 25L)
- (25C: Independent to departures from runway 18)
- Departures out of runway 25L need a release by DFTW. The release can be given once the departure from runway 18 is rolling
- During LVO both tabu zones for 25L and 25R need to be clear of traffic when starting the takeoff roll. Since this is almost impossible during high inbound traffic, all departures should receive the M/H SIDs during LVO so that only one taboo zone has to be considered.
**18 Departures:** Outbounds from runway 25C/25L with initial turn to the south need to reach 2000ft AMSL before the takeoff clearance can be issued. Outbounds from runway 25C directly to the north are completely independent to all 18 departures.
*dependencies during 25 operations*
**Missed Approaches:** Missed approaches from runway 25C and 25L are dependent to runway 18 departures. The takeoff clearance on runway 18 can be given, as soon as separation is ensured. Exception: Departures from intersection S are independent to missed approaches. However, a traffic information could increase the situational awareness of the pilot.
**Staffing with multiple tower:** If more than one Tower position is staffed, DFTW is responsible for the coordination between departures runway 18 and 25C/25L. DFTC/DFTS always needs a release by DFTW for all departures with initial turn to the south (M / W / H / K / N / F-SIDs to the south), if not coordinated otherwise. E.g. the phrases "Released" / "DLH123 released" / "MARUN released" may be used.
#### 07 Operations
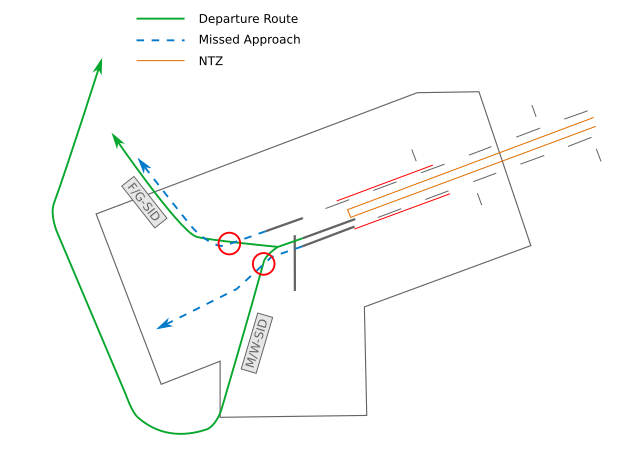
**Outbounds 07:** All outbounds out of runway 07C are independent to all arrivals on runway 07R and departures on runway 18.
In case of a go around on runway 07R, Tower has to ensure separation. In case of a southbound departure from RWY 07C, the missed approach should be turned to the south above the MVA and the departure should stay on runway track.
Missed approaches on RWY 07L and OBOKA/MARUN#E departures are **not** separated procedural. In case of go around on runway 07L, Tower has to ensure separation with departures out of runway 07C.
**18 departures:** Departing aircraft on runway 18 from N / N-South / L have to start their takeoff roll before any aircraft on final runway 07R is between 4 NM final and runway 18. Also, traffic departing from these intersections need to be separated by time-based wake turbulence behind arrivals on runway 07R (see table below).
For departures out of **intersection M** it must only be ensured that the inbound will not overfly the departing traffic on runway 18, so the 4 NM restriction does not need to be taken into account as well as wake turbulence separation. Departing traffic out of full length can taxi down the runway to intersection M (not via taxiway Y) to improve the departure sequence.
> DLH123, lineup runway 18, on the runway taxi down to intersection M.
Outbounds via **intersection S** are completely independent to arrivals for runways 07C and 07R.
##### Time-based wake turbulence separation 18 Outbound vs. 07R Inbound
| **Preceding** | **Succeeding** | **Separation** |
| Medium | Light | 2 min |
| Heavy
| Light | 2 min |
| Medium | 2 min |
| Super
| Light | 3 min |
| Medium | 3 min |
| Heavy | 2 min |
*dependencies during 07 operations*
#### Spacing on final
Due to the taboo zones, it might be necessary to coordinate a target spacing on final to get departures out, especially during an inbound rush. This can be done either individually for each departure (good preplanning is necessary - when the final is full, the next gap might take around 6 minutes) or by using a general spacing on final.
Recommended spacing values are:
- **07R arrivals:** 5 NM (minimum 4 NM at touchdown)
- **07L arrivals:** Radar Separation
- **25L arrivals:** 6 NM (minimum 5 NM at touchdown)
- **25R arrivals:** 5 NM (minimum 4 NM at touchdown)
### VFR Traffic
D-CTR of Frankfurt reaches up to 2500ft AMSL. For details see VFR charts.
**Runway used:** VFR Traffic should use runway 25L/07R for arrival, outbounds can depart from any runway (except 25R/07L) depending on the traffic situation and the intentions of the VFR traffic. VFR departures out of runway 25L/25C can be instructed not to overfly runway 18. Nevertheless, it is necessary to wait with an 18-takeoff clearance until the VFR departure turns away from runway 18. Low approaches / Touch and go's can only be performed on the center or southern runway, whatever facilitates the traffic flow. The northern runway is not allowed for VFR approaches due to noise abatement. However, the downwind of this runway can of course be used.
There are VFR holdings in the control zone north and south of the airport. Traffic in these holdings shall be instructed to stay clear of runway 18 or final runway 25R.
**VFR Squawk:** All VFR traffic inside the controlzone of Frankfurt will get the transpondercode 4447. Police (POL - 0036) and Christoph rescue helicopter (CHX - 4444) will remain their squawk.
**Helicopter Operation:** All helicopters always have to land or depart at an active runway at Frankfurt airport. Thereafter they need to air-taxi to their destination at the airport (usually a stand at the GAT or next to the accident side).
**Important Landmarks for VFR Flights**
- River Main
- Downtown Frankfurt (Northeast of the CTR)
- BAB 3 (west to east through the CTR)
- BAB 5 (north to south through the CTR)
- BAB 60 (Splitting of BAB 67 to the west)
- BAB 67 (north to the southwest of RWY 18)
- Frankfurt Uniklinik (Northeast of the CTR)
[VFR Charts - Openflightmaps](https://www.openflightmaps.org/ed-germany/)
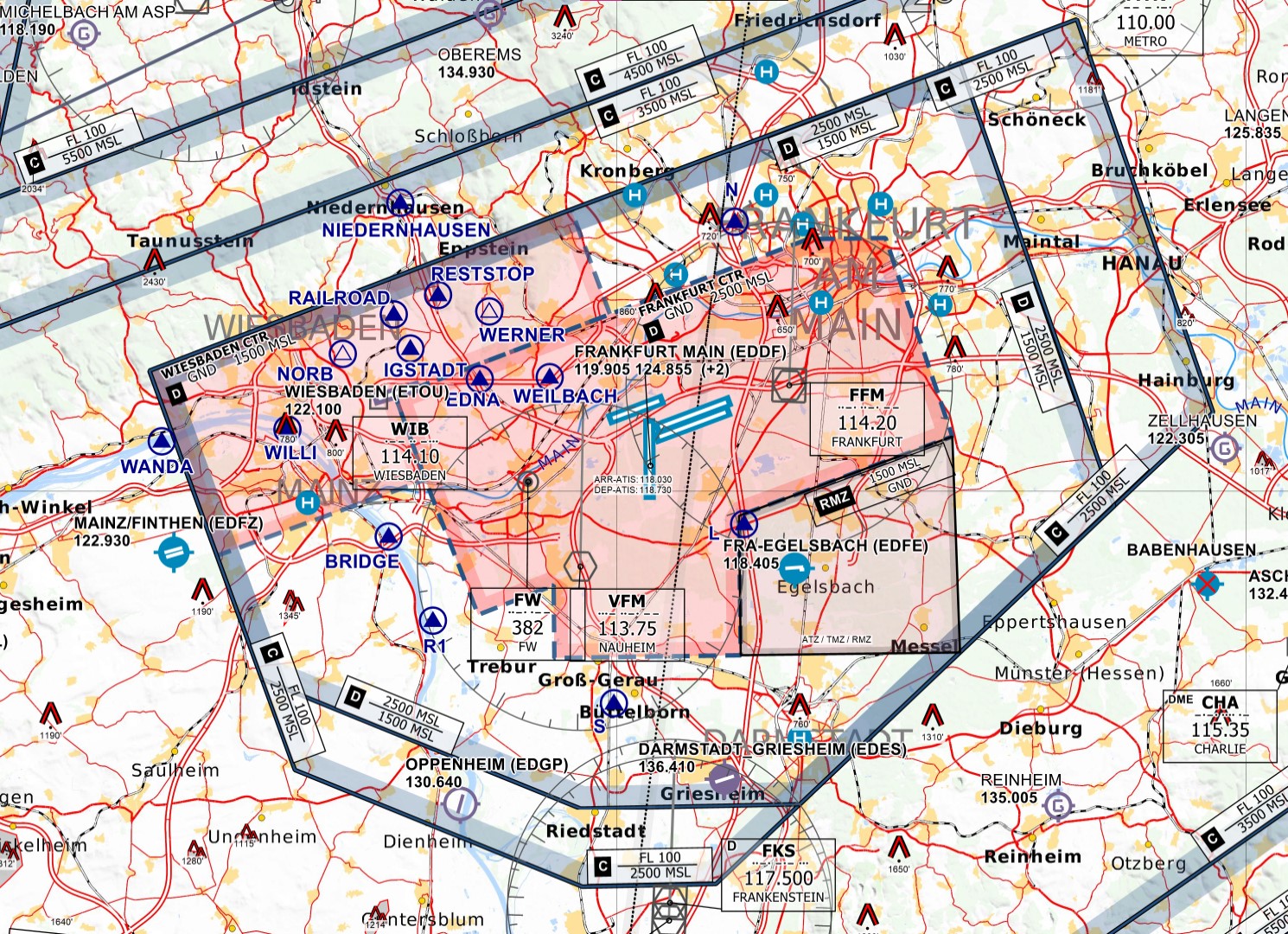
**Wiesbaden corner:** To facilitate traffic circuit operations at Wiesbaden airbase (ETOU), the Northwestern corner of the Frankfurt CTR can be delegated to Wiesbaden Tower up to 1500ft. In addition, controllers shall be aware that in addition to the traffic circuits, Wiesbaden VFR routes Echo and Apache also cross the Frankfurt CTR along Autobahn 66.
Wiesbaden corner
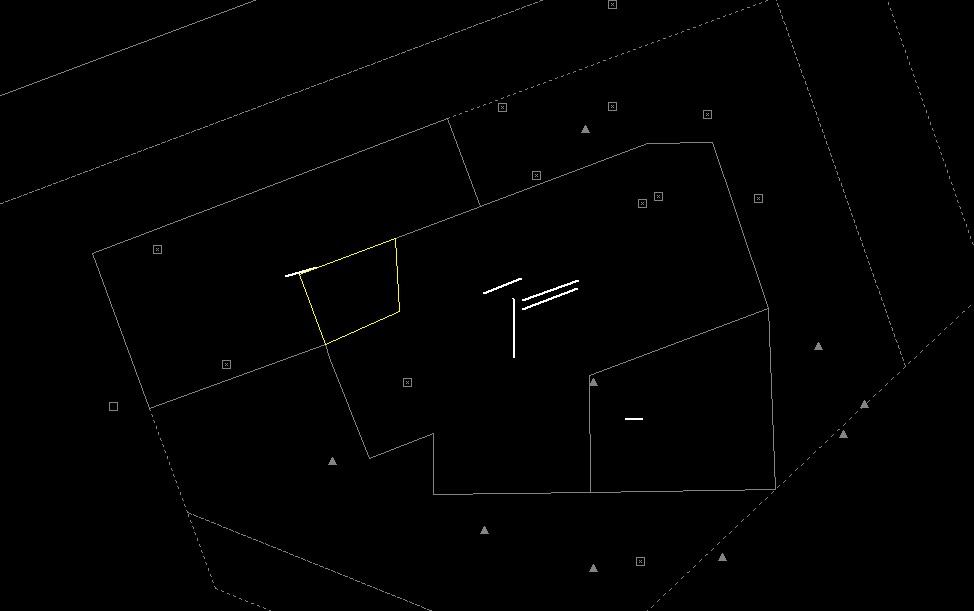
The Wiesbaden corner will automatically be displayed when Wiesbaden Tower is staffed, but can also be manually displayed via the TopSky maps, e.g. if there is circuit traffic at Wiesbaden while DFAN covers the airport topdown.
Tower will get Outbounds for runway 07C/25C short of the intersections. The intersection to use can be decided by Tower depending on the best departure sequence. Therefore only L1, L3, L4, L5, L6 and L9 can be used during 25 operations and L14, L16, L17, L19, L20, L21 for 07 operations. Tower needs to instruct the pilot to join the intersection.
Usage of Intersections
Only intersections with a published TORA (see charts) may be used for departures, even if the pilot reports that he would be able for a different intersection. As an exception, helicopters may depart from every part of the runway up to the runway end.
Generally, an intersection may only be assigned to a departing aircraft when the pilot either reports by himself that he is able for that intersection or agrees to it after a controller’s request - regardless of the aircraft type.
In theory, every pilot has to report the earliest possible takeoff intersection to the tower controller according to the AIP EDDF. This is often not done in practice though, therefore the tower controller still needs to ask if the pilot is able to use an intersection. Exemptions of this rule are intersections L and M of runway 18 during 07 operations. The ATIS states that these are to be expected for every aircraft and pilots have to report if they are unable for M.
Also, it is common practice to assign the following intersections without prior agreement since they only differ by a few meters from full runway length: L3 (25C), L20 (07C), N-South / L / W3 (18 - only applies for Mediums, Heavies have to be asked).
To protect the center runway, all traffic holding short **can** be instructed to stop at the CAT II/III holding point (real procedure)! As many pilots are confused by this instruction, a "normal" hold short of the runway can be used instead.
> **Frankfurt Tower**: DLH123A, taxi via M and M8, hold at CAT II holding point runway 25C.
> or
> **Frankfurt Tower**: DLH123A, taxi via M and M8, hold short of runway 25C.
During 07 Operations inbounds landed on runway 07L with parking position west of N11 should be transferred directly to West Apron.

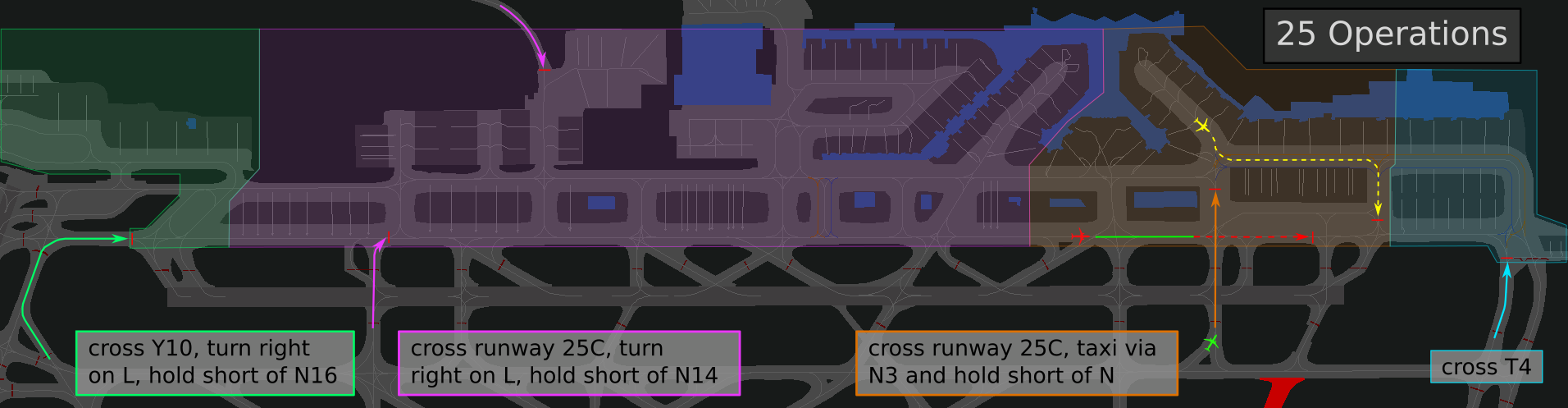
Inbound traffic entering the Apron without crossing the runway will be instructed according to the table below. Frankfurt Apron is always responsible for all GAT and movements at the southern apron!
| **Entry** | **Stand** | **Hold short of** |
| P | all except those via P1 | N11 |
| P1 | F231 - F238 and V266 - V270 | W |
| S4 - S23 | South Parking (S, V3xx, J, K, G) | S4 - S23, according to the stand |
Do not label hold shorts that are defined by the SOP!
### Visual Swingovers
Inbounds for runway 25L have the possibility to do a visual swingover (visual approach) to runway 25C when reaching the 7 NM final (2500ft MSL). Therefore the pilot has to have the runway in sight. During 07 operations a swingover is only available for safety reasons or to avoid a missed approach.
**Dependencies:** Visual swingovers must be separated by at least 2.5 NM to approaches on runway 25R/07L. They do not have to be coordinated with Langen Radar as long as separation to other aircraft is obviously great enough. If the 2.5 NM cannot be maintained, the procedure can still be applied if the **succeeding** aircraft confirms the parallel traffic in sight and maintaining visual separation.
**Missed Approach:** With the clearance for the visual approach the pilot has to be given a new instruction how to continue in case of a missed approach. Therefore runway track and a climb to 5000ft shall be used.
> **Frankfurt Tower**: DLH123, advise able for visual approach runway 25C and parallel A320 2 o'clock in sight?
>
> **Pilot**: Able and in sight, DLH123.
>
> **Frankfurt Tower**: DLH123, maintain own separation, cleared visual approach runway 25C, (do not overshoot to the north). In case of missed approach climb straight ahead 5000ft (and contact Frankfurt Tower 118.780).
A swingover can have several benefits. The taboo zone can be avoided (see below) or safety reasons e.g. to avoid missed approaches. Pilots are often happy about reduced taxi times on ground.
**Swing to depart**: A swingover can also be used to improve the outbound flow for runway 25C with M/W departures, as there is no 4 NM no-fly zone that need to be taken into account. A takeoff clearance on runway 25C can also be issued if the inbound is closer than 4 NM, which would not be possible if this traffic was approaching runway 25L.
The inbound will be handed over to the according apron, with a hold short of L, as soon as possible.
> **Frankfurt Tower**: DLH123, vacate to the right, hold short of L and contact Frankfurt Apron 121.855.
### Low Visibility Operations
LVO become effective once the **ceiling / vertical visiblilty is below 200ft or the vertical visibility cannot be detected or any RVR in the METAR is equal or below 600m.**
During LVO, the following procedures shall be applied:
- LVO shall be **announced** in the **ATIS** (Code "&lvp")
- Only the **Z ILS** for the northwestern RWY may be used
- All traffic shall be told to **hold at the CAT III holding points**
- The **RVR value for the corresponding runway** shall be given with the **landing clearance** and in the case of guided take-off (RVR ≤ 125m) with the take-off clearance
- **25 Departures** should only depart from RWY 25C via **M/W SIDs** (reason: F/G Departures and a missed approach on runway 25L would mean a loss of separation during bad weather, but M/W SIDs are independent to published missed approaches from runway 25R)
- **Runway crossings are not allowed**
- During RWY 25, landing traffic that would cross via M8 shall taxi via T and traffic that would cross via M30 shall taxi via Y
- During RWY 07, all landing traffic shall taxi via T
- Optional procedures for advanced controllers: Consideration of sensitive and critical areas of the ILS
- The sensitive and critical areas for every runway and aircraft category can be displayed in Euroscope via Functions -> Maps -> LVP
- [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-11/screenshot-20.png) Yellow areas show the sensitive areas
- [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-11/screenshot-22.png) Orange areas show the sensitive areas for non-orthogonal and non-parallel traffic
- [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-11/screenshot-21.png) Red areas show the critical areas
- The wake turbulence category always refers to the preceeding aircraft on the runway, not the suceeding on final
- For Light and Medium aircraft, there are no restrictions except that they must be clear of the CAT III holding point before the next inbound is over the runway threshold
- For Heavy / A388 aircraft:
- Sensitive areas must be clear as soon as the next inbound is within 2 NM final
- As a rule, sensitive areas are always clear when the aircraft has passed the CAT III holding point
- Critical areas must be clear as soon as the next inbound is within 4 NM final
- When applying these advanced procedures, the following spacing should be the coordinated with APP for arriving flights:
- 5 NM behind Light / Medium aircraft
- 7 NM behind Heavy / A388 aircraft
# EDDF - Arrival/Departure
Arrival can be split in 6 stations as shown in the table below.
| **Sector** | **Station ID** | **Login** | **Frequency** | **Remark** |
| **Pickup
|
| **Arrival North** | DFAN | EDDF\_N\_APP | 120.805 | primary
|
| **Arrival South** | DFAS | EDDF\_S\_APP | 125.355 | --
|
| **Feeder
|
| **Director North** | DFFN | EDDF\_H\_APP | 127.280 | secondary
|
| **Director South** | DFFS | EDDF\_L\_APP | 118.505 | --
|
| **Departure** |
| **Departure North** | DFDN | EDDF\_N\_DEP | 120.155 | --
|
| **Departure South** | DFDS | EDDF\_S\_DEP | 136.130 | --
|
All APP/DEP frequencies shall always be cross-coupled by the responsible controller.
### Terminal Maneuvering Area (TMA)
Below you can find the arrival sector of Frankfurt with its subsectors. In case there is only one controller online, the whole sector is controlled by them. All subsectors combined constitute the Terminal Maneuvering Area (TMA). The MVA chart is available via [chartforx.org](https://chartfox.org/eddf "chartfox.org") or as Topsky Map at Euroscope. The airspace structure can be found at [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/ "openflightmaps.org").
| [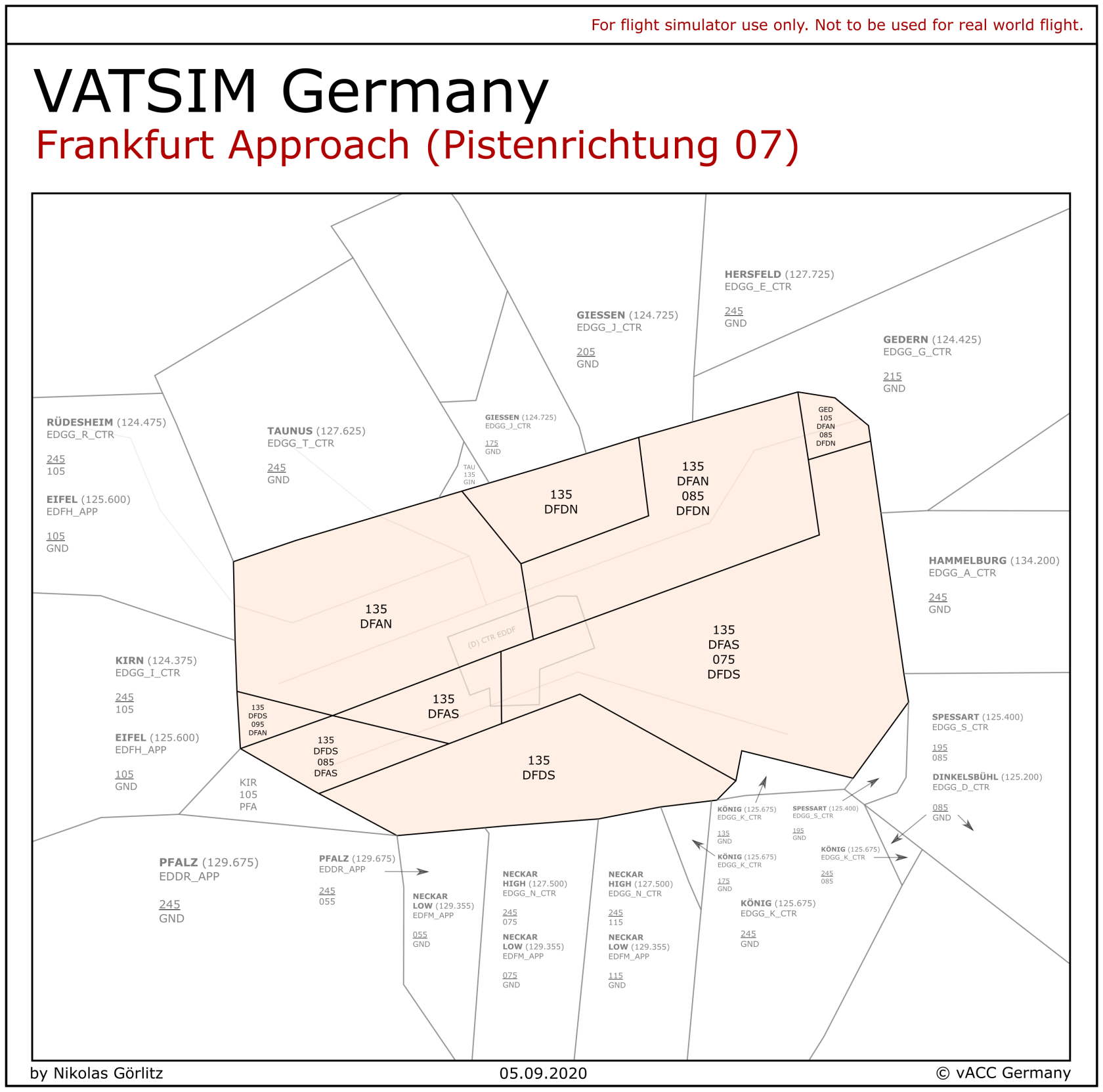](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-11/frankfurt-approach-sectors-07-config.png) | [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-11/frankfurt-approach-sectors-25-config.png) |
**Departure:** If only one Departure controller is online, he takes over the other Departure sector. If no Departure controller is online, Arrival North takes over Departure North and Arrival South takes over Departure South. If only one Arrival controller is online, he takes over the other Arrival sector.
**Director (Feeder):** Feeders do not have their own sectors. They are assistants of the Arrival controllers which is why Director North has the same sector as Arrival North and Director South has the same sector as Arrival South. If only one Director is online, he is the Director for both Arrival controllers.
### Arrival Procedures
#### General Procedures
**Arrival Routes:** As the clearance limits for all EDDF STARs are outside of the TMA, the appropriate Center controller issues the clearance for any STAR and initiates the handoff before sector entry. In normal operations, the RNAV STARs from SPESA, KERAX, (RASVO), IMCOM, ROLIS, (PETIX), EMPAX, DIXAT, and DEBHI are used. In this case, Center clears most aircraft from the north via the northern STAR and every aircraft from the south via the southern STAR. All aircraft unable for the northern runways, the restricted heavies (A380s, B747s, MD11s (and AN124/AN225)), as well as aircraft parking at the GAT, shall be cleared for the southern STAR in order to ensure that they will arrive in the southern downwind. The designators for the RNAV STARs are shown below. All other aircraft landing on the southern RWY should be cleared for the southern arrival as well.
| **Runway** | **STAR** | **Routing** | **Old Transition** |
| **25** | A | North | 25N-Transition |
| B | South | 25S-Transition |
| **07** | C | South | 07S-Transition |
| D | North | 07N-Transition |
**Alternative RNAV STARs:** These STARs via UNOKO, ROLIS, KERAX and SPESA are only used between 22 and 05 lcl for the RNP X approach.
| **Runway** | **STAR** | **Routing** | **IAF** |
| **25
| G
| North | ORVIV |
| South | KUGUK |
| **07
| R
| North | IBLUS |
| South | ULNOK |
Even after the clearance for the STAR, the Arrival controller can always use vectors for sequencing.
**Releases:** Traffic handed over from Center to Frankfurt Arrival is fully released for turns and further descent. Arrival needs to ensure sufficient spacing between traffic.
Inbounds should always stay clear of the departure sector even if Arrival handles departures as well.
#### Approaches
The following approaches are available at Frankfurt.
| **Approach**
| **Runways**
| **Remarks**
|
| **ILS**
| 07R/25L
| 3° glide path
*RNAV required*
|
| **ILS X**
| 07C/25C
| 3° glide path
*non-RNAV*
|
| **ILS Y**
| 07L/25R
| 3.2° glide path
*RNAV required*
|
| **ILS Z**
| 07L/25R
07C/25C
| 3° glide path
*RNAV required*
|
| **GLS Y**
| all
| 3.2° glide path
*shall only be used upon pilot request*
|
| **GLS Z**
| all
| 3° glide path
*shall only be used upon pilot request*
|
| **RNP X**
| 07L/25R
07C/25C
| noise abatement procedure
*(former RNP Y)*
|
| **RNP Y**
| all
| 3.2° glide path
|
| **RNP Z**
| all
| 3° glide path
|
**Usage of the different Approaches:** By default, ILS approaches are always used. Visual approaches should only be used if a pilot is unable to fly the ILS or RNP Z for any reason. In this case, the visual approach does not change any dependencies according to Operation Modes. All other approaches shall only be used on the pilot’s request and after coordination with all relevant stations (esp. Director and Tower). In high-traffic situations only ILS approaches are recommended.
Depending on the traffic load, the **RNP X** approach for runway 25C/L or 07C/R is used between 22 and 05 local time. Coordination with Tower required.
Intercepting below 4000ft should be avoided due to noise abatement. If a pilot missed the intercept and overshoot he could be turned back onto the ILS and descended below 4000ft in compliance with the MVA.
**Runway Assignment:** Usually inbounds from the north will get the northern runway while inbound from the south will get the southern runway. Arrival/Feeder can deviate from that if required or requested by the pilot. Traffic for the GAT and Cargo aircraft except GEC, FDX, BCS, and BOX will always get the southern runway.
**Non-RNAV:** All aircraft without RNAV capabilities need to fly the **ILS X** for runway **07C/25C** due to the missed approach procedure.
#### Runway 25R/07L (Nord-West-Landebahn)
Runway 25R/07L is not allowed for the following aircraft types: B747, A380, MD11, DC10, AN124, L-1011
**ILS Y/Z:** For runway 25R/07L an ILS-Z and ILS-Y exist. The ILS-Z approach has a 3°-glide slope and the ILS-Y has a 3,2° glide slope. The ILS-Y approach is the default one used. If there is a tailwind or LVO (CAT 2/3 operations) ILS-Z needs to be used.
The ILS approach in use has to be mentioned in the ATIS! Coordination between Tower and Arrival may be necessary.
Keep in mind, always the full approach name must be used (e.g. "expect ILS ZULU runway 25R”).
#### Target Spacings
As Tower must respect dependencies between departing and arriving aircraft, there are target spacings that should be present at touchdown for the highest efficiency of the runway system. Depending on the amount of departures, it is important that these minima are met whenever possible. Coordination is required if these can temporarily not be met or if Tower needs more spacing.
**Targetspacing** for inbounds only need to be applied by Arrival when **requested by Tower!** Otherwise radar or WTC seperation is used by default.
These target spacings at handoff are as follows:
- **07R arrivals:** 5 NM (minimum 4 NM at touchdown)
- **07L arrivals:** Radar Separation
- **25L arrivals:** 6 NM (minimum 5 NM at touchdown)
- **25R arrivals:** 5 NM
Wake Turbulence Separation must be applied where necessary all the time.
#### Separation on final
As per the AIP for EDDF, separation between two aircraft approaching the same runway can be reduced to 2.5 NM under some conditions:
> **4. Reduced minimum radar separation between approaches to runways 07L, 07C, 07R, 25R, 25C and 25L**
>
> 4.1 During approaches to runways 07L, 07C, 07R, 25R, 25C and 25L, the radar separation minimum of 2.5 NM applies on final approach between 10 NM and touchdown, provided the following conditions are met:
>
> 1. Wake turbulence separation is not applicable
> 2. The exit taxiways of the runway can be observed from the control tower visually or by means of surface movement radar.
> 3. The runway is dry.
>
> 4.2 The reduced radar separation minima may also be applied between staggered approaches to the parallel runways. In these cases, neither the line of sight of the exit taxiways (4.1 b) nor the runway conditions (4.1 c) need to be considered as a precondition.
Additionally, the separation between dependent parallel approaches to the parallel runway systems 25L/25R and 07L/07R can be reduced to 1.5 NM.
REQUIREMENTS AND PROCEDURES FOR DEPENDENT PARALLEL APPROACHES
Dependent parallel approaches should only be conducted to parallel runways when the following
conditions are met:
1. separate air traffic controllers are responsible for the sequencing and spacing of arriving aircraft to each runway;
**(Note: As an exception for DFS, this procedure may also be used with only one Director)**
2. the runway centre lines are spaced by 915 m (3 000 ft) or more;
3. the final approach course or track is intercepted by use of:
1. vectoring; or
2. a published arrival and approach procedures that intercepts with the IAF or the IF.
4. \[...\]
5. the instrument flight procedure that aligns the aircraft with the extended runway centre line is one of the following:
1. a precision approach procedure;
2. \[...\]
3. \[...\]
- an appropriate, documented safety assessment has shown that an acceptable level of safety can be met; and
- operations are approved by the competent authority;
6. aircraft are advised that approaches are in use to both runways;
7. the nominal tracks of the missed approach procedures diverge by at least 30 degrees;
8. \[...\]
9. a minimum of nominal 300 m (1 000 ft) vertical separation or a minimum of 5.6 km (3.0 NM) horizontal separation is provided between aircraft until established on the final approach courses or tracks of parallel approaches;
10. the minimum horizontal separation to be provided between aircraft established on the same final approach course or track is 5.6 km (3.0 NM), or 4.6 km (2.5 NM) horizontal separation if so determined in accordance with ATS.TR.215, unless increased longitudinal separation is required due to wake turbulence;
11. the minimum horizontal separation to be provided diagonally between successive aircraft on adjacent final approach courses or tracks is:
1. 1. \[...\]
2. [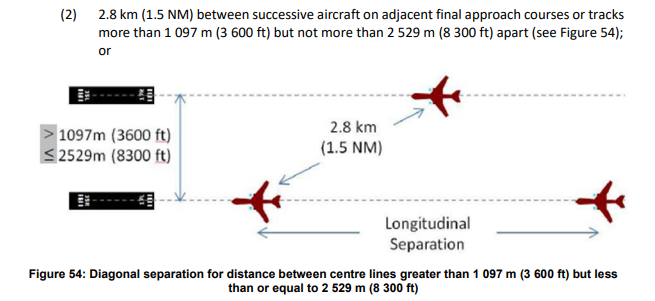](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-02/eddf-app-dependent.png)
Source: Regulation (EU) 2017/373, ANNEX IV — Part-ATS, 10.02.2023
It is very important not to drain out the final. Even if the Approach sector is too busy and traffic management holdings are necessary, usually there is no need to completely close sector entry for more than 5 minutes (around one orbit in the hold). After a short closure because of an overload on the Arrival/Director stations, it is recommended to set an aircraft rate per time, e.g. not more than one aircraft per 4 minutes via RASVO/IMCOM/ROLIS/KERAX and not more than one aircraft per 3 minutes via SPESA. Try to clear the holdings as quickly as possible. Due to the enormous capacity in parallel operations (up to 60 movements per hour), usually extensive holding usage is not necessary.
Besides the traditional holdings radar vectors along the downwind and final (without an approach clearance) can be used to delay inbounds as well. In this way, there is a lot of capacity to hold aircraft and it is easy to dissolve. It is recommended to use this procedure when the airport is completely closed for a short time. Do not have too many aircraft in this holding structure to make separation easy – the Center holdings can be used for any additional aircraft.
### Departure Procedures
Inbounds should stay above outbounds, clear of the Departure sector (at or above FL90). Outbound should stay at FL80 or below until they are clear of inbound traffic. If Departure and Arrival are staffed, a direct climb to FL110/FL130 can be coordinated if there is no conflict.
If the Arrival controller takes over the respective Departure sector, it is possible to let a departure climb above an arriving aircraft if the climb rate permits. Therefore make sure that at first inbound and outbound are vertically separated. Only when it is predictable that the outbound can overclimb the inbound, further climb should be issued.
Departing aircraft shall be handed over to the appropriate Center controller on the following flight levels to the following station:
| **Level** | **SID / Waypoint** |
| FL110 | CINDY / SULUS (out of RWY 18)
|
| FL130 | ANEKI / SOBRA / ULKIG / OBOKA / MARUN / TOBAK / SULUS (out of 07) |
All departing aircraft shall be handed over to the appropriate Center controller as early as possible, clear of any other traffic. **Traffic handed over from Departure to Center is fully released for further climb and turns.** Especially departing aircraft with the same routing, even for just some time, shall be separated by at least 10 NM laterally whenever possible. Otherwise, additional vertical separation shall be applied (e.g. for merging F and M/H routes if not solved by vectors, directs, or speeds).
### Modes of Operation
The runways system can be used in three different ways. This chapter explains these different modes of operation. In all systems, the main landing runways are 07R/25L and 07L/25R. Runway 07C/25C can be used as well (especially via visual swing-overs; see TWR SOP). In parallel operations, runway 07C/25C shall not be used by the Approach controllers and it shall not be used by the Tower controller for visual swing-overs two times right behind each other (swing-overs during 07 operations are only allowed for safety reasons anyways – see TWR SOP). If these rules are followed, visual swing-overs do not affect the following dependencies or independencies in any way.
Dependent operations are much easier to use but it does not have as much traffic capacity as parallel operations do. Usually, dependent operations are used on VATSIM. Especially during bigger events parallel operations may be the best way of handling the traffic.
#### Parallel Independent Operations
Arriving aircraft on runway 07L/25R are independent of arriving aircraft on runway 07R/25L as soon as they are established on the localizer.
1. The first Arrival controller to be contacted (not Director!) by the pilot assigns the runway. After the runway assignment, the handoff from one Arrival controller to another Arrival controller is necessary if the aircraft leaves one Arrival sector and enters another Arrival sector.
2. The pilot is handed over from the appropriate Arrival controller to the appropriate Director controller (Director North for all runway 07L/25R arrivals, Director South for all runway 07R/25L arrivals) no later than 10 NM before the expected turn onto the final (earlier handoff preferred).
3. Before hand-over from the Arrival to the Director controller, the aircraft must be instructed to descend to the intercept altitude (5000ft for 07L/25R, 4000ft for 07R/25L) whenever possible (this is strongly preferred!). If this is not possible, FL60/6000ft or higher could be used. Often it makes sense to instruct all pilots to maintain 220 KIAS before the handover to the Director controller.
4. The localizer or ILS clearance cannot be issued before the aircraft has reached the ILS intercept altitude.
5. Aircraft have to be at intercept altitudes inside the turn areas (see image). Any aircraft in the turn area not at intercept altitude has to be coordinated with both directors. If an aircraft is flying straight in and can not reach intercept altitude before entering the turn area, it has to be turned towards the downwind.
6. Outbound capacities can be reduced due to parallel operations. Target spacings (see above) should still be met wherever practicable.
With two Feeders it might be helpful to have all arrivals for runway 25L/07R (e.g. the ones not allowed on 25R/07L) on the southern downwind by clearing also arrivals from the north for the southern STAR. Inbounds from the north downwind for the southern runway will be handed over to FFS.
##### Procedures for parallel independent
- During this mode of operation, aircraft have to be able to fly 1 NM straight and level before intercepting the LOC and 2 NM straight and level before intercepting the GS (See ICAO DOC 4444).
- The Non-Transgression-Zone (NTZ) provided with the local Euroscope files defines a zone that must not be violated by approaching traffic. According to the ICAO definition, upon violation of the NTZ by one of the approaching aircraft, the aircraft in the adjacent approach must be instructed to perform a Go Around. It is not sufficient to instruct a Go Around for the aircraft violating the NTZ.
- The intercept of aircraft has to be performed so, that the aircraft establishes on the LOC inside the turn area.
- The line left of the turn area indicates the latest point at which an aircraft has to be established on the LOC, not below the published ILS intercept altitude, due to noise abatement reasons. Intercepts closer to the airport should be the exception if for example pilots overshoot the LOC and have to be turned back toward the ILS.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-07/eddf-turn-areas-25.png)*Turn areas for 25 configuration (green)*
##### Staffing
Possible staffing configurations (no others are possible!):
1. **DFDN, DFAN, DFFN** (recommended if no more controllers are available but there is too much traffic for staggered operations. Otherwise use staffing option 2 or use staggered operations.)
2. **DFAN, DFAS, DFFN, DFFS** (DFDN, DFDS) (recommended!)
3. **DFAN, DFAS, DFFN** (DFDN, DFDS) (not recommended!)
4. **DFAN, DFFN, DFFS** (DFDN, DFDS) (usually not recommended!)
5. **DFAN, DFFN** (only in exceptional cases where there aren't more controllers but the traffic amount does not allow staggered operations. This should be changed back to staggered operations as soon as practical.)
*Station in brackets: additionally one or more of these stations can be staffed.*
If just one Director is staffed, he takes over the other Director.
DFAS and DFAN, DFFN and DFFS as well as DFDN and DFDS can be interchanged if one of the frequencies is preferred due to the neighbor station.
In real life parallel operations can only be used with two Director controllers. On VATSIM parallel operations with only one director is possible if necessary, but not recommended. With two directors, only parallel operations are possible.
#### Dependent Operations
Arriving aircraft on runway 07L/25R are dependent to arriving traffic on runway 07R/25L. However, the separation for aircraft established on the parallel runways can be reduced to 1.5 NM. Wake turbulence separation has to be given at any time for aircraft approaching the same runway. It is also important that all aircraft have to fly a precision approach. If an aircraft is unable for a precision approach, it is required to switch to alternating operations for this aircraft.
##### Procedures
Director assigns the runway on the initial contact or very soon thereafter.
The handoff from Arrival to Director should take place no later than 10 NM before the expected turn onto the final (earlier handoff is preferred when able).
##### Staffing
Possible staffing configurations (no others are possible!):
1. **FAN** (FFN, FDN, FDS)
2. **FAN, FAS, FFN** (FDN, FDS) (not recommended!)
Station in brackets: additionally one or more of these stations can be staffed. FAS and FAN, FFN and FFS as well as FDN and FDS can be interchanged.
#### Alternating Operations
All arriving aircraft must maintain radar separation. Reduced Minimum Radar Separation (RRS) can be applied if necessary.
##### Procedures
Director assigns the runway on the initial contact or very soon thereafter.
The handoff from Arrival to Director should take place no later than 10 NM before the expected turn onto the final (earlier handoff is preferred when able).
##### Staffing
Possible staffing configurations (no others are possible!):
1. **FAN** (FFN, FDN, FDS)
2. **FAN, FAS, FFN** (FDN, FDS) (not recommended!)
Station in brackets: additionally one or more of these stations can be staffed. FAS and FAN, FFN and FFS as well as FDN and FDS can be interchanged.
### Minor Airports within the TMA
#### Egelsbach
Egelsbach (EDFE) is an uncontrolled airfield within the Frankfurt TMA. Egelsbach is handled the same way as any other uncontrolled airfield. If Egelsbach Radio is offline, it can be handled by DFAS if this controller has the VATSIM AFIS endorsement. Egelsbach airport can be delegated to Frankfurt Tower if this controller has the AFIS endorsement. If no controllers have the AFIS endorsement, Egelsbach airport cannot be covered with AFIS service.
Although Egelsbach is an uncontrolled airfield, a big ratio of the traffic is business traffic. This traffic is usually IFR but must depart or land VFR in Egelsbach. Standard procedures for IFR pickup or IFR cancellation apply. It is recommended to execute IFR cancellations southeast of EDDF at 4000ft or below. It is also recommended to instruct pilots inbound Egelsbach to leave airspace CHARLIE to below as soon as IFR is canceled.
Charts are available in the [AIP VFR](https://aip.dfs.de/BasicVFR/pages/C019C6.html "DFS AIP VFR EDFE").
#### Wiesbaden
IFR in-/outbounds to Wiesbaden (ETOU) need to be separated to Frankfurt in-/outbounds. Coordination between Arrival and Frankfurt Tower might be necessary.
An ILS approach is only available for runway 25 while both runways have RNP and TACAN approaches.
Wiesbaden's extended Northern pattern enters airspace D above the Wiesbaden CTR up to 2100ft. If use of the extended pattern is required, Wiesbaden Tower will request approval from DFAN.
IFR departures out of Wiesbaden are initially cleared to the final waypoint of the SID by Wiesbaden Ground. Further clearance to the destination is required once the aircraft is handed off to Langen Radar.
> **DUKE31**: Langen Radar, Duke 31, 2300ft, climbing 5000ft. **Langen Radar**: Duke 31, Langen Radar, identified, climb to FL130, cleared to Stuttgart via flight planned route.
> **DUKE31**: Duke 31, climbing FL130, cleared to Stuttgart via flight planned route.
Charts are available via [MILAIS GEMIL FLIP US DoD](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
Wiesbaden arrivals sometimes need to be descended earlier than Frankfurt arrivals to ensure a manageable descent profile. The following table shows some **tips on how to achieve this**.
| **Runway**
| **Direction**
| **Routing and descent profile**
|
| **07**
(RNP)
| from the Northwest
| direct to OU452 to cross OU452 at 5000ft, from OU452 cleared for the approach
|
| from the Northeast
| direct to OU455 to cross OU455 between 5000ft and 7000ft, from OU455 cleared for the approach
|
| from the South
|
| **25**
(ILS)
| from the Northwest
| direct to TAU to cross TAU between 5000ft and 8000ft, from TAU cleared for the approach
|
| from the Northeast
| direct to OU117 to cross OU117 between 4000ft and 7000ft, from OU117 cleared for the approach
|
| from the South
| direct OU115 to cross OU115 at 4000ft, from OU115 cleared for the approach
|
### Coordination
Before any session, the following coordination must be made:
**With Tower:** Runways in use (TWR decision), current ATIS information (TWR decision), mode of operation (APP decision)
**With Center:** STARs to use (APP decision), holdings usage (only if necessary – APP and CTR responsibility but APP decision)
All handovers are carried out as silent handovers as long as the relevant LOAs or additional agreements do not define a different procedure.
# EDDF - DeIcing
At Frankfurt de-icing is done around 50% at the parking position and 50% remote on the deicing pads. All outbounds should request remote deicing if required prior startup! Depending on the aircraft type (3/4 engine or A388) and departure runway (25C), remote deicing request can be denied and the outbound has to deice on position prior pushback.
### De-Icing Pads
For **departures out of runway 18 (and 07) DP1 and DP2 are primary used**, while for **departures out of runway 25/07 DP4 (and DP3)** are prefered if deicing on the position is not possible. Most of the pads have an east and west part, where simultanious de-icing is possible.
| **DP** | **Location** | **max. Usage** |
| **DP1** | west of runway 18
| **Code E +** B748
|
| **DP2C** | west of runway 18
| **Code E +** B748
|
| **DP2E / DP2W** | west of runway 18
| **Code C** (B739/A321)
|
| **DP3E / DP3W** | N7 blue/orange - **facing north** (!)
| **Code C** (B739/A321)
|
| **DP4E / DP4W**
| V159 / V161- **facing south** (!)
| max. 2 engined heavies
|
| **DP5** | G16A
| not used
|
Outbounds on the southern apron need to use one of the pads on the northern side if deicing on the position is not possible.
**A380s** have to **de-ice on position** prior pushback!
As soon as the aircraft is on the pad the pilot need to contact the "ice house" to coordinate the deicing process and further details (no Apron duty). After deicing the outbound needs to contact Apron again for further taxi to the holdingpoint.
> **Frankfurt Apron**: DLH123 continue to DP2 Center, hold abeam the eyeline and contact ice house.
Icehouse (all deicing duties itself and communication with the pilot) is not simulated at Vatsim Germany!
### Pad Usage
Outbounds with **3 or 4 engines** departing **runway 25C** should always be **deiced on position** prior pushback!
**DP1:** Primarily used for heavy traffic (prefered for 3/4-engine) for runway 18, possible for traffic departing runway 07C.
**DP2:** Pad East and West is primarily used for traffic departing runway 18 and can be used for traffic departing runway 07C when required. DP2C is rarely used and only if no code C aircraft is waiting for de-icing.
**DP3:** This pad is not prefered and should only be used when there is to much traffic for DP4 or DP1/DP2. Usually only used for traffic departing runway 25C/07C. When one of the pads is used, it's not possible to taxi via N7-orange/blue at all. Center Apron is always responsible for traffic to and from DP3.
**DP4:** Prefered for departing traffic out of 25C/07C, but can be used for traffic departing runway 18 as well. Center Apron is responsible for traffic to the de-icing pad. Traffic leaving DP4 need to be coordinated or transfered to West Apron for taxi out.
### De-Icing Apron
This position is only staffed during a high demand of remote deicing at DP1 and DP2. When the station is not staffed, West Apron is responsible for traffic to and from DP1 and DP2.
De-Icing Apron is **only responsible** for traffic sequencing planned on **DP1 and DP2** as well as the Apron area at N-North/P1 (incl. F231 - F238 and V266 - V270).
**[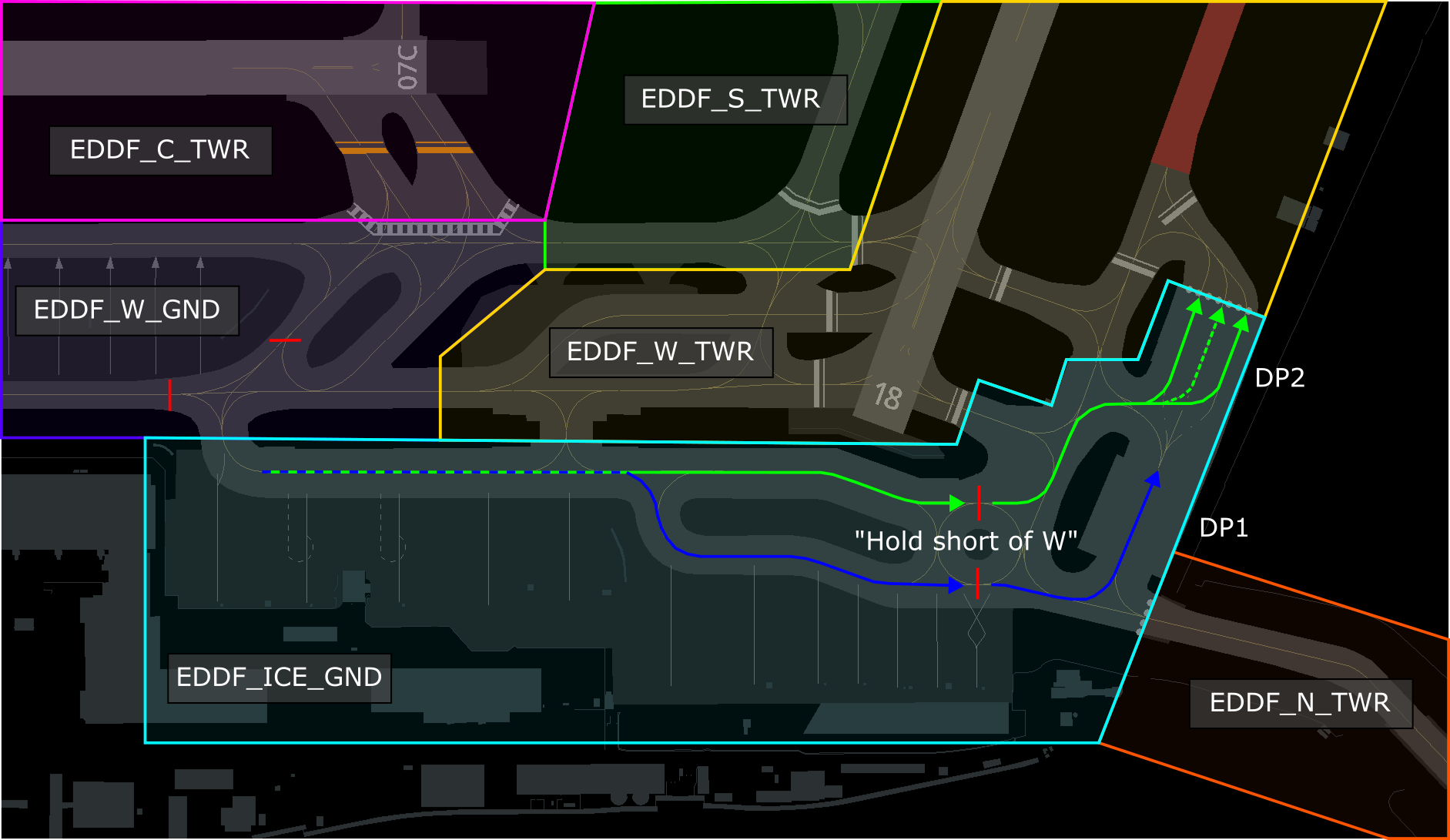](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/eddf-ice-gnd-aor.png)** *AoR De-Icing Apron*
Inbounds and traffic for the pads is handed over from West Apron free off conflicts short of N15/N. Outbounds for DP1 and DP2 will not cross runway 18, they always have to use N-North/P1! Outbounds on the positions in this area are handed over from Delivery direct to De-Icing Apron.
**Handoff Tower:** Outbounds from DP1 are send by Apron to W1 (18 departure) or W3 (07 departure for crossing runway 18) free of conflict. Outbounds from DP2 need to contact Tower to continue taxi to W3. All traffic is send to DFTW.
**07 Departures:** All 07C departures from DP1 and DP2 have to cross runway 18 via W3 - L. **Apron West is responsible to keep L** between runway 18 and L21 **clear** for traffic to runway 07C.
P1 can be closed on request by De-Icing Apron when to much traffic is waiting for deicing on P1/N-North.
# EDDL - Düsseldorf Airport
# EDDL - Overview
**All stations at Düsseldorf require a Tier 1 endorsement ([mentoring session necessary](https://training.vatsim-germany.org/lists "Training System")).** DEL and GND positions require the EDDL\_GNDDEL endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher. TWR requires the EDDL\_TWR endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. All APP/DEP positions require the EDDL\_APP endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
**Training:** Controllers with the S1 rating can staff TWR positions during their training (active EDDL\_TWR solo endorsement required). Controllers with the S2 rating can staff APP/DEP positions during their training (active EDDL\_APP solo endorsement required).
### Düsseldorf ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ADL
| EDDL\_ATIS
| 123.780
| --
| --
|
| **Delivery**
| DLC
| EDDL\_DEL
| 121.780
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)")
|
| **East Ground**
| DLGE
| EDDL\_E\_GND
| 121.605
| primary
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| West Ground
| DLGW
| EDDL\_W\_GND
| 121.680
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_GNDDEL](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **Tower** | DLT
| EDDL\_TWR
| 118.305
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_TWR](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **Approach**
| DLA
| EDDL\_APP
| 128.555
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| Arrival
(Feeder)
| DLAT
| EDDL\_F\_APP
| 128.655
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| Sector Bottrop
| BOT
| EDDL\_BOT\_APP
| 119.110
| -- | Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| Departure
| DLD
| EDDL\_DEP
| 121.355
| airborne frequency if DLD, DLA, BOT, or PADH is staffed;
covers BOT top down
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
### Düsseldorf Controlzone
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/eddl-ctr.png)*Düsseldorf Controlzone (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
# EDDL - Delivery
Düsseldorf Delivery is responsible for enroute and startup clearances for all departing IFR aircraft. VFR aircraft, except Police Helicopters, which call Tower directly, have to call Delivery for departure information.
**Startup:** Startup will normally be given when the pilot is ready for pusback and startup and not together with the IFR clearance. When startup clearance cannot be given immediately or the pilot is not ready for startup within the next 5 minutes during high traffic situations, the pilot needs to stay on Delivery frequency until he receives startup clearance. If an expected startup time (TSAT) exists, the pilot should be informed about it. This procedure might be necessary during events with a lot of outbound traffic. If Delivery notices the holding point getting too crowded startup intervals shall also be increased.
**Maximum active Startup Approvals** at the same time (status SUG until DEP) per runway (use the vSID startup counter):
**Single RWY OPS:** 10
**Parallel RWY OPS:** 13
Depending on the traffic situation, only for a short time more startup approvals shall be used.
With startup Delivery transfers the aircraft to the responsible Ground station depending on the current stand.
### Enroute Clearance
Runway 23L/05R is primary used for all departures. Delivery has to make sure that all SID restrictions are adhered to.
The **SID MODRU #K** shall only be assigned on pilots request when able to comply with climb restriction (9.5%) and RF-Legs. Prior coordination with Tower is mandatory. Decision on short notice to the pilot by Ground or Tower is possible, depending on the preceding traffic (see Tower section).
The **SID NETEX #K, #Y, #X, #U** are mandatory for flights to continue via NETEX DCT RASCA or NETEX DCT DELOM.
To ensure an efficient operation within the upper and lower airspace several restrictions should be met (check FPC column in Euroscope). To solve an invalid route, the pilot usually has to file a completely new route (valid routes for many destinations can be found on [grd.aero-nav.com)](https://grd.aero-nav.com/ "grd.aero-nav.com").
| **SID** | **Route** | **Restrictions** |
| **COL** | T911
| Flights to Frankfurt (EDDF) via COL must file a Requested Flight Level between FL150 and FL230 to ensure a correct sector order |
| **DODEN** | Y853
Y852 | Flights unable to comply with restrictions shall file via KUMIK
|
| **GMH** | Z841
L603 | RFL 140- |
| **KUMIK** | Y854
L603 | RFL 150+ |
| **LMA** | Z282 | Only for flights to EDLN or local IFR (subject to coordination) |
| **MEVEL** | Z44
L179
Y850 | 23L/R: Max. 190kt IAS until on NOR Radial 001° |
| **MODRU** | Z717
Z283
| Cross MODRU FL 210 or above |
| **NETEX** | Z282
Z283
| Not to be used if military airspace in the north of the EBBU FIR is active. Information about the activation of the military areas can be obtained from the EBBU controller. |
| **NVO** | M170
Q760
| RFL 90-
Flights with RFL 100+ shall file via MODRU
|
| **NUDGO** | Z858 | RFL 245- |
| **SONEB** | P55
P64 |
|
#### Visual Departure
Visual departures can be requested by pilots or offered by ATC when weather and visibility conditions permit. Visual departures are only permitted during daytime operations and require coordination between Delivery, Tower and Arrival. Visual Departures are only allowed for propeller aeroplanes of up to 5.7 t MTOW, with the exception of potential safety concerns (e.g. weather avoidance). Reasons for the pilot to request a visual departure include weather avoidance or shorter routing for efficiency. Further information can be found [here](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/ifr-lhx/page/visual-departure "Visual Departure Article")
#### Vectored Departure
Usually all RNAV capable aircraft that are available for flight simulators are able to fly a SID and most likely are looking for the wrong runway! If pilots nevertheless are unable to fly any SID (even an older version of the current SID or the LMA SID) a vectored departure can be coordinated between Delivery and Arrival. Usually runway heading and an initial climb of 5000ft will be used. Other coordinations are always possible. In the Departure/Startup List select the corresponding "RV" SID for this departure.
However, there is rarely a proper reason to fly a vectored departure, thus if a pilot requests this due to inability to fly any SID, question their capability to conduct IFR flight properly.
#### Local IFR
Local IFR flights are prefered via **LMA SID** (radar vector departure on request possible). Coordination with **Arrival (DLA)** prior enroute clearance as well as a **startup release** is required.
Local departures need to be advised to contact **DLA** on 128.555 immediately after departure.
### Datalink Clearance (DCL/PDC)
At Düsseldorf Airport we offer Datalink Clearance to the pilots via the **[Hoppie System](https://www.hoppie.nl/acars/ "Hoppie Datalink System")** and the Topsky Plugin. The airport code **EDDL** should be used (already preselected).
An example of the DCL message the pilot will receive can be seen below. By default every outbound has to call Delivery for startup.
CLD 2042 220117 EDDL PDC 026 SAS461L CLRD TO EKCH OFF 23L VIA MEVEL4T CLIMB 5000 SQUAWK 2055 ADT MDI NEXT FREQ 121.780 ATIS H REPORT READY ON 121.780
### High Traffic at EDDK
During high inbound peaks into Cologne with 13 operations, Cologne Approach may use the Düsseldorf Approach sector. Therefore traffic departing Düsseldorf out of runway 23L/R to the south (COL, DODEN, NUDGO, GMH, KUMIK, NVO) require a **startup release** by Düsseldorf Approach.
In case of startup delays, it might be useful to clear **outbounds to the south via MEVEL SID** and radar vectors to the filed first waypoint (no clearance via datalink for that). Additional coordination with APP required when this procedure should be used!
> ... cleared XXXX via MEVEL4T, expect radar vectors to DODEN/KUMIK/NUDGO/COL/NVO, flight planned route...
When the MEVEL SID is used, the flightplan need to be amended accordingly (e.g. "MEVEL DCT DODEN")
**vSID:** Use the alias command "**.nosouth**<space><enter>" to disable the automatic vSID assignment for outbounds to the south.
SIDs via "MEVEL DCT XXXXX" are highlighted.
# EDDL - Ground
Düsseldorf Ground is responsible for all ground movements at the airport and can be split into east and west ground. If more than one ground is staffed, Delivery needs to be staffed first.
### Area or Responsibility
The area of responsibility for each ground station can be seen on the image below. Each ground can only issue taxi clearances until the respective checkpoint. Any clearance beyond the checkpoints has to be coordinated. The handoff between ground stations should take place as early as possible so aircraft do not have to stop at one of the checkpoints
> EWG1PM, hold short of Checkpoint 1, contact Ground on 121.605.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-11/eddl-aor-gnd.png)*Sector Split Düsseldorf Ground West and East*
### Parking Positions
Parking positions are assigned automatically for all inbounds according to the real life conditions by the Ground Radar Plugin.
**Terminal A** is used by Lufthansa and Star Alliance Members for Schengen and Non-Schengen flights. **Terminal B** is only used for Schengen flights, while **Terminal C** is only used for Non-Schengen flights.
V01 should not be used as parking position.
The **A380** can only use Gate **C02A**. Stands V08B, V11B (and V38B if all other positions are occupied) are capable for the A388, but are not included in every scenery.
### Pushback
All **Heavy** aircraft are not allowed to push into the "terminal bays". They always have to push on taxiway T or P4.
In general only facings "north, south, west and east" are used. If traffic is instructed to push onto T or P4 this needs to be specified with the clearance: "Pushback approved, facing north, onto P4".
Only stands V61 - V72 and V75, V76 are taxi out positions. All other positions (incl. V70, V73 and V74) require a pushback!
Example Pushback Options
**1.** "*Pushback approved, facing north*" (Some pilots may not be able for this procedure)
---
**2.** "*Pushback approved, facing west onto T*"
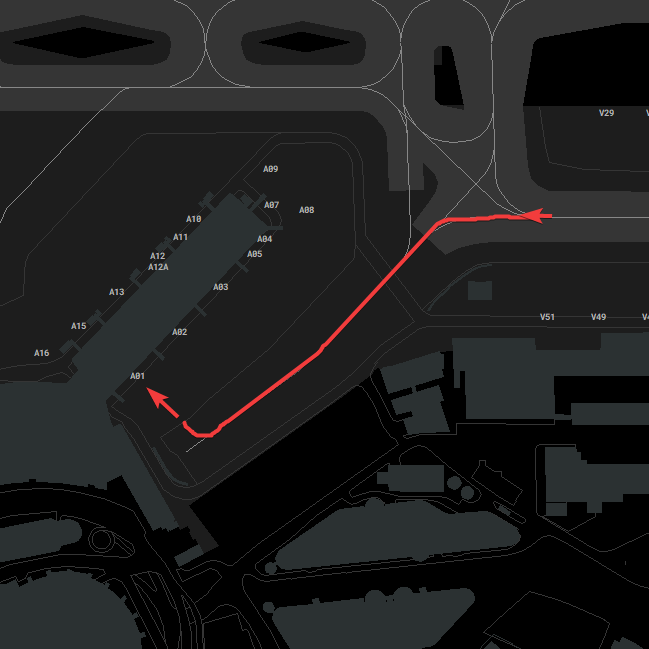
---
**3.** "*Pushback approved, facing east onto T, between P2 and P3*"
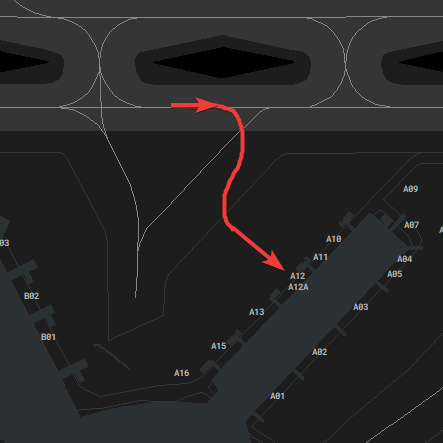
---
**4.** "*Pushback approved, facing north*"
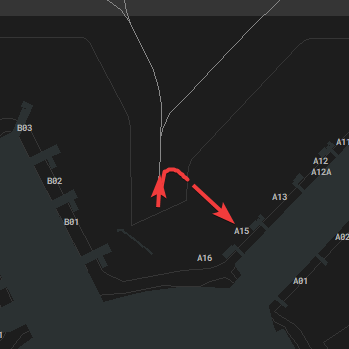
---
**5.** "*Pushback approved, facing east onto T, between P3 and P4*"
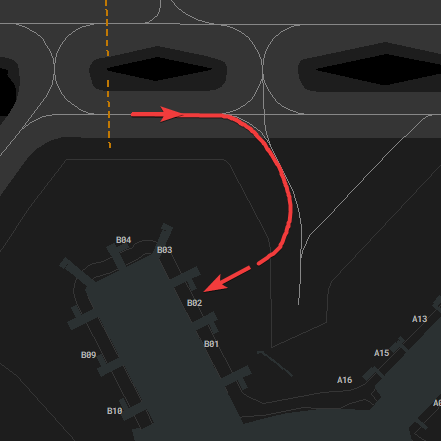
---
**6.** "*Pushback approved, facing west*" (Some pilots especially from Gate C01 and B11 may not be able for this procedure)
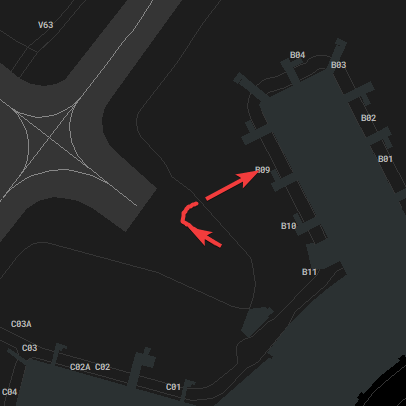
---
**7.** "*Pushback approved, facing north onto P4*"
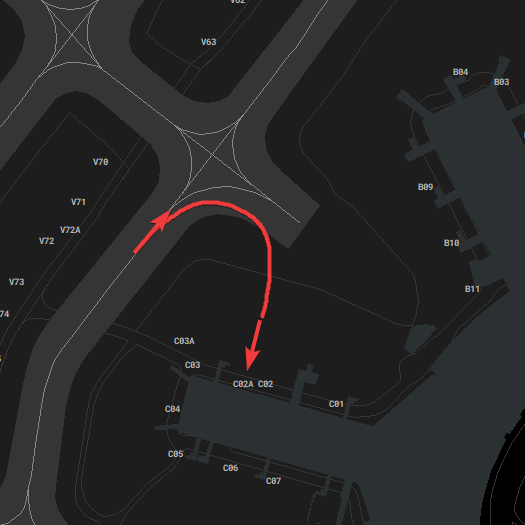
---
**8.** "*Pushback approved, facing north onto P4, south of R*"
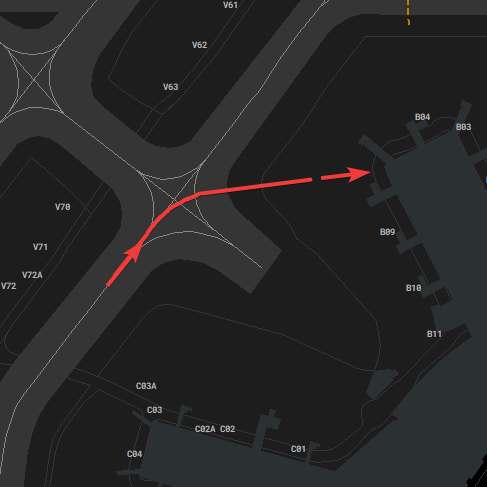
---
**9.** "*Pushback approved facing north/south onto P4, (stay clear of R)*"
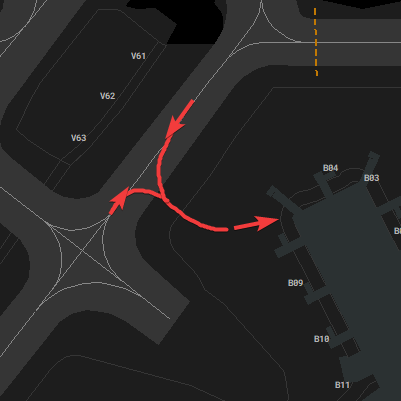
To enable an efficient traffic flow, pushback onto Y, T, P4 and R can be used instead of the "terminal bays" for all medium aircraft. This way up to 3 aircraft can push simultaneously.
### GA Apron
**Inbound** traffic to the GA Apron always needs to enter the apron via **taxiway H**. **Outbounds** parked south of the gas station (in the middle of the apron) will exit the GA Apron via **taxiway H**, outbounds parking north via **taxiway G**. The GA Apron is limited to aircraft with a maximum wingspan of 29 m.
### Taxiway Usage
Taxiway M is *normally* used in the direction towards the holding point of the active runway, depending on the current operating direction. Taxiways P1-P4 connect the Apron with Taxiway M.
#### Typical Conflicts
**Apron-to-Taxiway M Intersections**: The most common ground conflicts occur at the intersection points where apron taxiways (P1, P2, P3, P4, etc.) meet the main taxiway M. Special care should be taken to keep scanning the junctions for possible conflicts. One of the multiple solutions for this type of conflict can be to either use "Taxi via" and hold the traffic in front of M. Alternatively a taxi instruction with a give-way can be used just as well.
**Crowded holding point during 05 Operations:** Traffic approaching intersection L9 via M and via T1 have a high conflict potential when turning into the intersection. One of the multiple solutions for this problem can be to keep the junction before the holding point clear so the Tower can decide the departure sequence himself.
#### Use of Intersections
Ground will assign the intersections for departing traffic. The pilot always needs to be asked if able for an intersection when not using L1 or L9. This also applies to L2 and L8. Intersections a pilot is able for should be noted in the remarks. Outbounds shall be sent to Tower **as soon as they are clear of any conflicts**. Tower is always able to change the intersection according to the current traffic situation at the holding point and final.
If possible, Ground should sequence the outbounds on M by north/south or different SIDs when they are departing into the same direction.
**L2** is only used for "faster following" or WTS if there is no prior possibility to get outbounds in the best departure sequence on taxiway M. Consider taxiway restriction for overtaking traffic on L2. When there is no benefit (e.g. one inbound between two outbounds), L2 intersection should not be used.
Only intersections with a published TORA (see charts) may be used for departures, even if the pilot reports that he would be able for a different intersection. As an exception, helicopters may depart from every part of the runway up to the runway end.
Generally, an intersection may only be assigned to a departing aircraft when the pilot either reports by himself that he is able for that intersection or agrees to it after a controller’s request - regardless of the aircraft type.
Intersections should not be used if there is no benefit for the outbound!
#### Taxiway Restrictions
- **Taxiway P1 and L5:** While one of these taxiways is occupied by a B744/B777/A350, the other one is restricted to a maximum wingspan of 60.5 m (largest possible aircraft A330/A343).
- **Taxiway M and** **T/T1 between P1 and L9:** While one of these taxiways is occupied by an A380, the other one is restricted to aircraft up to a maximum of A310/B757. Parallel taxi is only possible for aircraft with a maximum wingspan of 65 m.
- **Taxiway M and T at L3:** Taxiing from taxiway M onto T, and vice versa, via L3, is restricted to maximum code C aircraft.
- **Taxiway L1 and L2:** L2 is restricted to a maximum of code E aircraft, as well as B777 and A346. Overtaking on L1 and L2 is only permitted for aircraft up to A330/A343
- **A380:** The A380 is limited to specific routings on the apron.
All relevant restrictions, as well as the A380 taxi routings, are available as a Ground Radar Map (Functions -> Map Selection -> Restrictions).
### DE-ICING Areas
During 23 operations De-Icing Area East (V01 - V11B) is used and during 05 operations De-Icing Area West (V61 - V72) is used. The detailed map is available as Ground Radar Map.
| **DE-ICING Area - West**
[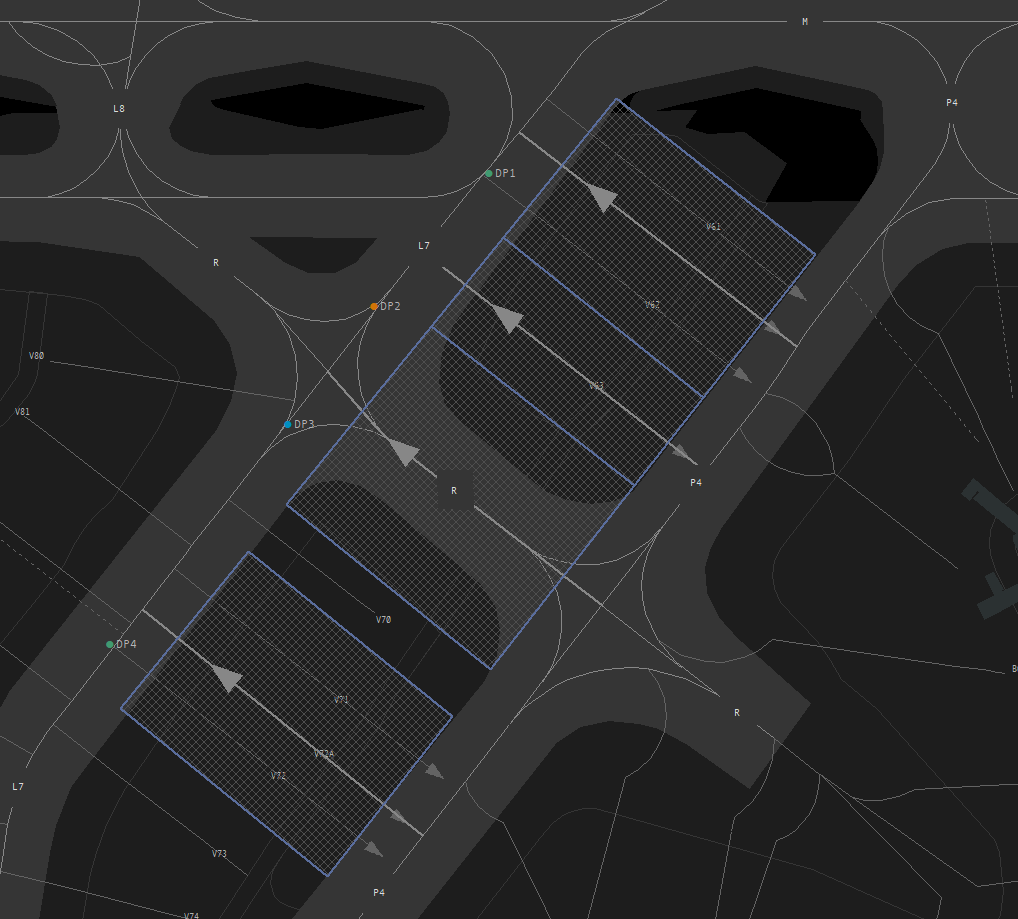](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-11/eddl-da-west.png)
**DP1** - max. Code E
**DP2** - max. Code C
**DP3** - max. Code F
**DP4** - max. Code E
| **DE-ICING Area - East**
[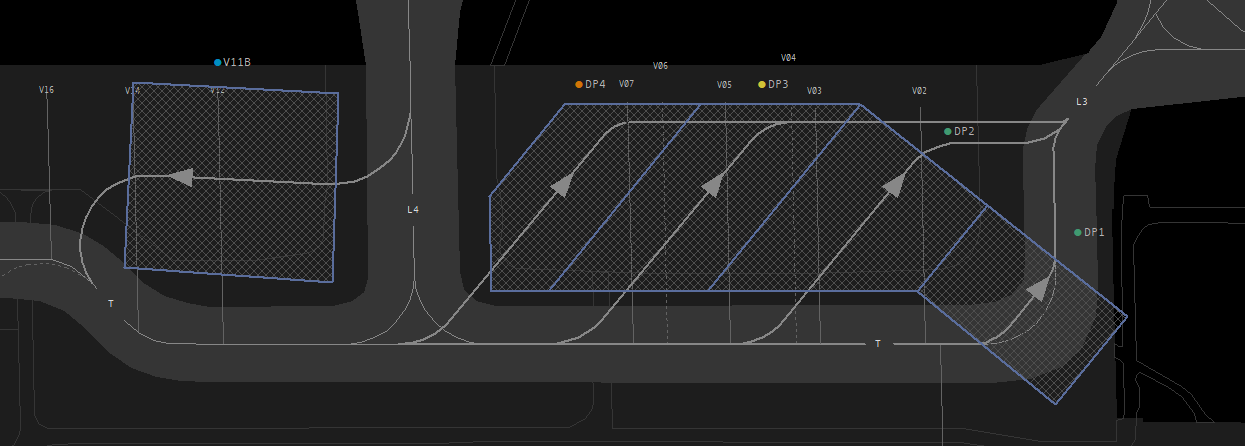](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-11/eddl-da-east.png)
**DP1** - max. Code E
**DP2** - max. Code E
**DP3** - max. Code D
**DP4** - max. Code C
**V11B** - max. Code F
|
### Arriving Traffic
**Vacating RWY 05R:** Traffic vacating RWY 05R via via L1, L3 or L4 (after landing or crossing) are instructed by Tower to turn right on M. The handoff to Ground will take place thereafter. This will prevent traffic to stop in the intersection and blocking the runway during frequency change.
It is **not** allowed to vacate/cross rwy 23L **via L7 and turn left on M**.
# EDDL - Tower
Düsseldorf Tower is responsible for the runway system and traffic within the [Düsseldorf CTR](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/link/1586#bkmrk-%C2%A0).
### Runway Usage
Düsseldorf Aerodrome has 2 main operating modes:
##### Single Runway Operations:
During single runway operations, the southern runway is used for all departures and arrivals, with the exception that VFR aircraft inside the traffic circuit **can** be allowed to use the northern runway to allow a more efficient flow between IFR flights and VFR traffic. During brief periods of higher simultaneous inbound and outbound traffic, it may be necessary to coordinate target spacing on final approach with Feeder.
##### Parallel Runway Operations
During parallel runway operations, the southern runway is used for departures, while the northern runway is used for all arrivals. This configuration should be used when traffic volume exceeds (or will exceed) the capacity of single runway operations, as it allows for tighter inbound spacing and increased overall throughput. The A380 shall not use the northern runway and will always land on the southern runway without requiring prior coordination.
### Parallel Runway Dependencies
The parallel runway system cannot be used for independent parallel approaches or independent parallel departures.
Segregated parallel operations may be conducted when arrivals use the northern runway and departures use the southern runway, with the exception of runway 23L departures utilizing early right-turning SIDs (SONEBxT, MEVELxT, NETEXxT, and LMAxT departures). Controllers may issue takeoff clearances without waiting for landing completion on the parallel runway, provided the controller has both aircraft in sight and no increased probability of missed approaches or track deviations exists. This procedure shall not be used when wake turbulence separation would be required between a preceding departure or a potential missed approach overtaking the departure.
During reduced visibility when visual contact cannot be maintained, the parallel runways must be treated as a single runway system, meaning a previously departing aircraft must have either overflown the end of the runway or initiated a turn before the landing aircraft crosses the threshold on the parallel runway. The procedure of not withholding takeoff or landing clearances can be applied while considering the parallel runways as one system. However, since there are physically two runways, landing clearance may be issued once the corresponding runway is clear, and takeoff clearance on the parallel runway may be given as soon as arriving traffic has touched down and begun decelerating. If runway separation cannot be guaranteed, any takeoff on the parallel runway must be aborted.
Since the runways in Düsseldorf are less than 760 m apart, wake turbulence separation between both runways must be ensured at all times.
#### Visual Swingover
When traffic conditions allow, aircraft may be cleared for a visual swingover from the northern runway to the southern runway. Prior to issuing the visual approach clearance, pilots must report the southern runway in sight. Along with the visual approach clearance, controllers shall provide missed approach instructions, typically consisting of runway track and climb to 4000 feet, as a missed approach procedure does not exist for a visual approach.
### Arriving Traffic
For inbounds, Düsseldorf Arrival is responsible for separation until transfer of communication. Düsseldorf Tower is responsible for maintaining separation of arriving traffic from transfer of communication until touchdown, if necessary by use of adequate means (e.g. speed control), and during the initial part of a missed approach.
**Vacating RWY 05R:** Traffic vacating RWY 05R via L1, L3 or L4 (after landing or crossing) should be instructed by Tower to turn right on M. The handoff to Ground will take place thereafter. This will prevent traffic to stop in the intersection and blocking the runway during frequency change. Traffic vacating runway 05R (or 05L via K1) are not permitted to taxi into L2.
#### Missed Approaches
All missed approaches are subject to immediate coordination with the appropriate approach controller. Upon notification of a missed approach, DLA will normally issue the tower controller a heading for the aircraft. If no alternative instruction is provided by DLA, the missed approach will fly the standard missed approach procedure as published. Tower may take immediate action to reestablish separation if required, but must inform the approach controller without delay. The handover takes place once separation is established. The next departure requires a departure release.
#### Runway Crossings
Traffic landing on the northern runway will have to cross the southern runway, before being handed over to ground. Traffic vacating 23R via K3 shall cross the runway into either L7 and L6, depending on their assigned Gate and shall be handed over to either east or west Ground. This will reduce congestion around the Checkpoints and avoid unnecessary frequency changes. It is not allowed to vacate runway 23L via L7 and turn left on M.
### Departing Traffic
All departures must be separated by at least 3 NM or wake turbulence separation, whichever is greater. If visual separation is used during VMC conditions to reduce initial departure separation, the tower controller has to ensure the succeeding aircraft remains on tower frequency until 3NM or 1000ft separation are ensured. During 23 Operations, it is necessary to observe the speed of both aircraft if initial separation is close to 3 NM, as the distance between both aircraft involved shrinks as soon as the first one starts its turn.
Increased separation on the same SID is **not** necessary, however precise monitoring of speeds is crucial and if the suceeding aircraft gets faster, the controller needs to react in terms of restrictive altitude instructions and/or restrictive speed instructions.
**Rule of thumb for 23 Operations:** Generally, if the distance between the two departing aircraft is higher than 3.5 NM prior to a 90 degree turn minimum separation should not be less than 3 NM provided that the preceding departure is faster.
**MODRU/NETEX #T** followed by **\#K** requires at least 4 minutes separation due to the shorter routing. Depending on the outbound sequence on taxiway M it might be useful not to use #K SIDs.
If separation has to be reestablished, such as during a missed approach on short final with departing traffic already airborne, or when departure spacing becomes too tight, transfer of communication shall take place only after Tower has ensured proper separation. In such situations, it may be necessary to instruct a departing aircraft to "remain on tower frequency" until separation is established.
**Transfer of Communication or "Auto Handoff":** Usually all departures on a SID have to contact Langen Radar according to the charts on their own when passing 2000ft AMSL. Departure frequency shall be published in the ATIS.
Independent lineup is possible for all intersections **with traffic information** for the second departure. Intersection L2 should only be used if there is a real benefit for departures.
Special Lineup RWY 23L
In case outbound traffic requires the maximum available runway length for runway 23L, the pilot can request a special lineup via L1. This lineup will take longer as usual.
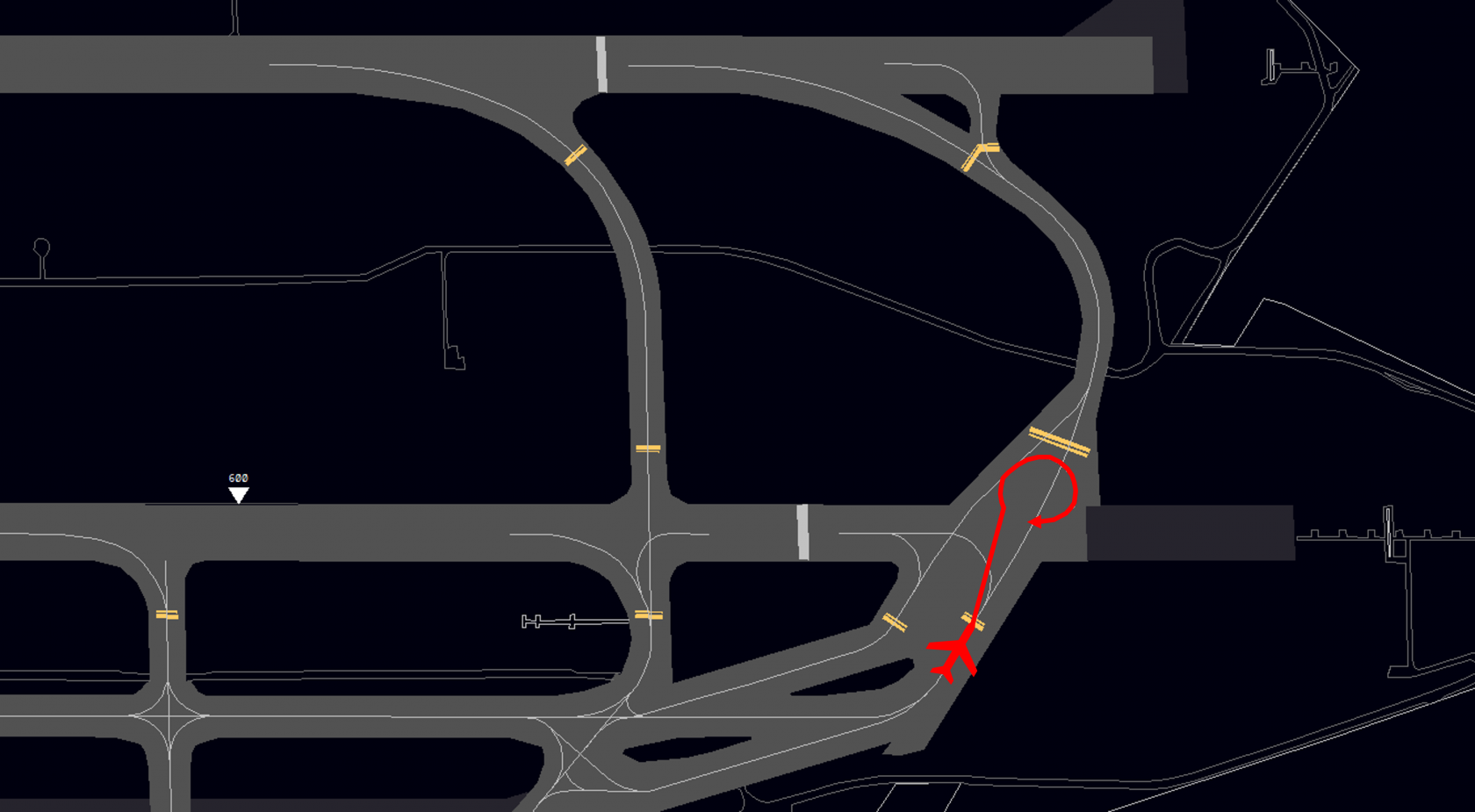
High Traffic at EDDK
During high inbound peaks into Cologne with 13 operations, Cologne Approach may use the Düsseldorf Approach sector. Therefore traffic departing Düsseldorf out of runway 23L/R to the south **requires a startup and departure release** by Düsseldorf Approach.
Tower will be informed by DLA and needs to inform Delivery!
| **Runway**
| **Preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 1**
| **Preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 2**
| **Preceding CAT 3**
**succeeding CAT 1/CAT 2/CAT 3**
|
| **05L/23R** | 600m | 1500m | N/A |
| **05R/23L** | 600m | 1500m | 2400m |
### VFR Traffic
The [Düsseldorf CTR](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/link/1586#bkmrk-%C2%A0) extends up to 2500ft AMSL. Neighboring the Düsseldorf CTR to the west is the Mönchengladbach CTR (EDLN), which extends to 2000ft AMSL. All VFR flights transitioning between the two control zones require coordination. Class C airspace is respectively lowered to 2000ft AMSL over the Mönchengladbach control zone and to 1500ft AMSL at the eastern border of Düsseldorf CTR due to proximity to Essen-Mülheim Airport (EDLE). For further details see VFR charts.
**Reporting Points and Holdings:** Düsseldorf has three mandatory reporting points: NOVEMBER (N), SIERRA (S), and ECHO (E). SIERRA and ECHO lead into published VFR holding procedures south of the field, while NOVEMBER has a published holding procedure north of the field. Without further clearance after passing one of the visual reporting points, aircraft will automatically proceed to their respective published holding patterns. During low traffic situations, direct control zone entries may be approved.
**Helicopter Operations:** The dedicated helipad in front of Hangar 10 is exclusively reserved for NRW police flight squadron (Hummel) and federal police (Pirol) operations, who may depart and land without contacting Delivery or Ground. All other helicopters must use the active runway for departure and landing operations. Christoph 9, stationed at BGU Duisburg approximately 2.2 NM southeast of NOVEMBER, frequently requests transit through the control zone during emergency missions.
**Important Landmarks for VFR Flights**
- Rhein River
- Autobahn A3 (commonly followed by VFR aircraft crossing from ECHO to NOVEMBER)
- Düsseldorf University Hospital (UKD) - approximately 3 NM north of SIERRA
- Berufsgenossenschaftliche Unfallklinik Duisburg (BGU) - approximately 2.2 NM southeast of NOVEMBER
### Low Visibility Procedures
LVO shall be announced in the ATIS and target spacing for arrivals shall be increased. Additionally, all traffic shall be told to hold at the CAT III holding points. RVR values will be given with the landing clearance and in the case of guided take-off (RVR ≤ 125 m) with the take-off clearance.
**Taxiway restrictions:** At runway visibility ranges (RVR) less than 350 m, taxiway K and L5 between RWY 05R and taxiway M are closed. Additionally, it is not possible to vacate runway 05R via L8 and runway 23L via L3 with runway visual ranges of less than 350 m.
Refer to this article for more information: [Low Visibility Operations (LVO)](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/practical-procedures/page/low-visibility-operations-lvo).
# EDDL - Approach
Düsseldorf Approach is primarily responsible for all arrivals and departures at Düsseldorf Airport **EDDL** and Mönchengladbach Airport **EDLN**. If sector Bottrop (BOT) is not staffed separately, its tasks are also taken over by Arrival, which means that arrivals and departures to/from Niederrhein-Weeze **EDLV** and Geilenkirchen **ETNG** also are within the area of responsibility.
## Sectorization and Airspace
### Düsseldorf Approach (DLA)
**Düsseldorf Approach (DLA)** is the **primary station** and is mainly responsible for the Düsseldorf TMA.
In general, the arriving aircraft should use the transitions, directs or vectors. STARs should not be used as they all lead to DUS VOR close to the airport as initial approach fix.
During a constant arrival stream into Düsseldorf on northern and southern downwind, Approach should hand over traffic with **6 NM or greater spacing per downwind** to enable Feeder to create an efficient final.
The arrival controller is responsible for clearing the procedures, but can also delegate this to the centre controller by agreement (exception: PISAP/LMA arrivals).
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/eddl-dla2x.png)
*Sector Düsseldorf Arrival (DLA)*
**Winter-MVA:** The 3200 ft AMSL MVA area south of the final runway 23L can be used down to -10 °C with summer MVA (3000 ft AMSL). The 2200 ft AMSL range around the airport can be used down to 0°C with summer MVA (2000 ft AMSL).
**High Traffic at Cologne:** During high traffic situations at EDDK with 13 operations and low traffic at EDDL, DKA can request a general airspace crossing to vector inbounds 13L/R through the DLA sector. Traffic need to stay at 5.000ft or below within AoR of DLA and at least 3 NM south of the extended centerline RWY 05R. Further individual coordination for level and extension possible when required.
Düsseldorf outbounds out of runway 23L/R to the south via DODEN, KUMIK, NUDGO, COL, NVO and GMH require a **startup and departure release** by DLA (expect departure around 10 - 15 minutes after startup)! For all waypoints outbounds can be cleared via **MEVEL SID and radar vectors** to the first filed waypoint.
Withdrawing the agreement requires around 10 - 15 minutes for DKA and should be done shortly after a startup release prior the departure release.
DLA has to inform DUS Tower when this agreement is in operation!
#### Important Areas
The Dortmund Area (shown in orange) is between GND and FL65 and permanently operates under PADL's responsibility for all Dortmund inbound and outbound flights. Düsseldorf Arrival must keep aircraft at or above FL70 in this area. When operating below this altitude, each aircraft requires an individual release from PADL.
The TEBRO Area (shown in red) spans from FL205 to FL245 and permanently operates under EHAA's control. Amsterdam departures pass through this area.
[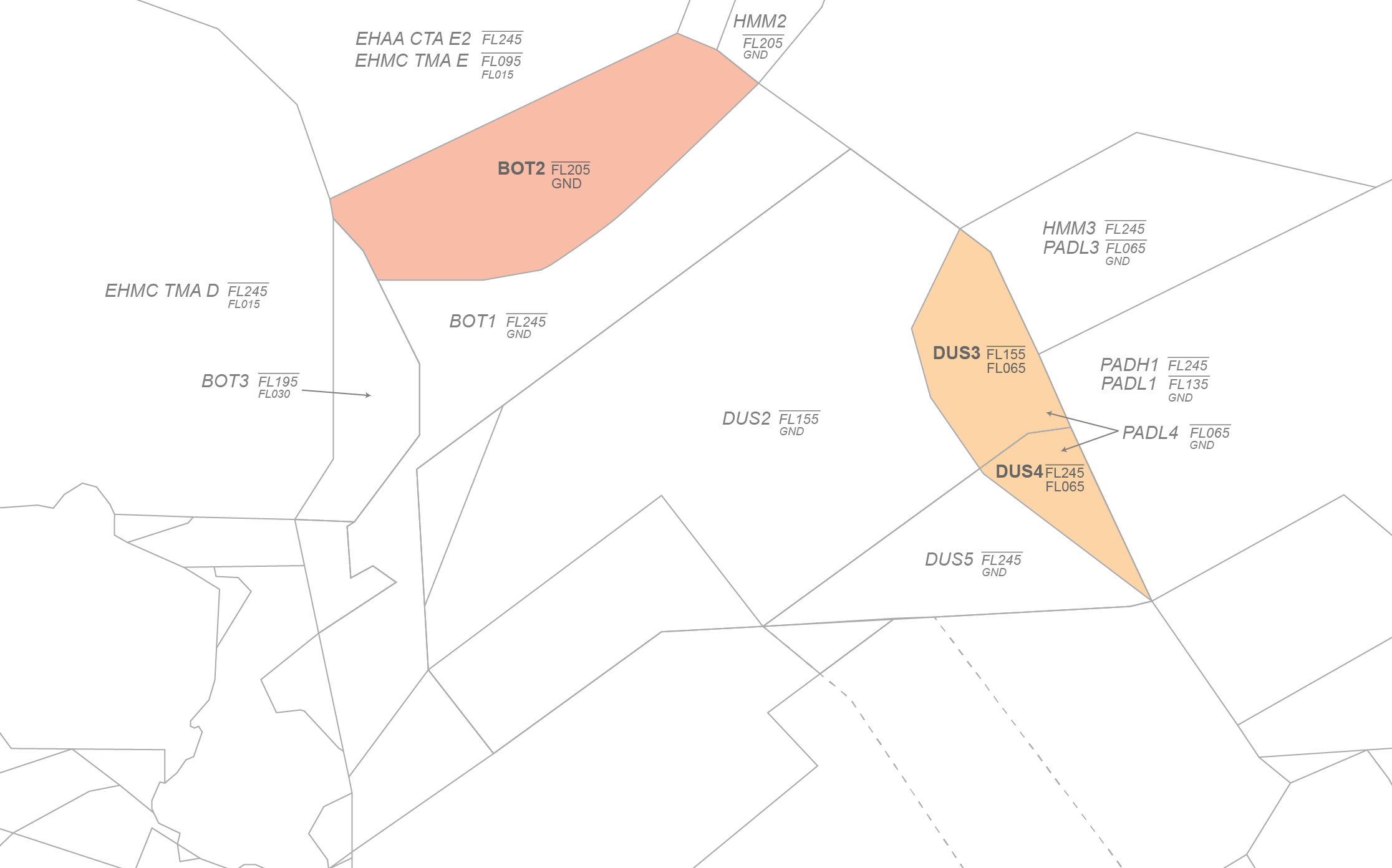](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/eddl-areas2x.png)
*Important Areas*
### Feeder - Düsseldorf Arrival (former Director) (DLAT)
Düsseldorf Arrival can be split into two units to distribute the workload along two controllers with a lot of traffic. DLAT takes on the tasks of the feeder, while DLA handles the tasks of the so-called pickup. Both operate within the same airspace, so there are no fixed transfer conditions. However, certain aspects should be taken into consideration:
- The pickup ensures that the aircraft have the correct ATIS, inform a/c about runway to land, and establishes a sequence. This is achieved by using speeds, vectors, or transitions, as well as appropriate and separated levels. Coordination of the sequence between both units is not required, as long as the pickup transfers the aircraft to the feeder in the order planned for the sequence. Any deviation from this order should always be coordinated.
- The feeder's task is to line up the aircraft on final approach with optimal spacing. The minimum spacing for the same runway is 3.0 NM. If the aircraft are landing on different runways, the separation can be reduced to 2.5 NM within 10 NM of the threshold.
- At the same time, there is a constant effort to balance the workload between both units. The pickup may also be occupied with other problems in the sector, which justifies the presence of a feeder even during heavy inbound traffic. Additionally, a feeder can, for instance, handle IFR cancellations for Essen inbounds on runway 23 or manage Mönchengladbach in- and outbounds during 05 operations, thereby relieving the pickup. This often makes sense because the feeder is already separating inbounds in this area anyway, which also reduces coordination to a minimum.
- If the pickup is very busy however the feeder has less traffic, handoffs can be done early and without sufficient spacing, vectors or speeds as long as separation exists. In this case the feeder has the capacity to establish sufficient spacing and is able to reduce the workload of the pickup controller.
- The workload balancing also works in the opposite direction. If the feeder becomes very busy and reaches his capacity limits, the pickup must ensure that aircraft are sent as simply and uniformly as possible. In such cases, aircraft should be transferred with sufficient spacing on the downwind at FL70 or FL80 and a speed of 220 knots. Significant deviations from the downwind make the feeder's job harder. If the aircraft are too low, there is a risk of entering the PADL Wickede during 23 operations. Additionally, this provides the feeder with enough levels to work with vertical separation effectively.
### Reduced Minimum Radar Separation
Minimum separation of IFR flights approaching the parallel runway system (23L & 23R or 05L & 05R) can be reduced to 2.5 NM, according to AIP, if no **wake turbulence separation** has to be applied:
> Reduced Minimum Radar Separation for Diagonal Staggered Approaches (Based on NfL I - 9/09)
>
> 1. The Minimum Radar Separation (MRS) for diagonal staggered approaches to parallel runways at Düsseldorf Airport is 2.5 NM between 10 NM and the touchdown point.
>
> 2. The reduced MRS will be applied to landing directions 05 and 23, provided
> the following conditions are met:
> \- Preceding and succeeding aircraft are approaching different parallel runways.
> \- Both aircraft are established on the final approach track.
*Quote from AIP Germany/AD 2 EDDL 1-23 (by the German Luftfahrt-Bundesamt), applicable on VATSIM.*
### Sector Bottrop (BOT)
Sector Bottrop is responsible for the lower airspace approximately north of Düsseldorf and a small part above the arrival sector. In addition to arrivals and departures for Niederrhein-Weeze (EDLV) and the Geilenkirchen military airfield (ETNG), its tasks primarily include through flights to and from Düsseldorf.
[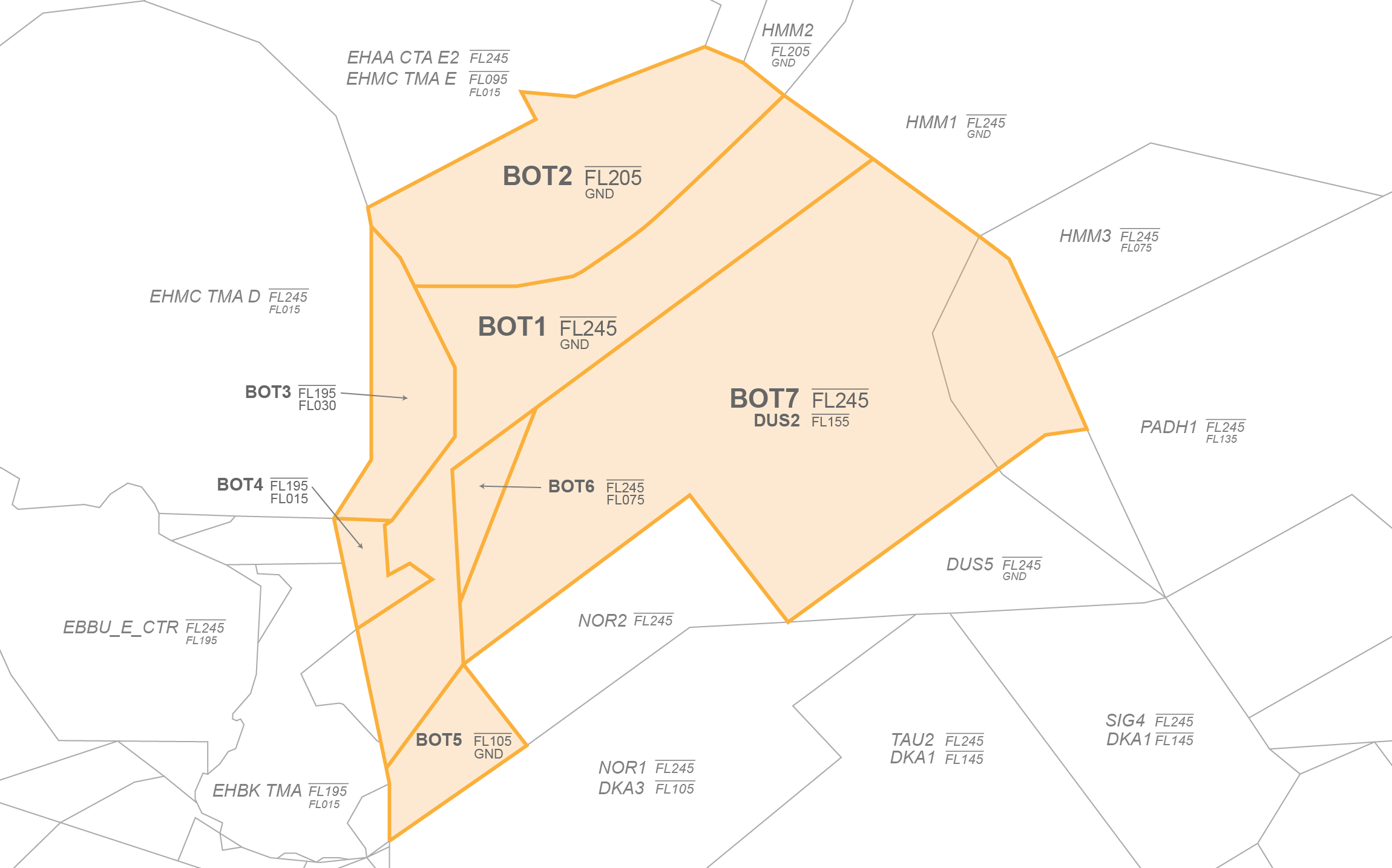](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/eddl-bot2x.png)
*Border Langen Radar Sector Bottrop (BOT)*
If the Bottrop sector is not staffed separately, it is taken over by Düsseldorf Approach by default.
**Flights through BOT:** In addition to the flights to and from Düsseldorf, there are also flights in lower airspace and to destinations in the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg. The respective transfer altitudes are published in the respective LoA. Flights to **Münster/Osnabrück (EDDG)** via BAMSU must be cleared for the BAMSU#J arrival before the transfer to the HMM sector takes place.
### Düsseldorf Departure (DLD)
Düsseldorf Departure is responsible for departures out of Düsseldorf EDDL and Mönchengladbach EDLN. According to the departure procedures, pilots have to contact Departure when passing 2000ft AMSL.
| [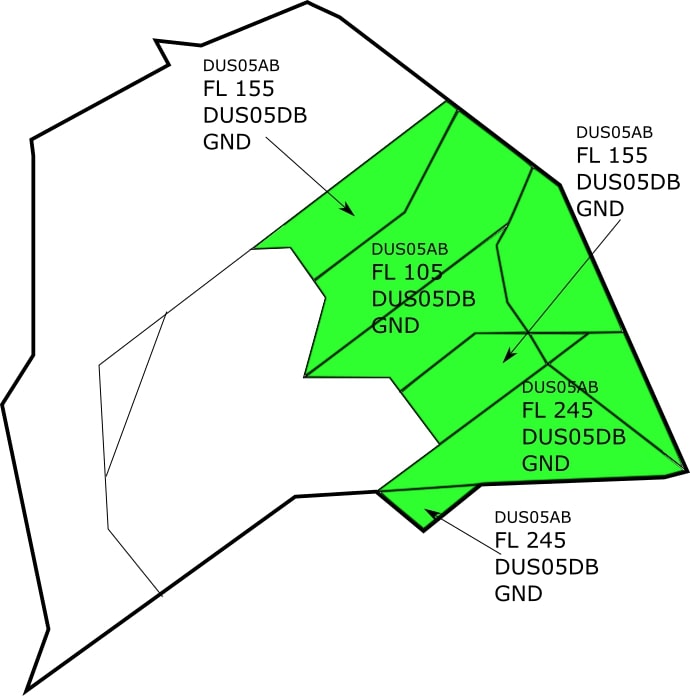](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddl-dus-d-05.jpg)
| [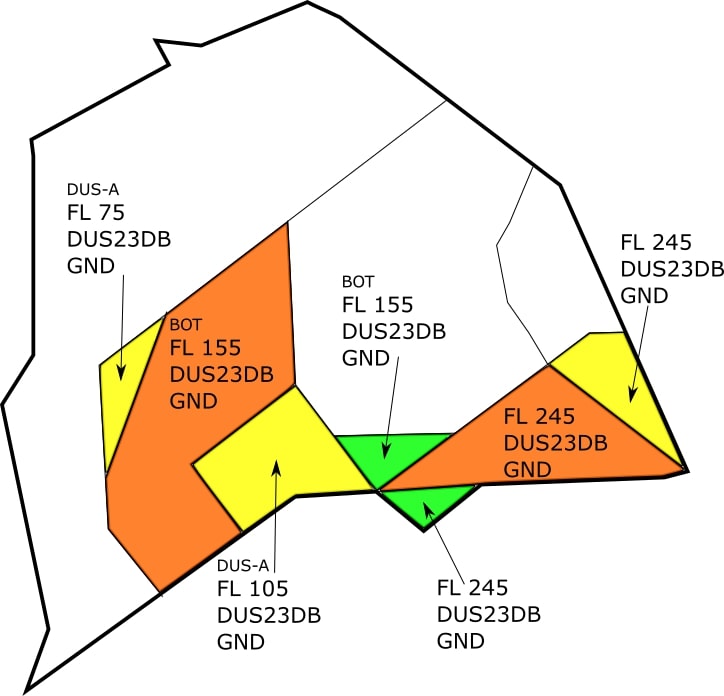](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddl-dus-d-23.jpg)
|
| *Departure Sector 05 Operations*
| *Departure Sector 23 Operations* |
### Frisbee Radar (TNGA)
The military approach sector Frisbee Radar is responsible for all departures from Geilenkirchen's (ETNG) runway 09 and approaches to Geilenkirchen's runway 27.
The transfer conditions for all approaches to runway 27 must be coordinated individually with Frisbee Radar. Departures from runway 09 flying an SID will be handed over at the sector boundary at 3000ft at the latest, unless otherwise coordinated; for departures on an OID, the handover conditions will be coordinated individually by Frisbee Radar. Frisbee Radar always has to obtain a release by BOT for all departures.
[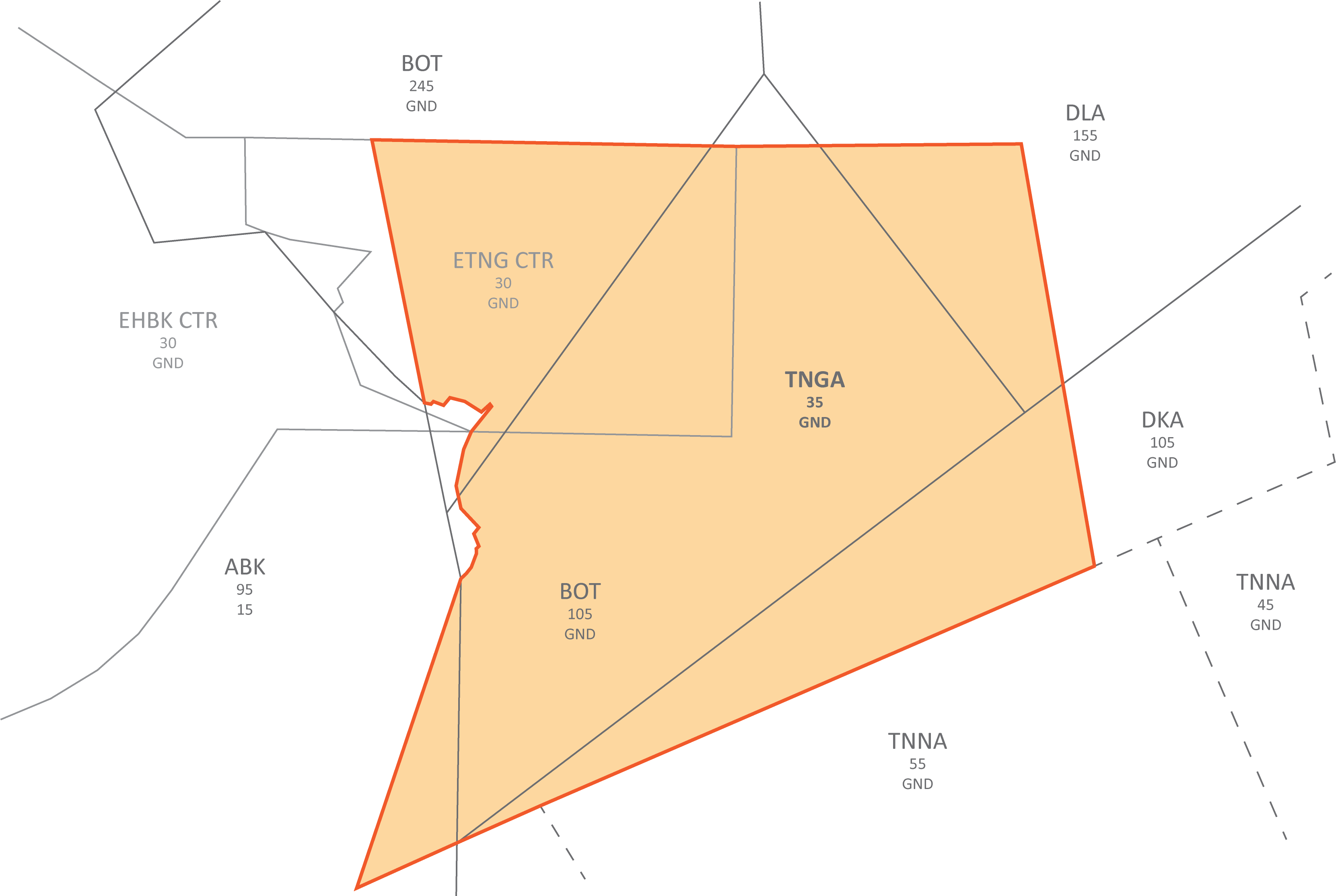](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-11/etng.png)Charts for military airfields are available within the german [Military-AIP.](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "milais.org")
### Potential Conflicts
#### 05-Operations
- After a short time, all outbounds on a SID cross the STARs or transitions of the inbounds (north via HALME, south via DOMUX). The outbound flights should be below (max. FL90) the inbound flights (min. FL100). After passing the crossing point, descent and climb can be continued.
- The STARs and transitions originating from PISAP, HALME and BIKMU ultimately all meet north of the airport at point GAPNU. Those from DOMUX and ELDAR (05 operations only) meet to the south at point DL502. Good advance planning and pre-sorting for the final approach is recommended here.
- The MODRU/NETEX SID not only crosses the approaching traffic coming via HALME, as mentioned above, but also the approaching traffic coming via PISAP. Whenever possible, attempts should be made to guide departing aircraft over the approaching aircraft.
- Both departures and arrivals can come via the LMA NDB. Here too, it is advisable to stagger the traffic vertically and initially keep departures below the arrivals until there is no longer a conflict for the further climb or descent clearance.
- EDLN departures from runway 13 cross the EDDL final approach shortly after departure. Mönchengladbach Tower therefore always requires a departure release from DLAT for 13 operations. In this case, DLAT and DLA should coordinate a sufficient gap between EDDL approaches and, if necessary, issue the departure release with the condition of an immediate take-off.
- EDLN approaches to runway 31 cross the EDDL final approach. DLAT and DLA should coordinate a sufficient gap between EDDL approaches. It also makes sense for DLAT to guide the EDLN approach to the final approach.
#### 23-Operations
- All aircraft departing via the southern SIDs cross the traffic approaching via BIKMU. As this crosses BIKMU at FL140, departures should initially be kept below FL140 and cleared for further climb after passing the conflict area.
- All STARs and transitions from points BIKMU, LMA, PISAP and HALME end at BOT NDB or meet at points XAMOD and DL426. Good advance planning and pre-sorting for the final approach is recommended here.
- Both departures and arrivals can come via the LMA NDB. Here too, it is advisable to stagger the traffic vertically and initially keep departures below the arrivals until there is no longer a conflict for the further climb or descent clearance.
- EDLN departures from runway 13 are not necessarily separated from EDDL departures, depending on the respective climb rates. Mönchengladbach Tower therefore always requires a departure release from DLD for 13 operations. DLD should therefore pay particular attention to separation in this situation. If necessary, DLD can also instruct Düsseldorf Tower to hold departures briefly to enable a safe EDLN departure.
### Holdings
In case holdings are required, traffic should be held by Approach and only the lowest inbound aircraft should be sent to the Feeder. These holdings should be used with caution as they are directly in the downwind sector.
- **DUS** (min. 3,000 ft AMSL, max. 24,000 ft AMSL)
- **DLA503** and **DLA524** - 05 operations (min. 4,000 ft AMSL, max. FL070)
- **DLA409** and **DLA429** - 23 operations (min. 4,000 ft AMSL, max. FL070)
#### Enroute-Holdings
As the above-mentioned holdings partly block the arrival sector and make working more difficult, published enroute holdings are preferably used for Düsseldorf.
- **ADEMI** (DOMUX Arrivals - min. 6000ft AMSL - Inbound 284° - Left)
- **HMM** (HALME Arrivals - min. 5000ft AMSL - Inbound 257° - Left)
- **DOMEG** (HALME Arrivals - min. 5000ft AMSL - Inbound 170° - Left)
- **ELDAR** (BIKMU Arrivals - min. 6000ft AMSL - Inbound 358° - Left)
- **NVO** (BIKMU Arrivals - min. 6000ft AMSL - Inbound 068° - Right)
### Crosscoupling of Approach Frequencies
Düsseldorf Approach (EDDL\_APP) cross-couples all other EDDL\_X\_APP frequencies via XC in Audio for VATSIM. This enables us to always use the correct departure frequency (published on the charts) when the approach/departure is staffed.
When EDLN is staffed, the controllers there must always be informed of the active operating direction in EDDL.
# EDDK - Köln/Bonn Airport
# EDDK - Overview
Köln/Bonn is a complex airport with crossing runways and very little space on the ground and in the TMA. On VATSIM, it usually has a medium amount of traffic but will regularly operate at or even above capacity during events.
**Köln/Bonn is an unrestricted airport.** DEL and GND are unrestricted and can be staffed by all controllers with an S1 rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. TWR position requires the EDDK\_TWR Tier 1 endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. All radar positions require the EDDK\_APP Tier 1 endorsement which can be acquired by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
Due to the high amount of complexity of the airport, it is highly recommended that **S1-rated controllers** have gained a great deal of experience at other unrestricted airports before staffing positions at Köln/Bonn.
**Training:** Controllers with the S1 rating can staff TWR during their training (active EDDK\_TWR solo endorsement required). Controllers with the S2 rating can staff APP positions during their training (active EDDK\_APP solo endorsement required).
With AIRAC 2404, the runway designators in Köln/Bonn were changed from 14/32 to 13/31. This can cause issues for pilots using MSFS if they are using AIRAC 2404 or later but have a scenery with the old designators as **they will not be able to select certain runway-specific procedures such as the SID** in their FMS. If a pilot reports this issue, **please refer them to [this addon](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/PXXa3gKYbb2Exkx "EDDK compatibility fix")** which will allow them to select runway-specific procedures even with an outdated scenery.
Whenever possible, **controllers should find workarounds that do not require pilots to restart their simulator**, e.g. using a conventional SID to NVO or WYP, potentially followed by radar vectors.
### Köln/Bonn ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ADK
| EDDK\_ATIS
| 132.130
| --
| --
|
| **Delivery**
| DKC
| EDDK\_DEL
| 121.855
| --
| unrestricted: [EDDK CBT Delivery](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=79 "Course EDDK (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Ground**
| DKG
| EDDK\_GND
| 121.730
| --
| unrestricted: [EDDK CBT Delivery & EDDK CBT Ground](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=79 "Course EDDK (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Tower**
| DKT
| EDDK\_TWR
| 124.980
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDK\_TWR](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)")
|
| Approach
(Pickup)
| DKA
| EDDK\_APP
| 135.350
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDK\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| Arrival
(Feeder)
| DKAT
| EDDK\_F\_APP
| 121.055
| secondary
| Tier 1: [EDDK\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
| **Nörvenich sector**
| NOR
| EDDK\_NOR\_APP
| 127.365
| primary | Tier 1: [EDDK\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
### Controlzone
[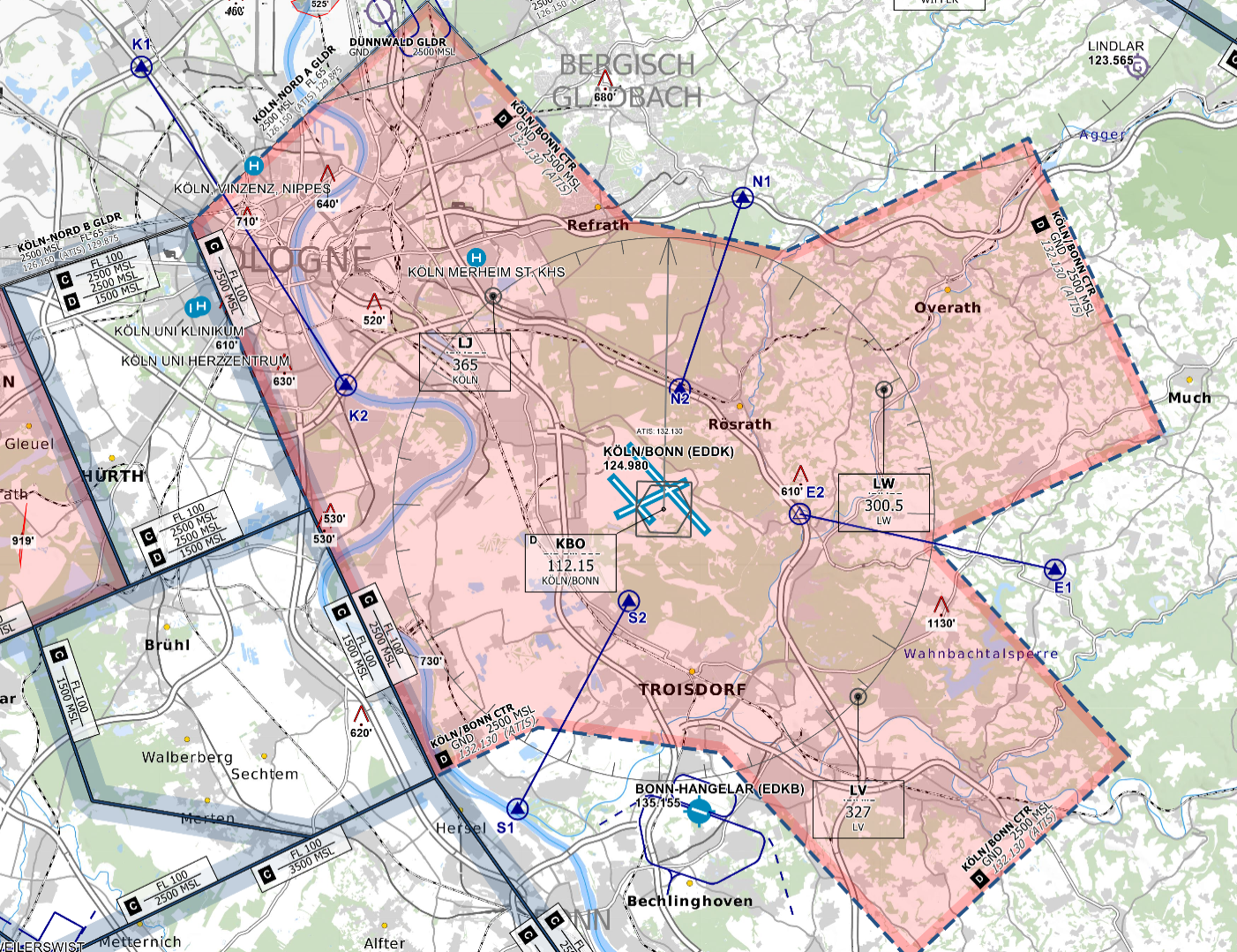](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/eddk-ctr.png)*Cologne-Bonn Controlzone (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
# EDDK - Delivery
VFR traffic, in contrast to real procedures, does not have to request startup at Delivery, but can report ready for taxi directly to the ground control.
**Startup:** When startup clearance cannot be given immediately or the pilot is not ready for startup within the next 5 minutes during high traffic situations, the pilot needs to stay on Delivery frequency until he receives startup clearance. If an expected startup time (TSAT) exists, the pilot should be informed about it. This procedure might be necessary during events with a lot of outbound traffic.
**Capacity:** Due to a limited capacity for outbound traffic on ground, there should not be more than **12** **active startup** clearances at the same time (including SUG, PBG, TXG).
**Euroscope:** Delivery shall ensure that the initial climb is set and the correct SID is coded into the flightplan (very important for Center!). When issuing startup the corresponding ground state "SUG" (Startup Given) and the clearance received flag need to be set.
### Departure Routes
The standard intrument departure procedures from Cologne-Bonn lead to the waypoints NVO, WYP, COL, PODIP and KUMIK. The initial climb for all departures is 5000 ft MSL. All SIDs except three non-RNAV departures have speed or altitude restrictions, the phrase "climb via SID" need to be used.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/wLxgrafik.png)*Departure Routes out of Cologne-Bonn*
**General Restrictions:**
- The standard departure routes via **COL** are only used for local training flights or for flights to Frankfurt/Main EDDF.
**Runway 06, 24 and 31L:**
- Designators **K** (RWY 06), **D** (RWY 24) and **M** (RWY 31L) are the available RNAV departures.
**Runway 13L:**
- **Designator F** is prefered for all RNAV departures.
- **Designator Q** requires RNAV and RF-Legs capability and should be used only if filed by the pilot or on request.
- **Designator X** is only used for 3-engines heavies (e.g. MD11).
- **NVO#P** is used for departures unable to comply with the climb restriction on the F or Q SID.
- **NVO#W** by ATC only and requires prior coordination with Radar as the SID will cross the inbound stream. It is only used, if certain glider-areas are active (which are not simulated on VATSIM). **Appropriate flights must be announced to the approach controller by the tower before take-off.**
**Runway 13R:**
- **Designator E** is prefered for all RNAV departures.
- **NVO#C** is used for departures unable to comply with the climb restriction on the E SID.
- **NVO#V** by ATC only and requires prior coordination with Radar as the SID will cross the inbound stream. It is only used, if certain glider-areas are active (which are not simulated on VATSIM). **Appropriate flights must be announced to the approach controller by the tower before take-off.**
**Runway 31R:**
- **Designator B** is prefered for RNAV departures **above 98t MTOW** (e.g. B757).
- **Designator R** is used for all RNAV capable outbounds with **MTOW below 98t** as well as for A300 and A330.
- **NVO#R** requires RNAV and RF-Legs capability and should be used only if filed by the pilot or on request.
**Non-RNAV Departures** are only available via **NVO** and **WYP** out of runway 13L (**Y**), 31R (**N**), 06 (**U**) and 24 (**T**).
**RWY13R / RWY31L** departures can be assigned on a daily basis to small general aviation aircraft, as well as aircraft up to the category of A320/B738 if required. After coordination with Tower, RWY 13R can be used for all light and medium aircraft during high traffic situations.
With westerly winds, outbounds should be asked if they prefere **runway 24** (when active) or runway 13L/31R for departure.
### Quicksheet - Standard Instrument Departures
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/eddk-sids-2404.png)
### Vectored Departures
If pilots are unable to fly a standard instrument departure (even an older version of the current SID) a vectored departure can be coordinated between Delivery and Arrival.
Primary **runway heading** and an initial climb of **4000ft** should be used. Other coordinations are always possible. At Euroscope the SID with RVxxxxx should be selected (xxxxx = first waypoint).
### Datalink Clearance (PDC/DCL)
At Cologne-Bonn Airport we offer Datalink Clearance to the pilots throughout the **[Hoppie System](https://www.hoppie.nl/acars/)** and the Topsky Plugin. The airport code EDDK should be used (already preselected).
An example of the DCL message the pilot will receive can be seen below. Due to plugin limitations, the current default setting is "startup approved"; the **Startup option in the DCL window shall be set to "No" for every DCL** as pilots need to request startup separately on frequency.
Other DCL messages can be enabled within the Topsky CPDLC settings file manually.
CLD 1051 240418 EDDK PDC 012 EWG6TG CLRD TO LEPA OFF 13L VIA KUMIK2Q SQUAWK 1000 ADT MDI NEXT FREQ 121.855 ATIS R REPORT READY ON 121.855
### vSID Rules
The following alias commands (.command**<space><enter>**) can be used to toogle vSID rules.
| **Alias** | **vSID Command** | **Description** |
| **.high** | .vsid rule eddk high | all L/M outbounds will get runway 13R/31L for departure.
|
# EDDK - Ground
### Airport layout
Cologne-Bonn airport has three crossing runways.
[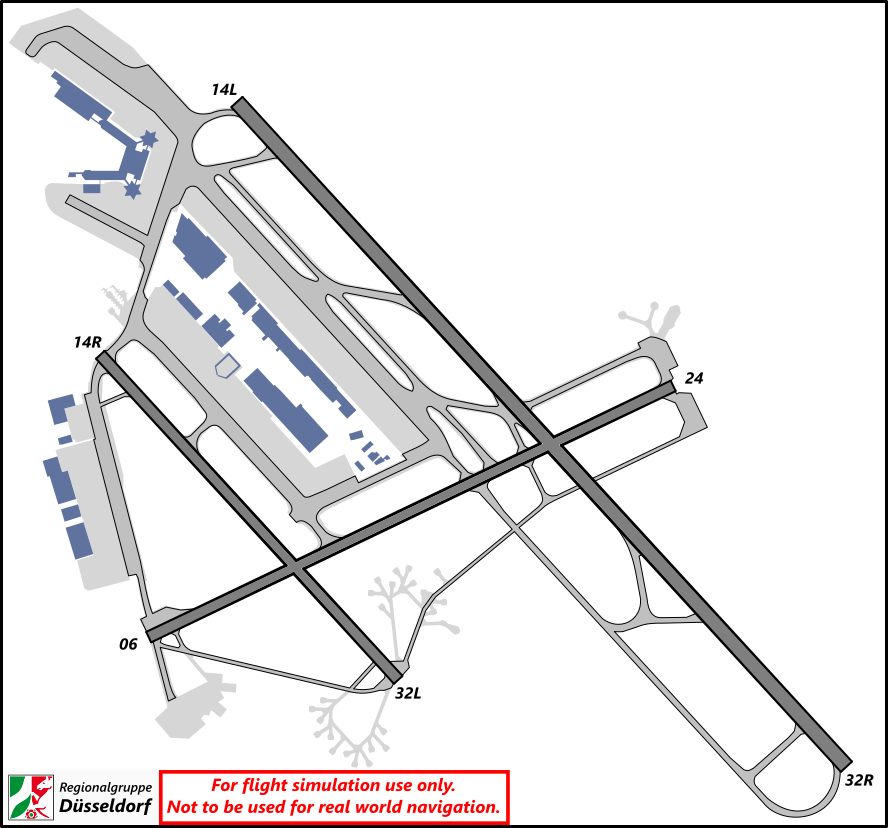](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddk-overview.png)*airport layout*
The airport has two passenger terminals. Terminal 1 with its two distinctive stars accommodates aprons A, B and C, and Terminal 2 with the apron area D.
[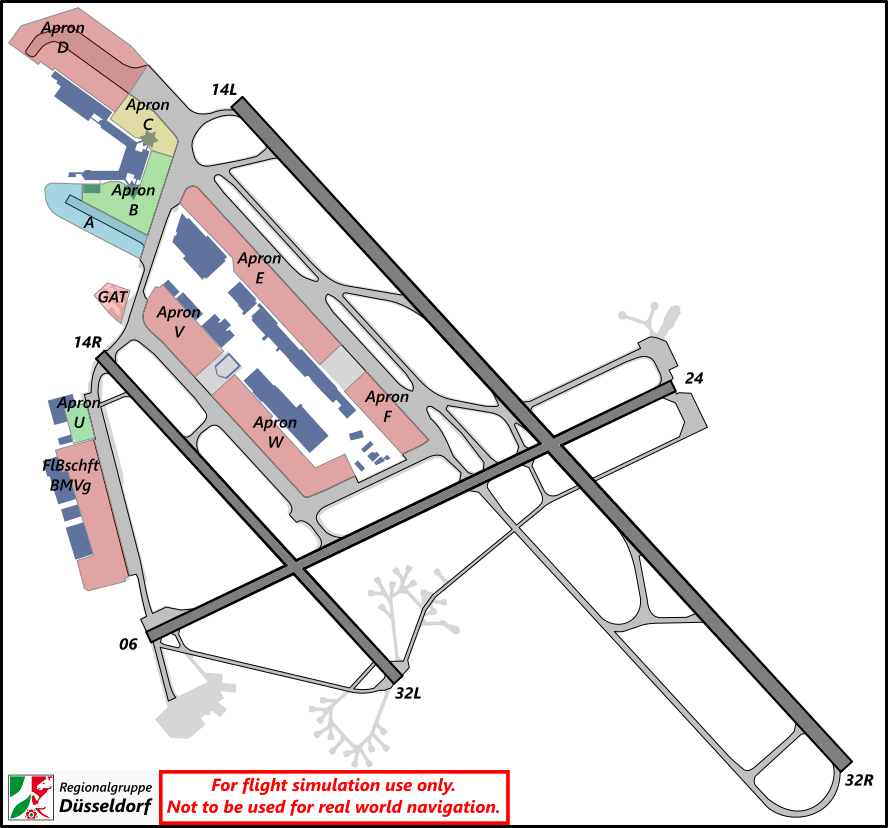](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddk-apr.png)*Apron areas*
The cargo area is used by several airlines and is located in the middle of the airport between the runways. It contains the apron areas E, F and W.
Apron V close to the cargo area is used for general aviation and business jets.
The military part of the airport is located west of runway 13R/31L at apron U. The military part of the apron is the home of the german Flugbereitschaft.
### Area of Responsiblility
The area of responsibility of Ground is located between the three runways and includes all aprons except the military apron U (see image below). If RWY 24/06 is closed (not in use), the runway crossing can be delegated to the Ground controller.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddk-aor.png)Area of Responsibility - *Cologne-Bonn Ground*
**Runway Crossing:** The crossing of all runways is within the responsibility of Tower, but can be delegated to Ground if the appropriate runway is not in use.
### Parking Positions
Parking positions are assigned by the Ground Radar Plugin based on airline and aircrafttyp according real world usage. It is recommended to use the assigned stands. The maximum aircraft size for all parking positions can be displayed in Euroscope (Tower) with shortcut `ALT + B`.
**Aprons A - D:** These aprons are the passenger terminal aprons. Aprons A-C are used for Terminal 1, while Apron D is located at Terminal 2.
**Aprons E, F, V, W:** All of these aprons are home to the big cargo-city at Cologne airport. Most of the heavy lifting cargo fleet (e.g. B747), are parked on aprons E and F, while aprons Vand W are home to the small feeder fleet (e.g. B737, ATR and B757/B767).
**Apron U:** Apron U is used by two maintenance companies for customers' aircraft. Parking positions U10 - U14 can be used up to code C (A321/B739) and parking positions U16 - U26 only for code A (wingspan < 15m).
**Apron V:** Apron V is used for business jets and general aviation. Depending on the position, aircraft up to the size of a B737-BBJ can be parked.
**GAT:** The GAT has no real permanent home. Previously it was located as shown on the map below, northeast of the RWY14R threshold. Nowaday, general aviation is parking mostly on the aprons V and U (partially civil, partially military). The original GAT as shown on the map, is home to the helipad of the Christoph 3 rescue helicopter.
**Military:** Cologne/Bonn is a double purpose airport. While it mostly handles civilian aviation (either pax or cargo), it's also home to the Köln-Wahn Airbase, of the Luftwaffe. On the western part of the airport (west of 13R/31L), the so called "white fleet" (A350, 340, GLEX) is stationed. To complete the fleet stationed at EDDK, the MRTTs (Multi-Role-Tanker-Transport) A321 and A330 are also located there.
**Antonov AN225 special parking procedure:** Parking parallel to taxiway A on Stands E09 to E15, main gear on E12, facing north-west.
### Taxiway Usage
The primary used taxiway is A, running parallel to runway 13L/31R.
[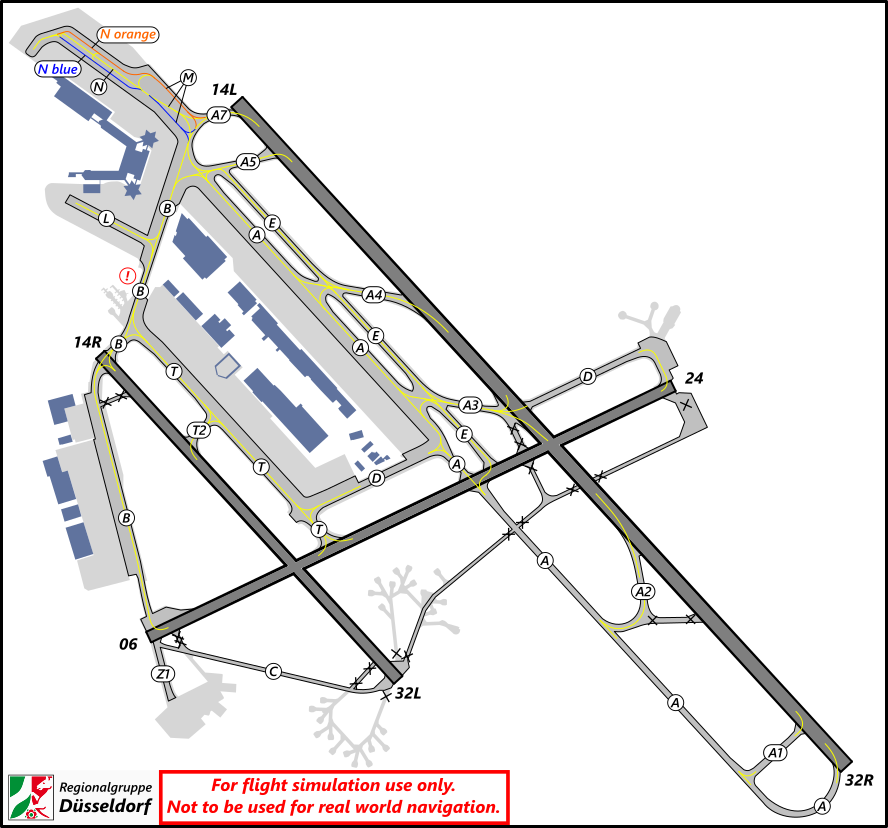](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddk-twy.png)Taxiways at *Cologne-Bonn*
**31-Operations:** During 31-Operations, traffic from the terminals taxiing southbound will be using TWY-A, while inbound traffic vacating the runway continues on TWY-E, to A5. If there is traffic requesting pushback on the E and F stands, outbound traffic can be rerouted via TWY-E. However, this may be blocking inbound aircraft vacating from RWY 31R.
**13-Operations:** During 13-operations, inbound traffic vacating RWY 13L, heading for the terminals, will be taxiing northbound on TWY-A primarily. However, if there is traffic on aprons E and F asking for pushback, the parallel TWY-E can be used as alternative, so that the traffic on those aprons is able to push.
**Runway 24/06 for taxi:** It is possible for in- and outbound traffic to use runway 06/24 for taxi.
> GAF1GH, taxi to holding point runway 31R via Bravo, enter runway 06 and Alpha, cross runway 31L.
> DAFHK, taxi right via runway 24 and continue T.
After landing or before takeoff, the word "backtrack" has to be used.
> EWG1PC, backtrack runway 24, vacate T.
> RYR7AF, backtrack and lineup runway 24.
### Taxiway Restrictions
Taxiway **B** and **T** can only be used up to **Code E** aircraft. Taxiway **C** is limited to **Code C** aircraft. Taxiway **D** between A and T can only be used by max. **Code E** aircraft. The part of **D** east of runway 13L/31R can also be used by a B748.
**Parallel taxi on A and E with Code F aircraft:** If an Airbus **A380** is on taxiway A, taxiway E is limited to **Code D** aircraft. If a **B748** or an **AN124** is on taxiway A, taxiway E is limited to **Code E** (in case of a B748 limited to Code E + B748).
**Colored lines:** In front of Terminal 2 aircraft up to code C can use the orange and blue line simultaneously up to position D51.
On taxiway **B** between L and T (marked with (!)) only aircraft with a **wingspan of max. 52 m** (Code D) and max. weight of 200t are allowed to taxi on it's own. Aircraft up to 234t may be towed over or taxi on their own power over the bridge **if guided by a marshaller.**
### Potential conflicts at the ground
Due to it's layout and placement of aprons, there are several critical areas at Cologne/Bonn Airport, which can either lead to congestion or taxi conflicts.
**1. The holdingpoint dilemma:**
The number one area marked on the map, is the area around the holdingpoint A5/A7, the northern ends of TWYs A and E, as well es TWYs B and M, around the C-Star (Terminal 1). Especially during 13-Ops, this area heavily suffers from congestion. Departing traffic will be queuing mostly at A7, some at A5, while inbound traffic will be taxiing northbound, via TWY A, B and M, to get to Apron D. Possibilities to solve at least some of the congestion issues, will be described on the following pages.
**2. A3-Area**:
Number two on the map, is the A3-Area. This areas is critical in different scenarios.
- During 31-Operations, A3 is the first suitable highspeed-turnoff for landing traffic. Due to the speed of landing and vacating aircraft, they often fail to stop short off E and continue through to A.
- Another critical situation occurs, in the case of 24-departures. 24-departures need to cross RWY 31R at A3. Whenever traffic is instructed to taxi in the direction of the A3 holdingpoint, Ground needs to coordinate with Tower and inform him about the traffic, as TWR needs to inform landing pilots, that A3 is unavailable to vacate the RWY.
**3. Taxiway B-Bridge**
The third critical area is placed on TWY-B. Between Taxilane-L and the GAT (marked with (!)) taxiway B leads over a bridge where only aircraft with a wingspan of max. 52 m (Codeletter D) and max. actual weight of 200 t are allowed to taxi on it's own. A332/A333 and A343 with an actual weight of up to 234 t may be towed or can taxi with a marshaller on ther own power over the bridge.
**4. Taxiway D**
On taxiway D only Code E aircraft and below are allowed, except the part east of runway 13L/31R where also a B748 is allowed.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddk-risk.png)*Potential conflicts on ground*
### De-Icing
There are no de-icing pads available at EDDK. Every outbound has to be deiced **on position prior pushback!** In case deicing is required when the outbound is already offblock, it has to return to a position.
# EDDK - Tower
### Runways
The airport has three runways, two of which run parallel and one of which crosses two runways.
#### Runway 13L / 31R
Runway 13L/31R is the longest runway at 3815 x 60m and is primary used for all inbound and outbound traffic. Runway 31R and 13L are both equiped with ILS CAT III.
#### Runway 13R / 31L
At a distance of about 1km southwest of runway 13L/31R is the much shorter parallel runway 13R/31L, which is 1863 x 45m long.
Due to its length and technical equipment, this runway is preferably used for VFR traffic. Because of its proximity to the military section, it is also frequently used by military aircraft. Runway 13R/31L is only approved for aircraft up to code C (e.g. B739, A321). During high traffic situations, this runway can be used for all light and medium traffic that is able (TORA 1863 m).
For **non-precision approaches** to runway 13R, a flight and ground visibility of at least 2.1 km must be provided due to the shortened approach lighting.
#### Runway 06 / 24
Across runways 13/31 is the intersecting runway 06/24, measuring 2459 x 45m. Only landing direction 24 is equipped with an ILS (CAT I). For RWY 06 only non-precision approaches are available.
Runway 06/24 is only approved for aircraft up to code letter E, including the B748.
For **non-precision approaches** to runway 24, a flight and ground visibility of at least 1.5 km must be provided due to the obstacle situation.
RWY24 can be used to taxi aircraft as well. Either because of wingspan limitations on TWY D or to the military apron, as well as for aircraft landing RWY13L to vacate the runway and to avoid the sharp turn into A3.
> DLH123, wind 140 degrees 4 knots, runway 13L cleared to land, runway 24 available for taxi.
### Control Zone
The D-CTR of Cologne-Bonn Airport extends from the ground to 2500ft MSL.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/eddk-ctr.png)
*Controlzone Cologne-Bonn (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
**Airfields:** South of the control zone lies the airfield Bonn-Hangelar EDKB, which, including its traffic circuit, is located outside the control zone.
To the north, also outside the control zone, is Leverkusen EDKL airfield. Its traffic circuit, however, extends into the control zone at an altitude of 1100ft on its southern side.
Please note the following: "From SR-30 until SS+30, the control zone in the depicted Dünnwald sector is not active. The general airspace classifications G (up to 1000ft AGL) and E (above 1000ft AGL) apply." (Source: [*AIP VFR Germany VOC EDKL*](https://aip.dfs.de/BasicVFR/pages/P0034A.html))
**Hospitals:** Several hospitals with helipads are located in the urban area of Cologne.
In the extended centerline of runway 13L, approx. 1.5 km north of the NDB LJ, is the hospital Merheim. Approaches to runway 13L fly over the hospital at approx. 1500ft. Helicopters may approach the landing area below the approaching traffic. Appropriate traffic information must then be provided to avoid missed approaches.
On the north-western edge of the control zone in Cologne-Nippes, on the CTR boundary, is the rather seldom approached St. Vinzenz Hospital.
On the west side in the Lindenthal district, just outside the control zone, is the University Hospital of Cologne.
To the west of the control zone is the Nörvenich ETNN airbase. Despite their proximity, the control zones of the two airports do not border directly on each other, but are separated by a narrow strip of type C airspace.
### VFR-Traffic
There are 7 mandatory reporting points and 1 optional reporting point available for VFR traffic at Cologne.
| **Reporting Point**
| **Location**
|
| **NOVEMBER 1** | BAB 4, exit Bergisch Gladbach-Bensberg |
| **NOVEMBER 2** | BAB 3, motorway service station Königsforst-Ost |
| **ECHO 1** | Church in the middle of Neunkirchen |
| **ECHO 2**
*(Optional)*
| BAB 3, service area Sülztal |
| **SIERRA 1** | Marina at the mouth of the Sieg River into the Rhine |
| **SIERRA 2** | Sports facilities north of the village of Troisdorf-Spich |
| **KILO 1** | BAB 1 / BAB 57, motorway interchange Köln-Nord |
| **KILO 2** | BAB 4, rhine bridge Rodenkirchen |
**VFR Routings:** The most popular VFR route through the control zone follows the Rhine along the Cologne Cathedral and the Old Town and connects the mandatory reporting points S1, K2 and K1.
Just as popular for flights from / to the Bergisches Land are take-offs or landings in Bonn-Hangelar combined with a flight through the control zone via the S and N routes.
**VFR Squawk:** All VFR traffic inside the controlzone of Cologne will get the transpondercode **7003**.
**Helicopter traffic:** The airport has frequent helicopter traffic. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that a helicopter squadron of the Federal Police is located at Bonn-Hangelar Airport and training traffic also takes place there. On the other hand, two rescue helicopters are stationed at the airport. "Christoph 3" (CHX3) has its landing pad at the GAT, while the intensive care transport helicopter "Christoph Rheinland" (CHX75) of the ADAC has its base at the north-western edge of the V- Apron towards Taxiway B. Only "Christoph 3" though, is allowed to land and depart directly from it's helipad. Every other helicopter has to either land on the runway or the runway threshold (e.g. 13R) and has to air-taxi to it's final position afterwards.
### Direction of Operation
Up to a tailwind component of 5kt, operations will be handled via runways 31R and 31L. Runway 24 is also used if necessary up to a tailwind component of 5kt.
Operating direction 06 is used extremely rarely because the wind through the Cologne Bay preferably blows from a northerly to northwesterly direction.
In order to accelerate the taxiing of traffic and after prior coordination with ground control, the tower may give taxiing traffic (taxiways A3-A4) an initial taxi instruction into taxiway A or taxiway E (depending on the take-off direction) and then hand it over to ground control. Most commonly, tower will give an initial right turn on E, to hold short of A5.
### Parallel Operations
Due to the distance of only approx. 1150 m between the runway centrelines of 13L/31R and 13R/31L, independent parallel runway operations between these runways for IFR and/or SVFR traffic are not permitted.
Radar and runway seperation need to be applied, wake turbulence separation is not required.
### Seperation and Spacing:
Depending on the amount of departures, Köln Tower may request arrivals to runway 31/13 with 5 or 6 miles. Coordination is required if more spacing is needed.
Targetspacing for inbounds only need to be applied by Arrival when **requested by Tower!** Otherwise radar or WTC seperation is used by default.
Note: In order to maintain seperation Köln Tower may reduce aircraft after transfer of communication.
While not neccesary, it is recommended to only use speed control after prior coordination with the Arrival Controller.
#### Reduced runway separation
RRS minima may be applied by Köln/Bonn Tower, according to the following table:
| **Runway** | **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 1**
| **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 2**
| **preceding CAT 3**
**succeeding CAT 1/CAT 2/CAT 3**
|
| **13L/31R** | 600m | 1500m | 2400m |
| **13R/31L** | 600m | N/A | N/A |
| **06/24** | 600m | 1500m | N/A |
### RECAT-EU procedures
According to new wake turbulence minimum separation values established by Eurocontrol, the familiar categories established by the ICAO (Light, Medium, Heavy, Super) have been divided into new sub-categories, thus offering the possibility of separating aircraft in certain categories even more closely.
The DFS has decided to apply the procedure at Cologne Bonn, but only in the “Lower Heavy/Lower Heavy” category and restricted to aircraft types A300, B757 and B767.
This means that two consecutive aircraft **(WTC H)** can be seperated by 3 miles and do not have to be seperated by 4 miles, as required by ICAO guidelines, if the preceeding aircraft is one of the of the above-mentioned aircraft type. For further information: [RECAT-EU](https://www.eurocontrol.int/publication/european-wake-turbulence-categorisation-and-separation-minima-approach-and-departure)
### Missed Approaches
For all published approaches, missed approaches will be executed as published unless otherwise coordinated.
EDDK Tower has to ensure initial separation between departures and between departures and missed approaches. He therefore may take action to ensure or reestablish seperation. Radar shall be informed immediately of the action taken. Transfer of Communication then takes place, once seperation is established. Missed Approaches should be tranfered to Feeder (DKAT), if not otherwhise coordinated. The next departure requires a departure release.
### Crossing Runway Operations
Combined operation of runways 13L/31R and 24 has the highest capacity. When runway 13R/31L is used as well, runway 24 is blocked for significantly longer.
It is important during crossing runway operations that the preceeding traffic (landing or departing) has crossed the runway cross before the succeeding traffic (landing) for the other runway has reached the 1 NM final. Otherwise the succeeding traffic has to go around.
**Example:** Departing traffic runway 31R has passed the runway cross before the inbound reaches 1 NM final for runway 24.
### Nörvenich sector A
If the military approach sector for Nörvenich (ETNN) has activated sector A, **NVO SID´s out of runways 24 and 31, as well as COL departures out of runway 24 may no longer depart. Coordination with DKA required.**
Usually, this sector will only be active for short periods of time to allow TNNA to vector arriving traffic to final approach during 24 operations at ETNN; however, when there is local IFR traffic at ETNN, the sector may be activated for longer periods.
After coordination with DKA NVO outbounds should be recleared to runway 13 or, on a different SID (e.g. COL/WYP) to expect vectors to NVO after departure.
**DKA** (or TNNA, if DKA is offline) **will inform Tower when sector A is activated and deactivated**.
### Transfer of Communication "Auto Handoff":
Köln/Bonn utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the arrival controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP **when passing 2.000 ft MSL** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# EDDK - Arrival
The area around Cologne is divided into four sub-sectors. In addition to the Approach and Arrival stations, sector NOR handles the lower airspace west and above Cologne up to Maastricht/Rhein Radar.
NOR is the primary station and covers all other Sectors top-down. If only DKA is staffed, this sector will not cover NOR.
DKA frequency shall always be cross-coupled by the responsible controller.
Please also **check the [ETNN TWR/APP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/chapter/etnn-norvenich-airbase) and [EDDK Tower, Ground, and Delivery](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/chapter/eddk-kolnbonn-airport) SOPs** to familiarize yourself with relevant procedures for Arrival operations and to enable the necessary coordination with the ground stations.
## Sectorization and Airspace
### Cologne Approach (DKA)
Approach is responsible for the area around Cologne/Bonn Airport up to the Belgian border. The sector handles all departures from Cologne and presequences all inbound flights for the feeder. If arrivals or departures from Nörvenich (ETNN) take place without Nörvenich Radar (TNNA) being staffed, this traffic is also handled by Approach.
| [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/ozxdka-sector-at-2x-cropped.png) |
| *Area of Responsibility Arrival*
|
### Langen Radar Sector Nörvenich (NOR)
Langen Sector Nörvenich NOR is located west of the airport above sector DKA and is primarily responsible for the pre-sequencing of inbound flights to Düsseldorf from IBESA via ELDAR and BIKMU. In addition, the sector is responsible for all departures from Cologne to Belgium via NVO.
Frankfurt Outbounds via DITAM - OBOKA also pass through the sector, as do inbound flights to Brussels ACC via UMUPU - GEBSO and NEREL - AGENI.
| [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/jZhnor-at-2x-cropped.png) |
| *Area of Responsibility Sector Nörvenich*
|
##### UMUPU & DEVRU Area and Upper Sector Boarders:
The red area shown below reaches up to FL265 and is delegated airspace of EDUU sector Nattenheim. It therefore boarders to MUAC Sectors Ruhr & Olno. The orange part reaches up to FL255 and is delegated by EDYY Olno.
Minimum Radar Seperation above FL245 is increased to 5 NM, which also applies to flights within this area. It is mainly used for Frankfurt outbounds via DITAM-OBOKA and flights to Brussels Group via UMUPU - GEBSO.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/dka-umupu-area-at-2x-cropped.png)
###
Feeder/Arrival (DKAT)
The Feeder (Arrival) works within the sector of Approach (DKA). Especially during 13 operations the small area between FAF and the Düsseldorf Arrival sector border might require closer coordination between DKA and DKAT. The Feeder has no delegated AoR but instead operates within the same Airspace as DKA. There are no specific transfer conditions. Usually, traffic is handed off descending to FL70. DKA has the discretion to hand off traffic at any level, as long as seperation is ensured.
### Nörvenich Radar (military position)
For arrivals to, departures from, and local traffic at the military airbase Nörvenich (ETNN), the station Nörvenich Radar (TNNA) can be staffed. This position is delegated part of the DKA airspace when it is online. Due to the close proximity to EDDK and EDDL, **coordination between all positions is essential**.
The most eastern part of the Nörvenich approach sector, **sector A, is generally not delegated to TNNA** and can be used by DKA. However, **while there is inbound traffic for ETNN's runway 24, TNNA can activate this part of the sector** to be able to guide traffic onto the final approach course. Nörvenich Radar shall inform DKA immediately when activating and deactivating sector A and shall make sure to open the sector only for the absolute minimum amount of time required.
While sector A is active, **approaches to runway 06 in EDDK need to be coordinated** (airspace crossing with ETNN). Both final approaches courses are procedual seperated by more than 3 NM.
**Approaches to RWY 24** in EDDK are generally possible. In case of missed approach, immediate coordination between DKA and TNNA is required. It may therefore be beneficial to point out traffic approaching runway 24 in advance to TNNA.
Additionally, **NVO departures out of runways 24 and 31, as well as COL departures out of runway 24** are suspended/need to be coordinated in form of airspace crossing with TNNA.
**DKA shall immediately inform Tower when sector A is activated and deactivated**.
Nörvenich Radar may use the entire lateral range of the sector. Langen Radar (DKA) is responsible for maintaining full radar separation to the TNNA sector borders.
> **TNNA**: DKA, Nörvenich Radar.
> **DKA**: Go ahead.
> **TNNA**: Sector A now active.
> **DKA**: Roger.
>
> **DKA**: Tower, DKA.
> **DKT**: Go ahead.
> **DKA**: Nörvenich sector A active, hold all 24 & 31 NVO departures and 24 COL departures.
> **DKT**: Roger, holding 24 and 31 NVO departures and 24 COL departures.
[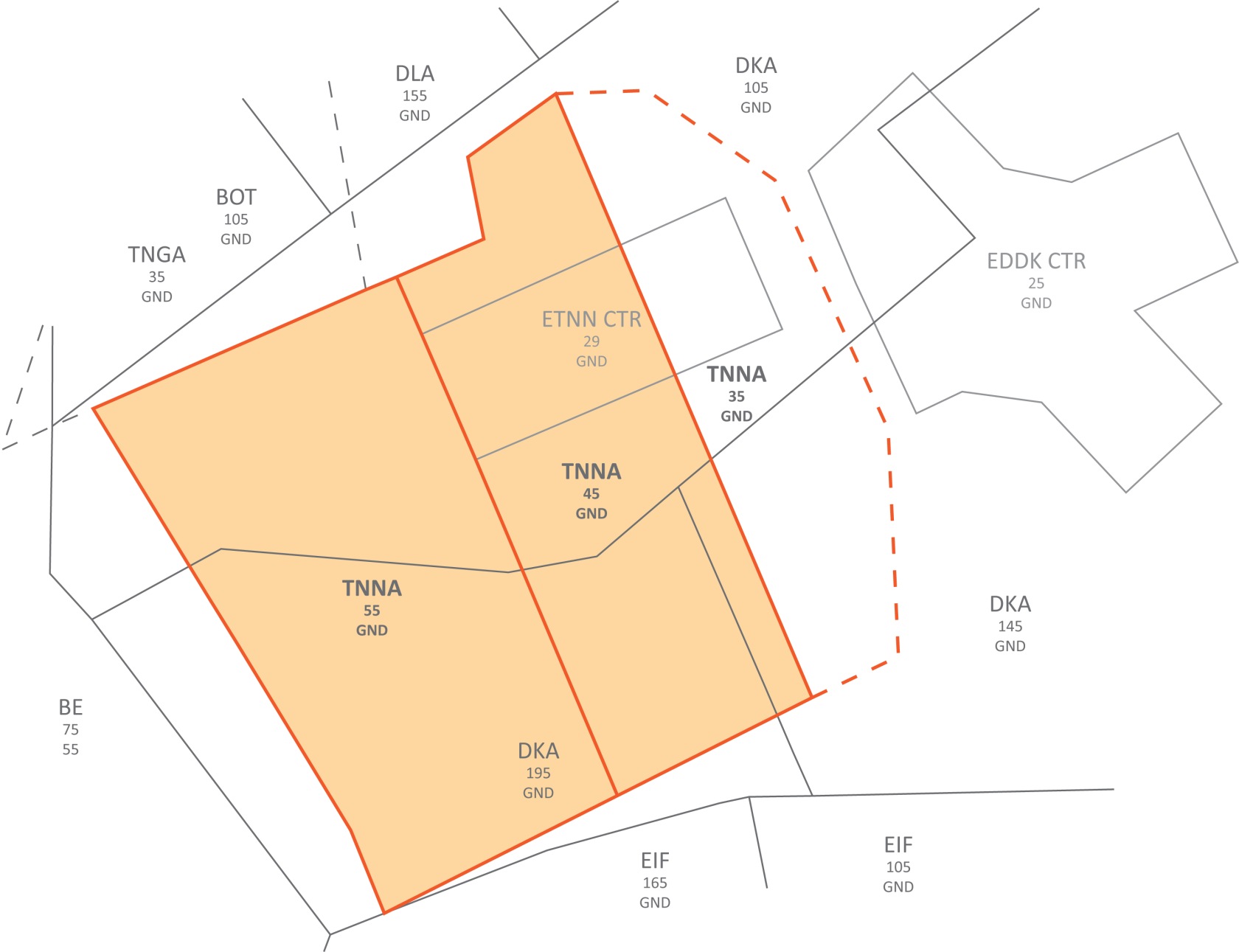](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etnn.png)
*delegated sector to Nörvenich Radar (TNNA)*
Additionally, a small section of the **military position Frisbee Radar (TNGA) protrudes into DKA** airspace in the Northwest if it is active.
### Airspace Structure
One of the most complex airspace structures in Germany is located around Cologne and Düsseldorf airports, because several airports are located next to each other in a very small area.
Around Cologne there is pirmarily airspace C. Due to the close proximity to the Düsseldorf TMA, the airspace C in Cologne is directly connected to the airspace C in Düsseldorf.
A more detailed representation of Airspace C borders can be found at [openflightmaps](https://www.openflightmaps.org/ed-germany/).
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/airspace-structure-eddk.jpeg)*Airspace EDDK - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
### Minimum Vectoring Altitude (MVA)
| [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/eddk-app-winter-mva.png)
| [](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2025-01/eddk-app-summer-mva.png)
|
| *EDDK Winter MVA*
| *EDDK Summer MVA*
|
###
For Approaches to runways 31 and 24, the MVA is exactly at the intercept altitude for the published instrument Approaches.
In case of an overshoot, the controller must pay special attention to the MVA.
### Range/Noise-Abatement Rings
When selecting the active runways in the EDDK\_APP sector file, green rings will appear around the intermediate Fixes DK455 (13), DK654 (31), DK554 (24) and DK755 (06), respectively for the selected runways.
They show a 13 NM radius to the specified waypoint. In real-life, they are primarily used for noise-abatement reasons, as between 22:00 lcl time and 8:00 lcl, traffic may only descend below FL70 within these circles. For aircraft types B747 and MD11, this restriction applies throughout the day.
For Vatsim, they are especially useful to create a proper inbound sequence and calculate remaining track miles to intercept/touchdown. Any traffic on the border of a circle will have exactly 26 NM to touchdown, if taken straight-in. Therefore, if two aircraft from opposite direction reach the circle at the same time, one will have to be delayed. This significally simplifies estimating sufficient delay for inbounds from opposite directions, especially for presesequencing inbounds to the crossing runway system and within the small area between Final Approach Point for runway 13/31 and the DUS/TAU sector border.
*[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-12/eddk-grune-kreise.png) Noise-Abatement Rings for all runways*
## Arrival and Approach Procedures
**Arrival Routes:** The standard arrival routes for Cologne-Bonn start at five waypoints: KOPAG, ERNEP, GULKO in the east and DEPOK in the west and lead to the Initial Approach Fixes WYP and COL.
*[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddk-kopag.png)STARs into Cologne/Bonn*
### Clearance Limits
For all arriving aircraft via KOPAG and GULKO, those Points are also the clearance limit. Special attention must be paid to give a further lateral clearance in time, before the aircraft approaches the waypoint.
For aircrafts arriving via DEPOK or ERNEP the STAR point itself does not have a clearance limit and can be therefore followed until reaching the Initial Approach Fixes WYP (13) and COL (31). Those IAF are already located close to the final approach sector (on downwind), so normally radar vectoring is used for all inbounds.
**Transitions:** RNAV transitions to the final approach are published for all runways. Their use depends on the current traffic situation and should be flexible accordingly. These Transitions only exists out of GULKO, KOPAG & NVO and are designed for Continous Descend Operations (CDA).
The transitions to runway 13 enter the 1.5 NM boundry to DLA. Therefore, these transitions can only be user after prior coordination with the respective controller covering DLA.
Since they are more or less leading straight in, they are not really designed to sequence a bigger amount of inbounds. **Instead radar vectoring should be used.**
**S-Transitions:** An exception are the transitions with Designator S to Runway 13L. These extend deep into the approach airspace of Dusseldorf . On VATSIM, these transitions should only be used in close coordination with the controller responsible for Düsseldorf in order to avoid conflicts with approaches and departures from Düsseldorf. Airspace crossing needs to be coordinated individually.
**N-Transitions:** The transitions with Designator N to runway 31R reaches with the base part into the sector Taunus TAU, which on Vatsim is usually served by Langen sectors Kitzingen (KTG), Gießen (GIN) or Rüdesheim (RUD). Its use has to be coordinated with the controller responsible for TAU/SIG.
**Approaches:** Besides the Surveillance Radar Approach (SRA), which is available for all runways, the following Instrument approach are available and can be used upon pilots request:
- RWY 13R/31L/06: only RNP
- RWY 13L/31R: ILS (CAT III) and RNP
- RWY 24: ILS (CAT I) and RNP
The SRA Approach should only be used during low traffic periods and when feeder (DKAT) is staffed. Only one aircraft should be on Feeder frequency, when commencing SRA approaches. For further information: [Surveillance Radar Approach](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/military-procedures-4ok/page/military-radar#bkmrk-surveillance-radar-a)
### Potential Conflicts
Due to its size and the close proximity of approach and departure routes, the Cologne Arrival sector in the east of Cologne/Bonn has the greatest potential for conflict. Especially between the points KOPAG and COL near PODIP, several routes cross, so that special attention must be paid to (vertical) separation there.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/eddk-sidstarconflict.png)
### Arriving Traffic
#### Seperation and Spacing
Depending on the amount of departures, Köln Tower may request arrivals to runway 31/13 with 5 or 6 miles. Coordination is required if these can temporarily not be met or if Tower requires more spacing.
Targetspacing for inbounds only need to be applied by Arrival when **requested by Tower!** Otherwise radar or WTC seperation is used by default.
Note: In order to maintain seperation Köln Tower may reduce aircraft after transfer of communication without any prior notification.
#### RECAT-EU Procedures
According to new wake turbulence minimum separation values established by Eurocontrol, the familiar categories established by the ICAO (Light, Medium, Heavy, Super) have been divided into new sub-categories, thus offering the possibility of separating aircraft in certain categories even more closely.
The DFS has decided to apply the procedure at Cologne Bonn, but only in the “Lower Heavy/Lower Heavy” category and restricted to aircraft types A300, B757 and B767.
This means that two consecutive aircraft **(WTC H)** can be seperated by 3 miles and do not have to be seperated by 4 miles, as required by ICAO guidelines, if the preceeding aircraft is one of the of the above-mentioned aircraft type. For further information: [RECAT-EU](https://www.eurocontrol.int/publication/european-wake-turbulence-categorisation-and-separation-minima-approach-and-departure)
This Procedure is limited to the lateral and vertical sector limits of DKA and only applicable at or below FL100.
#### Missed Approaches
For all published approaches, missed approaches will be executed as published, unless otherwise coordinated. Tower has to ensure initial separation between departures and between departures and missed approaches. He therefore may take action to ensure or reestablish seperation. Radar shall be informed immediately of the action taken. Transfer of Communication then takes place, once seperation is established. Missed Approaches should be tranfered to Feeder (DKAT), if not otherwhise coordinated. The next departure requires a departure release.
#### High Rate of Inbound Traffic
**DLA Agreement:** During high traffic situations at EDDK with 13 operations and low traffic at EDDL, DKA can request a general airspace crossing to vector inbounds 13L/R through the DLA sector. Traffic need to stay at 5.000ft or below within AoR of DLA and at least 3 NM south of the extended centerline RWY 05R. Further individual coordination for level and extension possible when required.
The use of this crossing may be withdrawn, depending on the amount of departing southbound traffic in EDDL. Prior notification should be given around 10-15 minutes before withdrawal by DLA.
**TAU/EIF Agreement:** To use the sectors of EIF or TAU individual coordination required.
### Crossing Runway Operations
It is important during crossing runway operations that the preceeding traffic (landing or departing) has crossed the runway cross before the succeeding traffic (landing) for the other runway has reached the 1 NM final. Otherwise the succeeding traffic has to go around.
Arrival/Feeder has to ensure, that traffic cleared on the approach of crossing runways is separated in a way, that the preceeding traffic has passed the runway crossing point, before the succeeding traffic reached it's 1 NM final. Therefore it is necessary, that both aircraft are cleared on the approach, with at least 2 NM separation between each other. Especially factors like headwind and aircraft performance has to be taken into account.
**Runway 13L/31R + Runway 24 Operations:** Due to the shorter distance from the **FAF** (Final Approach Fix) to the crossing point between RWY13L/31R and RWY 06/24, arrivals on **RWY 24** shall be cleared as the preceeding aircraft whenever possible.
# EDDK - High Traffic Procedures
### Runway allocation
**Outbound 13 operation:** All outbounds with WTC Light and Medium are assigned runway 13R for departure. The 1863 m runway should be sufficient for most outbounds. If the pilot reports unable, he will be assigned runway 13L like all Heavies.
ATIS Code "**&eddk13r**" shall be used:
ALL DEPARTING LIGHT AND MEDIUM TRAFFIC EXPECT RWY 13R FOR DEPARTURE. REPORT UNABLE ON INITIAL CONTACT.
**Inbounds 13 operation:** Primary use of runway 13L for all inbounds, runway 24 should not be used.
**Outbound 31 operation:** All outbounds are assigned runway 31R.
**Inbounds 31 operation:** All inbounds with WTC Light and Medium are assigned runway 24. Inbounds Code D (B767/A306) should be asked if possible whether they can accept runway 24. All others will be given runway 31R.
**Start-up:** A maximum of two or three Heavies should be started up at the same time for 13L.
### Seperation and Spacing
Target spacing on runway 24 is 4 NM or WTC staggering if necessary (note staggering to inbounds runway 31R!).
Target spacing for runway 13L/31R of 6 NM by touchdown must be explicitly requested by the tower.
### Holdings
Primarily, only the holdings at **GULKO** and **KOPAG** in the centre's area of responsibility should be used. The holding via NVO should not be used due to the outbounds via NVO, **ERUKI** holding should be used instead.
Which holding is used for inbounds via ERNEP (GULKO or KOPAG) must be coordinated individually depending on the traffic situation (incl. transfer level).
To relieve DKA, PADH and GIN, the TAU/SIG sector combination can be used to manage the holdings. For KOPAG holdings above FL140, the transfer from PADH to SIG takes place at individually coordinated levels.
If holds in the APP area are required at short notice, only WYP (13L) and COL (31R, 24) are to be used, as otherwise there will be conflicts with outbounds. If only inbounds need to be delayed on the 31R, the COL holding in the APP area should be used for this.
Every 3 minutes (or every 6 minutes per ‘holding waypoint’), one aircraft from the KOPAG, GULKO or ERUKI holding can leave the holding (one orbit takes about 4 minutes). It should be noted that NVO/DEPOK inbounds are not prioritised and the delay is evenly distributed. Depending on the situation on the ground, the worst inbound rate is 12 inbounds per 30 minutes!
The inbounds are sent from the centre to WYP (13) or COL (31 and 24) at the normal transfer level to clear the holding. Individual arrangements are possible at any time.
**Inbounds 0 - 11:** no holds expected
**Inbounds 12 - 17:** consider outbounds, from 12 outbounds in 30 minutes, holds not excluded
**Inbounds 18 - 24:** take outbounds into account, from 6 outbounds in 30 minutes, holds likely
**Inbounds more than 24:** Inbounds exceed the maximum capacity even without outbounds, holdings unavoidable.
# EDDS - Stuttgart Airport
# Overview
Stuttgart is a medium-sized and very interesting airport, especially when there's a lot of traffic. With only one runway, preplanning is important to run the airport efficiently. Like in reality, the typical traffic at the airport is a mix of VFR and short to medium haul IFR flights.
**Stuttgart is an unrestricted airport.** DEL and GND are unrestricted and can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. All radar positions can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
Due to the high amount of complexity of the airport, it is highly recommended that **S1-rated controllers** have gained a great deal of experience at other unrestricted airports before staffing positions at Stuttgart.
**Training:** Controllers with the S1 rating can staff TWR during their training (active EDDS\_TWR solo endorsement required). Controllers with the S2 rating can staff APP positions during their training (active EDDS\_APP solo endorsement required - sector NOR not included).
### Stuttgart ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ADS
| EDDS\_ATIS
| 126.130
| --
| --
|
| **Delivery**
| DSC
| EDDS\_DEL
| 121.915
| --
| unrestricted: [EDDS CBT Delivery](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=80 "Course EDDS (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Ground**
| DSG
| EDDS\_GND
| 118.605
| --
| unrestricted: [EDDS CBT Delivery & EDDS CBT Ground](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=80 "Course EDDS (VATGER moodle)") |
| **Tower**
| DST
| EDDS\_TWR
| 118.805
| --
| unrestricted: no course |
| VFR Tower
| DSTV
| EDDS\_VFR\_TWR
| 119.055
| relief station during high amount of inbound VFR traffic
| unrestricted: no course |
| **Sector Stuttgart**
| STG
| EDDS\_STG\_APP
| 125.050
| primary
| unrestricted: no course |
| Sector Reutlingen
| REU
| EDDS\_REU\_APP
| 119.200
| relief station during high amount of traffic in the TMA
| unrestricted: no course |
| Arrival
(Feeder)
| DSAT
| EDDS\_F\_APP
| 119.850
| --
| unrestricted: no course |
### Controlzone Stuttgart
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/8K4grafik.png)
*Stuttgart Controlzone (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
# Delivery
Stuttgart Delivery is responsible for enroute and startup clearances for all departing IFR aircraft. VFR aircraft have to call Delivery for departure information. **For all departures (IFR and VFR) Stuttgart Delivery is the first station to contact**, except for police helicopters, which may also contact Ground initially.
### Enroute Clearance
Delivery shall ensure that the initial climb is set (always 5000ft) and the correct SID is coded into the flightplan. Additionally, Delivery has to make sure that all SID restrictions are adhered to.
##### Both Arrivals staffed
If both Arrivals are staffed, Delivery needs to inform all south departures (via **ROTWE, SUL, KUNOD, and ABTAL**) to contact 119.200 immediately when airborne as part of the enroute clearance. For all other departures the ATIS remark remains valid and no additional information is required.
> **ATC**: DLH123, revised airborne frequency 119.200.
Alternatively, to avoid confusion for the pilots, the departure frequency can be completely removed from the ATIS. In this case, Delivery has to **inform all pilots about their respective departure frequency**.
##### Local IFR
Local IFR flights are possible via **TEDGO** and **STG** but need to be coordinated and **require a startup release by Arrival (STG) or Director (DSAT), if online**. When Director is online, local departures need to be advised with the enroute clearance to contact 119.850 immediately after departure.
> **ATC**: DLH123, revised airborne frequency 119.850.
Departures planning to perform **IFR training at Schwäbisch Hall (EDTY)** also **require a startup release by Arrival (STG)**.
##### SID Restrictions
To ensure an efficient operation within the upper and lower airspace several restrictions should be met. To solve an invalid route, the pilot usually has to **file a completely new route** (valid routes for many destinations can be found on [grd.aero-nav.com)](https://grd.aero-nav.com "grd.aero-nav.com").
| **Waypoint** | **Restriction** | **Remark** |
| **DKB** | only via **N869** or **DEST EDDN, EDTY, EDQ\*** |
|
| **ETASA** | only **DEST EDDF, EDFC, ETOU, EDFE** |
|
| **GEBNO** | only via **Z76** & max. RFL **FL180** |
|
| **KRH**
*Karlsruhe*
| max. RFL **FL80 (Mo - Fri)** &
only **DEST EDDR, EDRZ, EDSB, ETAR**
| **other DEST** via VESID \[...\] |
| **OKIBA** | min. RFL **FL200** |
|
| **ROTWE** | **if via NATOR:** jet only
| **reroute props** via SUL Y125 NATOR |
| **STG**
*Stuttgart*
| only **local IFR** |
|
| **SUL**
*Sulz*
| **Jet:** only **DEST EDTL, EDNY, LSZH, LSZR** | **reroute jets** via ROTWE Y126 TUBLO N850 NATOR |
| **TAGIK** | only **via ABUMO/ASKIK** & max. RFL **FL240** |
|
| **TEDGO** | only **local IFR** or **DEST ETHL** | |
CLD 2042 230615 EDDS PDC 026 DLH8AL CLRD TO EDDF OFF 25 VIA ETASA4B SQUAWK 1000 ADT MDI NEXT FREQ 121.915 ATIS P REPORT READY ON 121.915
### Startup
When startup clearance cannot be given immediately or the pilot is not ready for startup within the next 5 minutes, the pilot needs to stay on Delivery frequency until they receive their startup clearance. To create an efficient startup flow, the **[vACDM plugin](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/vacdm "vACDM Guide") should be used**. If the vACDM plugin is not used, a startup clearance can be issued roughly every 2-3 minutes.
##### Runway Capacity
To ensure smooth operations and an acceptable level of workload for following stations, **Delivery has to make sure the startup rate is regulated to the current airport capacity**. The following table shows the maximum capacity of Stuttgart airport.
| **Normal operations**
|
| max. movements per hour
| 48
|
| max. departures per hour
| 40
*(with no arrivals)*
|
| max. arrivals per hour
| 40
*(with max. 8 departures)*
|
| **LVP**
|
| max. movements per hour
| 14 |
Maximum capacity **might have to be adjusted downwards** in case of high complexity (e.g. high level of differing aircraft performances for inbound and/or outbound traffic) or a high amount of VFR movements.
**Maximim active Startup Approvals** at the same time (status SUG until DEP) per runway (use vSID startup counter):
**RWY 07:** 8 - 10 (due to limited space at the holdingpoint)
**RWY 25:** 10 - 12
##### Outbound Taxi Times
The average time between startup approval and takeoff clearance is **5-10 minutes during 07 operations** and **15-20 minutes during 25 operations**. More accurate times are available through use of the vACDM plugin.
# Ground
Stuttgart Ground is responsible for all ground movements at the airport (including pushback).
### Parking positions
Stands are automatically assigned according to airline and aircraft type. Cargo and US military aircraft (other military aircraft park at an appropriate stand in the North, usually at the GAT if they are small enough) are parked in the Southern part of the airport.
**Stands 40 - 56** are **taxi out positions**, so no pushback is required. Stands **61 - 64** are **available for taxi out if the opposite stand is not occupied**. If necessary, aircraft may taxi through stands 40 - 56. Only stands 9 - 16 have jetways.
##### Relocated stands
During construction works, stands 40 - 48 were relocated. This means that, depending on their scenery, **pilots might take the wrong stand**. The automatic stand assignment is based on the current real world layout.
### Pushback
##### Distance between simultaneous pushbacks
**At least two stands have to be between two simultaneously pushing aircraft**. This can be reduced to one or even no stand by issuing special pushback instructions. The following example will explains these special pushback instructions.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-06/push-1-stand.jpg)*SWR45SZ and EWG2478 have both requested pushback but there is only one stand between them*
Assuming both aircraft shall push back facing east, the following pushback instructions will allow for simultaneous pushback.
| **if SWR45SZ pushes first**
| SWR45SZ is instructed to make a long pushback
once SWR45SZ is aligned with the taxiway, EWG2478 is instructed to make a normal pushback
|
| **if EWG2478 pushes first**
| EWG2478 is instructed to make a short pushback
once EWG2478 has finished pushing back, SWR45SZ is instructed to make a normal pushback
|
If there is no stand between the two aircraft, a simultaneous pushback is **only possible with the scenario in which SWR45SZ pushes first**; EWG2478 then has to also make a short pushback.
##### Orange line
The orange line at stands 71-75 allows pushback of aircraft with a **maximum wingspan of 36m** to allow simultaneous taxi operations of aircraft with a maximum wingspan of 36m on N. For pushbacks on this orange line, there are **mandatory pushback directions** according to the table below (pushbacks onto N can still face both directions).
- **71 and 72:** facing west
- **73:** facing west or east
- **74 and 75:** facing east
When stands 71A or 74A are occupied, the orange line is not available for pushbacks. Additionally, orange line pushbacks are **not available for stands 71A and 74A**.
### Taxi
**Taxiway N is always used opposite to the direction of the active runway**. In 25 configuration, N is therefore used for departing traffic, in 07 configuration for arriving traffic. Taxiway S is always used opposite to N.
General Aviation aircraft are usually sent to intersection C (25 operations) or G (07 operations).
##### Vacating Traffic
**Tower will give the initial turn** onto N or S after vacating according to the current standard taxi direction. The handoff will take place thereafter.
##### Runway Crossing
Runway crossings can only be conducted between K and Y. Traffic can either be sent to Tower for the crossing or remain on Ground frequency, depending on the traffic situation (during high traffic, it may be easier to send the aircraft to Tower for a more efficient crossing).
If the aircraft remains on Ground frequency, **Tower has to release the crossing** and Ground has to inform Tower once the runway is clear again. The following communication helps to keep Tower informed on the status of the crossing.
> *Traffic is cleared to cross:* **Ground (to Tower):** Crossing in progress.
>
> *Traffic is clear of the runway:* **Ground (to Tower):** Crossing complete.
##### Taxiway Z
Taxiway Z west of taxiway Y **should only be used for military aircraft**. Depending on the amount of traffic, deviations are possible. The **extended centerline** may only be crossed on Z under the following circumstances:
| **07 operations**
| crossings always have to be released by Tower
|
| **25 operations (CAT I)**
| **aircraft < 14m height** *(all Light and Medium aircraft)*: Tower informed about crossing
**aircraft ≥ 14m height**: crossing released by Tower
|
| **25 operations (LVP)**
| **aircraft < 6m height** *(most smaller business jets)*: Tower informed about crossing
**aircraft ≥ 6m height**: crossing released by Tower
|
##### Large aircraft (wingspan larger than B748)
Due to wingspan restrictions on most parts of the Northern apron, **special taxi procedures are necessary for aircraft with a wingspan larger than B748** (above 68.5m). These aircraft may not use TWY N between TWYs F and D.
During **07 operations**, outbound traffic can simply depart via intersection K or Y, but inbound traffic requires a **special routing via S**. Due to wingspan restrictions on other exits, these aircraft will have to vacate via B or A. They can't turn immediately onto S from those intersections, but instead need to first taxi via N and then switch to S at D.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-06/748-taxi-in-07-annotated.jpg)
During **25 operations**, outbound traffic has to **taxi via S, opposite to the standard direction** and switch to N at D. This means that inbound traffic can't be sent left onto S by Tower - there are multiple possible solutions to this, but the easiest one is for the Tower controller to hand off inbounds holding short of S if there could be a conflict.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-06/748-taxi-out-25-annotated.jpg)
The **handling of an inbound code F aircraft during 25 operations depends on the current traffic**. During periods of low traffic, the aircraft can be allowed to vacate the runway via Y, but during periods of high traffic it might make more sense to instruct the aircraft to vacate to the right via F or H and later cross the runway at K.
##### Cargo Traffic
Cargo traffic should primary taxi to the cargo positions via Y. **Inbounds from runway 25** can vacate via W (depending on wingspan) or Y, while **inbounds from runway 07** need to taxi via N or S and K to cross runway 07. During **high traffic 07 operations**, a crossing on Z might be more efficient.
### Ground Movement Strategies
While the **best strategy always depends on the individual situation**, the following paragraphs give an overview over the most useful strategies which are also regularly used in the real world.
##### Roundabout
During **07 operations**, inbound traffic usually switches from N to M via H, so that L2 and L3 can be used for outbound traffic. Whether traffic pushing back from stands 9-19 should push back facing east- or westbound depends highly on the traffic situation. However, during high traffic situations it **usually makes more sense make all pushbacks facing west** to keep all traffic on M moving in the same direction.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-06/07-h-m-strategy-annotated.jpg)
*CFG228G (inbound for stand 14) is instructed to taxi via H and M, while EWG2478 (outbound from stand 16) taxis via L2 and K*
As the **apron can get crowded really quickly during 07 operations**, it can make sense to move outbounds from the Northern apron to the holding point via Z and Y. Keep in mind that crossings on Z always need a release from Tower during 07 operations!
During **25 operations**, outbound traffic often switches from M to N via H so that L2 and L3 can be used for inbounds. If there is a lot of outbound traffic, it **might make sense to also use L2 for outbounds**; keep in mind that you will then have to merge the traffic streams again at H, though.
##### Outbound Sequencing at K
During high outbound traffic situations with 07 operations, it is **good practice to only send aircraft through to the holding point once they have reported ready for departure**. A good strategy for ensuring this is to **instruct aircraft to hold short of K** (if coming from O, N, or S) **or of N** (if coming from L2). Then, once a pilot has reported ready, they are instructed to continue to the holding point and to contact Tower.
> **ATC**: EZY47RJ, taxi via N, hold short of K, report ready for departure.
> **Pilot**: Taxi via N, hold short of K, wilco, EZY47RJ.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-06/07-ready-message-strategy.jpg)*three aircraft holding short of K/N*
> **Pilot**: SWR45SZ, ready for departure.
> **ATC**: SWR45SZ, taxi to holding point runway 07 via K and contact Tower 118.805.
> **Pilot**: SWR45SZ, taxi to holding point runway 07 via K and contacting Tower 118.805.
>
> *SWR45SZ taxis forward to the holding point and switches to Tower.*
>
> **Pilot**: EZY47RJ, also ready for departure.
> **ATC**: EZY47RJ, taxi to holding point runway 07 via K and contact Tower 118.805.
> **Pilot**: Taxi to holding point runway 07 via K and contact Tower 118.805, EZY47RJ.
>
> *EZY47RJ taxis forward to the holding point and switches to Tower.*
>
> **ATC**: AUA75SW, taxi to holding point runway 07 via K and when ready for departure contact Tower on 118.805.
> **Pilot**: AUA75SW, taxiing to holding point runway 07 via K, Tower on 118.805, wilco.
As there are no further aircraft currently taxiing towards the holding point, there is **no need to wait for AUA75SW to report ready for departure to Ground** once SWR45SZ and EZY47RJ have been moved to the holding point.
### De-Icing
Stuttgart has four deicing pads. **Deicing operations are only conducted on those deicing pads**. Aircraft always have to **enter the deicing pad from N**. For exiting the deicing pad, the procedures are as follows:
- **DP1**: westbound via S
- **DP2**: eastbound via S
- **DP3**: westbound via S
- **DP4**: eastbound via S
During 25 operations, it is also possible to allow aircraft that have been deiced on DP2 to make a sharp left turn and join N by crossing H. There are guidance lights for the pilots to follow, but there is **no dedicated taxiway**. If you want to use this procedure, you should give a very detailed instruction on how to leave the deicing pad in order to **make sure pilots understand how the procedure works**.
> **ATC**: DLH123, make a left turn, cross taxiway H to join N, thereafter taxi to holding point runway 25 via N and A.
##### Restrictions
Each deicing pad has a **maximum wingspan limit** according to the table below.
| **Deicing Pad**
| **Wingspan limit**
|
| DP1
| Code E (max. 65 m) except B747 and AN124
*(e.g. A359)*
|
| DP2
| Code F (max. 80 m)
*(e.g. A388)*
|
| DP3
| Code C (max. 36 m)
*(e.g. B738)*
|
| DP4
| Code C (max. 36 m)
*(e.g. B738)*
|
During deicing operations, the **relevant sections of taxiway S are closed for taxi operations**:
- **DP1/DP2**: between I and H
- **DP3/DP4**: between H and F
Additionally, depending on the length of aircraft on the deicing pads, the **relevant sections of N have different wingspan restrictions** according to the table below.
| **Length of aircraft on deicing pad**
| **Wingspan restriction on N**
|
| < 50 m
*(e.g. A310)*
| max. 60 m
*(e.g. B742)*
|
| 50 - 60 m
*(e.g. A332)*
| Code D (max. 52 m)
*(e.g. B788)*
|
| 60 - 65 m
*(e.g. A339)*
| max. 42 m
*(e.g. B701)*
|
| 65 - 70 m
*(e.g. A124)*
| Code C (max. 36 m)
*(e.g. B738)*
|
| > 70 m
*(e.g. B748)*
| max. 24 m
*(e.g. CRJ7)*
|
### General Aviation Terminal (GAT)
The GAT itself is uncontrolled. Ground only assigns the GAT exits.
**Exit 1** can be used for aircraft with a wingspan up to **22 m** while **Exits 2 and 3** can be used for aircraft with a wingspan up to **29 m**. **Multi-engine aircraft and jets** shall always use **Exit 2 or 3**. Aircraft parked at the **Southern stands on Apron GA3** can also taxi directly onto N.
**Apron GA2** is only available for aircraft with a [**MTOW of 2000 kg**](https://contentzone.eurocontrol.int/aircraftperformance/default.aspx "Eurocontrol Aircraft Database") or below (D-Mxxx, D-Exxx and D-Gxxx). **Apron GA3** can be used for every aircraft with a maximum **wingspan of 29 m** and a **length of 30.3 m**.
During recent real world construction work in the GAT area, the [Exits have been renamed and repositioned](https://board.vatsim-germany.org/threads/07-08-23-26-10-23-partial-closure-of-twy-n-at-edds-permanent-restructuring-of-edds-gat-exits.70739/ "NAV Forum post on EDDS construction work"). While these changes are now complete and the new names are available in the latest charts, **most pilots will not have up to date sceneries**. Due to this, both Ground ASRs will use the old layout but with updated Exit names.
Keep in mind that **some pilots may not be able to use Exit 3 due to their scenery**, so it is good practice to ask them if they are able before assigning it.
# Tower
Stuttgart Tower is responsible for the runway and traffic within the Stuttgart CTR.
Please also **check the [EDDS Arrival SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/arrival "EDDS Arrival SOP")** to familiarize yourself with Arrival procedures relevant for Tower operations to enable the necessary coordination with Approach.
### General
##### Operating direction
Runway in use is based on the direction of the wind (METAR and TAF) and general weather conditions. While there is technically **no preferred runway direction** at Stuttgart, 25 is normally used whenever conditions allow.
##### Taxiway Z
Taxiway Z is **controlled by Ground**. To avoid low altitude overflights on short final during 07 operations and ILS interference during 25 operations, crossings of some high aircraft **on Z between O and R** require **approval by Tower** to cross the extended centerline according to the rules below. Ground has to inform Tower of crossings that don't require approval as well. If the restrictions are not met, the **aircraft on final has to go around**.
| **Height**
| **Restriction**
|
| **07 operations**
|
| **any**
| sensitive area has to be clear when traffic is within 2 NM final |
| **25 operations** |
| **> 14 m (CAT1)**
| traffic must be able to proceed without ILS guidance within 4 NM final
|
| **> 6 m (LVP)** | sensitive area has to be clear when traffic is within 4 NM final
|
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-06/z-restricted-area-annotated.jpg)
*the sensitive area (red) can be estimated in extension of the holding points*
Additionally, during 25 operations, Tower shall **inform aircraft on final about potential ILS interference** from crossings on Z that require approval.
> **ATC:** Lufthansa 123, expect short term ILS interference by Airbus A320 crossing on Z.
#### Reduced runway separation
RRS minima may be applied by Stuttgart Tower, according to the following table:
| **Runway** | **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 1**
| **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 2**
| **preceding CAT 3**
**succeeding CAT 1/CAT 2/CAT 3**
|
| **07/25** | 600m | 1500m | 2400m |
### Outbound Traffic
##### Intersection Departures
Pilots always need to be asked if they are able for any intersection except full length. **Smaller aircraft** are usually sent to intersection C (25 operations) or G (07 operations).
##### Bypass Area
If outbound traffic is not ready for departure, it can wait at bypass area P1 or P2 **(max. B739/A321)**. The bypass area also makes it possible to change the departure sequence when the preceding traffic is instructed to hold short of S and the succeeding traffic to taxi to the holding point via P1 or P2 and S.
##### Separation
Stuttgart Tower is responsible for separation until the aircraft reaches the initial climb altitude.
During 07 operations, special attention must be paid to aircraft on **K-SIDs departing after traffic on a H-SID that also makes a right turn to the West after takeoff (ROTWE, STG, SUL, and TEDGO)**. To ensure separation, Tower has two options:
- departure release by the appropriate Langen Radar sector
- guaranteed minimum 1000ft vertical separation (e.g. due to climb rate or if the H-SID reaches FL60 before the K-SID reaches 4000ft)
##### Opposite Departures
Departures against the current operating direction always require a **departure release** by Stuttgart Director (DSAT), if online, and otherwise by Langen Radar (STG).
A rule of thumb for when such a release can usually be expected is when the next inbound is **at least 20 NM from touchdown**. Due to other factors, a release might still be granted later or not anymore, though.
##### Visual Departures
To increase efficiency, Tower can utilize visual departures for **prop and turboprop aircraft up to 5.7t MTOM**. These have to be **coordinated with Arrival and accepted by the pilot**. Separation always has to be ensured.
> **ATC:** DEABC, advise able to accept visual departure. **ATC:** DEABC, when airborne turn right heading 340, maintain visual reference to the terrain until passing 3500ft, climb 5000ft, remain on tower frequency.
| **SID** | **Heading** |
| **07 North**
| 350
|
| **07 South**
| 160
|
| **25 North**
| 340
|
| **25 South**
| 200 |
The handoff to Arrival takes place when the **aircraft has passed the MVA**.
### Inbound Traffic
##### Vacating Traffic
Tower shall give the initial turn onto taxiway N or S when vacating. This will ensure an efficient traffic flow and prevent blocking the runway exits with traffic holding during the frequency change. The handoff should take place after the instruction to turn on N or S.
##### Missed Approaches
By default missed approaches are flown as published, deviations are only possible if necessary to ensure separation and Arrival has to be informed as soon as possible. Once separation is ensured the aircraft is handed off to Stuttgart Director (DSAT) if online, and otherwise to Langen Radar (STG).
After a missed approach, the next IFR departure requires a **departure release**.
### VFR Traffic
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/8K4grafik.png)
*Stuttgart Controlzone (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
Stuttgart has a D-CTR from GND to 3500 feet AMSL. VFR traffic circuits can be flown North and South of the airport.
##### Reporting points
The following mandatory reporting points exist around the airport:
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
|
| **W**
| highway intersection A8 and A81
|
| **E**
| between Fernsehturm Stuttgart and Fernmeldeturm Stuttgart
|
| **L**
| Fernmeldeturm Waldenbuch/Dettenhausen
|
| **S**
| Aichtalviadukt (B27)
|
| **O**
| Neckarbrücke Nürtingen |
##### VFR Tower
Stuttgart has a VFR Tower that is **responsible for incoming VFR traffic**. If this position is staffed, VFR pilots entering the CTR initially contact this controller. The VFR Tower will then give instructions on how to enter the CTR as well as inform the pilot about the QNH and the active runway. The pilots are then handed off and instructed to report the mandatory reporting point to Stuttgart Tower (DST) who is then responsible for all further instructions.
After coordination with Tower, traffic only crossing the CTR may remain on the VFR Tower frequency.
VFR Tower has to **keep a close eye on the general traffic situation** to gauge which VFR requests can be accommodated and when VFR inbounds have to be delayed.
##### SVFR
The **maximum altitude for SVFR** traffic within the CTR is 3000ft AMSL.
### Helicopter Operation
Stuttgart has two helipads. Helipad North is located south of taxiway S, between taxiway F and taxiway E. Helipad South is located west of the threshold of runway 07 and north of the military apron. **Helicopters must use the helipads or the runway for takeoff/landing**.
### Auto-Handoff
Stuttgart utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# Arrival
Stuttgart Arrival covers not only Stuttgart (EDDS) but also Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden (EDSB) and Lahr (EDTL) when Strasbourg Approach (LFST\_APP) is offline, as well as the uncontrolled airfield Schwäbisch Hall (EDTY), which has instrument procedures.
Please also **check the EDDS Tower, Ground, and Delivery SOPs** to familiarize yourself with Tower procedures relevant for Arrival operations to enable the necessary coordination with the ground stations.
### Sector Splits
Stuttgart Tower shall be informed immediately about **any changes in sector configuration** (e.g. DSAT is opening or closing).
##### Arrival
**Sector Stuttgart (STG)** is the Northern arrival and the **primary station**. It is responsible for the Northern half of the sector. This means it covers EDTY as well.
Sector Reutlingen (REU) is the Southern sector and responsible for the Southern half. This means it covers EDSB and EDTL as well when LFST\_APP is offline.
**Before REU can be staffed, Stuttgart Director (DSAT) has to be online.**
##### Director
Stuttgart Director does not have a separate sector. The handover from the respective Arrival to Director should take place at the latest on downwind. The **handover altitudes between Arrival and Director have to be coordinated**, e.g. 5000ft in the South and FL60/FL70 (depending on the transition level) in the North.
During a constant arrival stream on both downwinds, Arrival should hand over traffic with **16 NM or greater spacing per downwind** to enable Director to create an efficient final.
##### Departure
Stuttgart does not have a Departure position. If both approach sectors are staffed, REU gets all departures to the South (ROTWE, SUL, KUNOD, and ABTAL), while STG gets all departures to the North (KRH, VESID, TAGIK, ETASA, OKIBA, GEBNO, and DKB).
Traffic departing via TEDGO and STG is handed off directly to Director by Tower.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/LvUgrafik.png)*Stuttgart Arrival Sector*
### Airspace
Around Stuttgart there is primarily airspace D, which makes it easier to handle VFR transits. However, there is also a larger area above the control zone of Stuttgart with airspace C between 3500 ft and 5500 ft AMSL.
A detailed representation of the airspace structure is available at [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/ed-germany/ "openflightmaps").
### Arrival Procedures
##### Releases by Center
On handoff from Center to Arrival aircraft are released for turns but not for climb/descend as long as they are inside center's sector. Flights via **TEKSI** and **REUTL** are released for turns passing DODIL – LUPOL line.
##### STAR Assignment
Stuttgart Arrival needs to clear the desired STAR/Transition unless other arrangements have been made with Center. Out of BADSO, TEKSI, and REUTL, there are STARs that lead directly to an IAF (LBU or STG).
### Approach Procedures
During approaches to runway 07, **aircraft up to 5.7t MTOM** may use all published approaches. For all other aircraft, the **ILS approach is mandatory** and exceptions are only possible in rare cases (e.g. after a runway change). However, the RNP approach may also be used by heavier aircraft if the **visibility is at least 4000m and the ceiling at least 1000ft AGL**.
During approaches to runway 25, all aircraft may use all published approaches.
Arrival - or Director if staffed - shall **inform Stuttgart Tower about every aircraft not flying the standard approach broadcast in the ATIS**.
##### Short Approaches
Approaches that intercept the localizer after VATER or UNSER have to be **approved by Stuttgart Tower**.
##### Visual Approaches
**Non-jet aircraft up to 5.7t MTOM** can be cleared for a visual approach after coordination with Tower.
| **07 inbounds from the North**
| traffic shall fly via reporting point W and the adjacent forest area and avoid built-up area
|
| **07 inbounds from the South**
| traffic shall avoid built-up area
|
| **25 inbounds from the North**
| traffic shall avoid built-up area
|
| **25 inbounds from the South**
| traffic shall follow highway A8 and avoid built up area |
##### 10 NM check
Approach shall **inform Tower once an inbound reaches 10 NM final** (10 NM check) under any of the following circumstances:
- approaches with intentions other than full stop landing
- first approach after a runway change
- opposite landings
### Departure Procedures
As far as possible, a continuous climb should be made possible and the transfer to Center should take place early and without conflict. On handoff all departures are full released for further climb and turns.
Check [Langen ACC (internal)](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg/page/langen-acc-internal) for all procedures of coordination.
**Stuttgart Tower has to be informed immediately** of any traffic being turned off the SID below 5000ft.
### MVA
Due to high terrain around Stuttgart, special care must be taken here. The MVA for the entire sector can be found in the Topsky maps for Euroscope. Due to the MVA, it is not possible to, e.g., let approaches via TEKSI descend directly to 4000ft; instead, at least one intermediate altitude must be used.
For users of a chart service such as Navigraph, an MVA chart for EDSB and EDTL is available through the charts for LFST.
### VFR Transits
VFR flights above 5500ft AMSL will fly through airspace D around Stuttgart. Between 3500ft and 5500ft AMSL the controller need to **take care of airspace C**! Flights through C airspace are not recommended but possible with the CVFR clearance.
### Holdings
The following holdings are published around Stuttgart:
- **BADSO** (MHA 5000)
- **TEKSI** (MHA 5000)
- **REUTL** (MHA 6000)
- **LBU** (MHA 6000)
- **STG** (MHA 7000)
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/xbYgrafik.png)*holdings within Stuttgart Arrival*
### Possible Conflicts
- For descending flights, the existing MVA must always be considered, especially below 5000 ft AMSL and west of the airport!
- The potential for conflict between intersecting approaches and departures must be taken into account.
- Even in the case of different departure routes, attention must be paid to the necessary separation of departures due to the fact that they follow the same track in some places.
- Due to the Black Forest (elevated terrain) between EDSB/EDTL and EDDS, the MVA in this area is 6300 ft AMSL, so IFR flights must be at least at FL70 there.
# EDDG - Münster/Osnabrück Airport
# Overview
Traffic at the airport is usually characterized by VFR and holiday flights, mixed with some scheduled flights. A specialty of Münster/Osnabrück are the two uncontrolled grass runways North of the hard surface runway.
Additional weather information for the airport are available here: [https://dwd-wetter.fmo.de/](https://dwd-wetter.fmo.de/)
**Münster/Osnabrück is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. GND and TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. The Hamm sector (APP) and Münster/Osnabrück Director can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
### Münster/Osnabrück ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ADG
| EDDG\_ATIS
| 127.180
| --
| --
|
| **Ground**
| DGG
| EDDG\_GND
| 121.880
| --
| unrestricted: [EDDG GND & TWR CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=60 "Course EDDG Tower (VATGER Moodle)")
|
| **Tower**
| DGT
| EDDG\_TWR
| 129.805
| --
| unrestricted: [EDDG GND & TWR CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=60 "Course EDDG Tower (VATGER Moodle)")
|
| **Director** | DGAT
| EDDG\_F\_APP
| 129.180
| relief position
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Hamm sector**
| HMM
| EDDG\_HMM\_APP
| 129.300
| airborne frequency if HMM or PADH is staffed
| unrestricted: no course |
All aerodrome stations at Münster/Osnabrück use the **callsign "Münster"**, e.g. "Münster Tower".
The Director station uses the full airport name as the callsign, i.e. "Münster/Osnabrück Director".
The normal radar station uses the default "Langen Radar" callsign.
### Quickview
[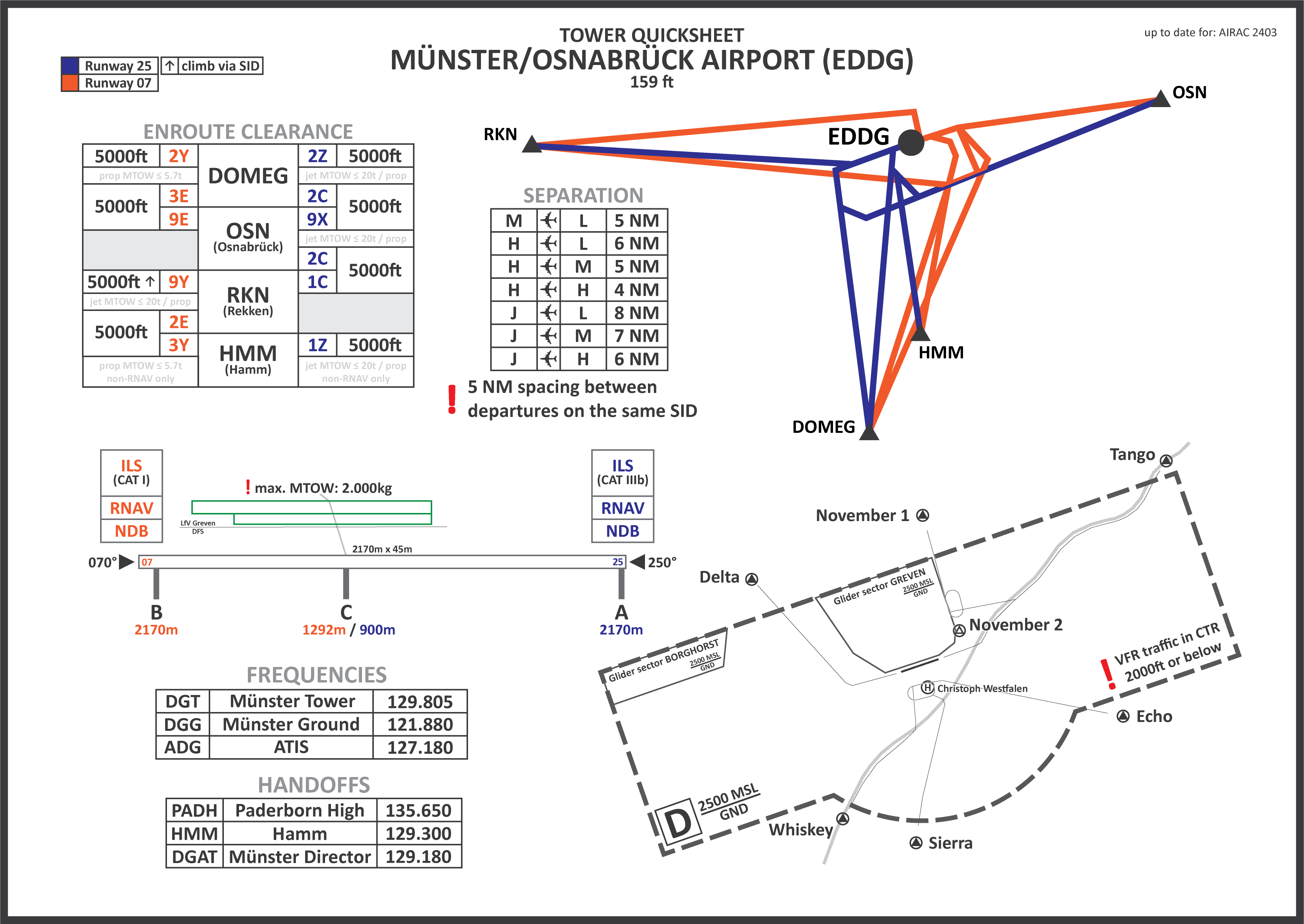](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/BxBMGnRZnSJbKri "EDDG Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Ground
Münster Ground is responsible for startup and enroute clearance and all aircraft movements at the airport.
### Departure Routes
Initial climb for all departure routes is 5000ft AMSL.
| **Waypoint**
| **RWY 07**
|
| **RWY 25**
|
|
| **DOMEG
| **E**
| --
| **C**
| --
|
| Y
| Prop/Turbuprop up
to 5.7 t MTOW
| Z
| Jet up to 20 t MTOW
& Prop/Turboprop
|
| **RKN**
*Rekken*
| **E** | **-** | **C
| --
|
| Y
| Jet up to 20 t MTOW
& Prop/Turboprop
|
| **OSN**
*Osnabrück*
| **E
| --
| **C**
| --
|
| X
| Jet up to 20 t MTOW
& Prop/Turboprop
|
| **HMM**
*Hamm*
| Y | Prop/Turbuprop up
to 5.7 t MTOW
| Z
| Jet up to 20 t MTOW
& Prop/Turboprop
|
**Bold Designator** are primarily used.
Departures via **HMM** are NON-RNAV only!
**Vectored Departures:** If pilots are unable to fly a standard instrument departure (even an older version of the current SID), a vectored departure can be coordinated between Ground and Radar.
Primary **runway heading** and an initial climb of **5000 ft** should be used. Other coordinations are always possible. At Euroscope the SID with RVxxxxx should be selected (xxxxx = first waypoint).
### Parking Positions
For aircraft up to Code C (A321/B739) stands 9 to 10 and 13 to 14 are taxi out positions. Gates 11 and 12 are approved as taxi out gates, but due to the short distance between the gates, a normal pushback is always required. All aircraft with a wingspan of more than 36 m always need a pushback out of stands 9 - 14. Stands 12-14 are available for flights to destinations inside the Schengen-area, as well as destinations outside the Schengen-area.
Stands 21 and 24 are suitable for "heavy" aircraft, but they have to park with facing NNW towards the runway, oppsotite to the markings at the ground.
The **GAT** is placed on the western part of the apron, on stands 101 - 406. The wingspan limitation for stands 301-303 is 20 m, for stands 401 - 406 it is 12 m.
**DE-Icing** is possible at stands 24 and 25.
# Tower
Münster Tower is responsible for the runway and traffic within the D control zone.
**Runway in use:** Runway 25 is used up to a tailwind component of 5 KT.
**Approaches:** For both runways ILS (25 CAT III, 07 CAT I), RNAV and NDB approaches are available.
### Control Zone
The control zone of Münster/Osnabrück reaches from ground up to 2500 ft AMSL.
*[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/eddg-ctr.png) Münster/Osnabrück Control Zone (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
**VRP:** The following visual reporting points are available at Münster.
| **VRP**
| **Entry / Exit**
|
| **D**
| exit rwy 25
|
| **N1 - N2**
| both |
| **T**
| exit rwy 07 + entry
|
| **E**
| both |
| **S**
| both |
| **W**
| both |
Special: All VFR routes**, leading into or out of the control zone via the VRPs, have a **maximum altitude of 2.000ft MSL**. Overflights of villages Ladbergen and Greven shall be avoided, as far as possible. Corresponding information can be found on the Navigraph VFR chart or the VFR AIP, of the DFS.
**TMZ:** Outside the control zone is a TMZ where all VFR aircraft must set transponder code 6104.
**Helicopter:** The helipad for Christoph Westfalen is located south of the airport between the runway and the highway. There is no clearance required for take-off and landing, but for entering and leaving the CTR.
**Run-up:** Traffic not ready for departure that need to perform a run-up can use the bypass area at both runway ends to stay clear of the taxiway for other outbound traffic.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/eddg-runup-area.png)*Bypass Area at each runway end*
**Grass Runway:** North of the runway paved runway, there is the grass runway of the "Luftfahrtvereinigung". Due to historical reasons, pilots can depart at this runway on own discretion, like at small airfields with information service. Parallel landings and take-offs are possible, and traffic information should be provided! Nevertheless, this traffic is controlled inside the control zone.
> **Pilot:** DEABC, C172, nördliche Abstellfläche, VFR über S, erbitte Rollen, Abflug über Gras.
> **ATC:** DEABC melden Sie abflugbereit Piste 25 Gras, QNH 1014.
> **ATC:** DEABC, Verkehr Boeing 737 im kurzen Endanflug Piste 25, fliegen sie in die rechte Platzrunde Piste 25, Wind 230 Grad mit 5 Knoten, Start nach eigenem Ermessen.
#### Reduced runway separation
RRS minima may be applied by Münster Tower, according to the following table:
| **Runway** | **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 1**
| **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 2**
| **preceding CAT 3**
**succeeding CAT 1/CAT 2/CAT 3**
|
| **07/25** | 600m | 1500m | N/A |
### Auto-Handoff
Münster/Osnabrück utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures, where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach/center controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP/CTR **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# Arrival - Sector Hamm
Responsible for all arrivals and departures into Münster/Osnabrück is Langen Sector Hamm (HMM). Most of the time this sector also covers sector Paderborn Low (PADL) which is responsible for Dortmund EDLW and Paderborn/Lippstadt EDLP.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/edgg-hmm.png)*Langen Sector Hamm HMM*
### Münster Arrivals/Departures
**Inbounds:** All flights into Münster have to use BAMSU (inside DLA sector) or DOMEG as last waypoint. All STARs end at HMM, thereafter the published ILS, RNP or NDB approach can be cleared. If using vectors to the final, the MVA need to be taken into account. Inbounds via BASUM are already cleared for the STAR by the previous controller. It's also possible to coordinate directs with the previous controller to HMM without using the published arrival, especially when coming from Amsterdam FIR.
Inbounds from Amsterdam via **SONEB Z841 DOMEG** will enter the sector from the west and are released for turns and descend. Inbounds on the **BAMSU STAR** will enter the sector descending to reach level at HMM.
### Traffic Flows
**Inbounds Düsseldorf:** One of the main duties at Hamm is to sequenze the inbound flow into Düsseldorf EDDL. Three routings entering the sector coming from Bremen/Maastricht via OSN, RORUS and DENOL, merging at HMM to continue via T851 to **HALME**. Inbounds to **EDLV** and **EDLN** will leave the sector via **SOVUX**.
After coordination with Düsseldorf Arrival, sector Hamm may already clear the appropriate arrival/transition for the inbound via HALME.
**Outbounds Düsseldorf:** Outbounds Düsseldorf will enter sector Hamm via **MEVEL** and will leave the sector climbing FL240 to Maastricht in north-eastern direction.
**Inbounds Amsterdam EHAM and EHAA FIR:** Most of the inbounds to Amsterdam EHAM and the EHAA FIR (e.g. EHRD, EHLE...) will overfly sector Hamm towards **NORKU** and will always stay clear of the sector. Some lower routings lead via **HMM T281 NORKU** as well as **HMM L602 RKN** and are transfered according to the [LoA](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg/page/amsterdam-fir-ehaa-langen-fir-edgg "LoA EDGG - EHAA").
**Inbounds Dortmund and Paderborn:** If sector Paderborn Low PADL is staffed, inbound traffic to Dortmund EDLW and Paderborn/Lippstadt EDLP need to be coordinated individually. Usually FL80 is used.
**Active runways for EDDL** has to be set for correct level assignments and sector borders! **Only** set the **DEP RWY**, no need to activate the airport itself.
### Restricted Area
There are several ED-Rs within the eastern part of sectors PADL and HMM. The military **ED-R 203A** "Münsterland" reaches from **FL80 up to FL150**. Above this is the **ED-R 203B** between **FL150 to FL200**. Both ED-Rs are regular active. Additionally ED-R 162 "Lanta Paderborn" is located within the mentioned ED-Rs reaching from 3.500 ft AMSL up to FL125. All restricted areas are automatically activated in Euroscope according the real world airspace use plan. When active, all flights should stay outside the active ED-Rs.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/edgg-padl-hmm-edr203.png)*ED-R 203A from FL80 to FL150 (red area) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
### VFR Traffic
In real life the sector is known for a lot of VFR and training flights due to many flight schools located in this area.
**FIS:** All VFR traffic that are provided with Flight Information Service should get Squawk 7742.
**TMZ:** VFR Ttraffic within the TMZ of Münster not using flight information services should set transpondercode 6104.
### Holdings
If holdings are required (e.g. for Düsseldorf inbounds) **HMM** VOR (257° L | 5000+) should be used for that up to FL240.
Sector Hamm should not use holdings at OSN VOR (207° R | 5000+) for transfering traffic, this traffic need to hold above FL70 within the responsibility of Bremen Radar.
# EDDR - Saarbrücken Airport
# Overview
Saarbrücken is a small airport located directly at the German-French border and in 2018, it became the first remote-controlled airport in Germany. Its very simple layout and low traffic levels make it a perfect airport for new controllers trying to collect initial experience or controllers looking for a calm, relaxing controlling session.
The airport is **unrestricted** and part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/atc/chapter/s1-training "S1 Training Guide (VATGER Knowledgebase)"). GND and TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the required moodle courses. Sector Pfalz can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
### Stations
| **Station** | **ID** | **Login** | **Frequency** | **Remarks** | **Endorsement** |
| **ATIS** | XDR | EDDR\_ATIS | 125.480 | -- | -- |
| Ground | DRG | EDDR\_GND | 118.555 | relief station for DRT | [unrestricted](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=65 "EDDR SOP Test (VATGER moodle)") |
| **Tower** | DRT | EDDR\_TWR | 118.355 | -- | [unrestricted](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=65 "EDDR SOP Test (VATGER moodle)") |
| Pfalz | PFA | EDDR\_PFA\_APP | 129.675 | -- | unrestricted |
# Tower
Saarbrücken Tower is responsible for all enroute and startup clearances, ground movements, the runway, and all traffic within the CTR Saarbrücken. When necessary, Saabrücken Ground can be opened to reduce the workload of Saarbrücken Tower, taking over responsibility for enroute and startup clearances as well as ground movements at the airport.
| **Station** | **ID** | **Login** | **Frequency** | **Remarks** |
| Ground | DRG | EDDR\_GND | 118.555 | relief station for DRT |
| **Tower** | DRT | EDDR\_TWR | 118.355 | -- |
### Enroute Clearance
#### Routing restrictions
| **Via** | **Restrictions** |
| **EDDR** | non-RNAV1 equipped aircraft only |
| **GTQ**
([Grostenquin](https://youtu.be/dSdle8Q26Yc&t=5 "Grostenquin pronunciation (YouTube)")) | -- |
| **IXWIB** | -- |
| **TOMPI** | -- |
#### SID assignment
Controllers shall use the vSID plugin to assign the correct SID and initial climb.
The GTQ#M SID may be manually assigned if the pilot reports unable to comply with the climb gradient of the GTQ#S SID.
##### Omnidirectional departures
Omnidirectional departures shall only be assigned to non-RNAV1 equipped aircraft and require coordination with PFA before the clearance can be issued.
#### IFR training flights
IFR training flights planning to conduct practice maneuvers, e.g. repeated approaches, at EDDR, EDFH, EDRZ, ETAD, ETAR, or ETSB or within sectors EIF or PFA always require a **startup release** by PFA.
### Ground operations
Saarbrücken has **very limited apron space**. The airport can only accommodate **six aircraft up to code C** as well as a number of smaller general and business aviation aircraft. Due to this, it may occasionally be necessary to coordinate delays for inbound aircraft when there are a lot of aircraft at the airport simultaneously.
#### Parking positions
Parking positions N1 thru N5 and S1 thru S5 are the **same parking positions respectively**, they are **differentiated only be the direction from which they are entered**. Positions labeled N (with the exception of N6) are entered via TWY N (from the North, facing South) while positions labeled S are entered via TWY S (from the South, facing North).
The GAT is located in the West of the airport between TWYs B and L.
All parking positions at the airport are taxi-out positions.
### Runway operations
#### Operating modes
There is no preferred operating direction at EDDR and the active operating direction should be chosen based on prevailing weather and traffic conditions. Regardless, tailwind conditions shall never exceed 5 kts.
Only RWY 26 is equipped with an ILS, however, the airport is **not equipped nor certified for low visibility operations**.
During 08 operations, the **RNP approach** should be used, and during 26 operations, the **ILS Z approach** should be used (the ILS Y is only used for aircraft that are unable to comply with the RNAV-requirements of the ILS Z missed approach).
#### Departure releases
A departure release by PFA is required in the following situations:
- omnidirectional departures
- first departure after a missed approach
- departure planning to conduct practice maneuvers at EDDR, EDFH, EDRZ, ETAD, ETAR or ETSB or within the EIF or PFA sector
- whenever requested by PFA to accommodate operations at EDRZ and/or ETAR
#### Reduced runway separation
RRS minima may be applied by Saarbrücken Tower, according to the following table:
| **Runway** | **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 1**
| **preceding CAT 1/CAT 2**
**succeeding CAT 2**
| **preceding CAT 3**
**succeeding CAT 1/CAT 2/CAT 3**
|
| **08/26** | 600m | 1500m | N/A |
### CTR operations
#### Airspace
The EDDR CTR extends **up to 3600ft** and directly **borders the EDRZ RMZ** in the East. Additionally, the Saarbrücken hospital heliport is located within the CTR, as well as two hospitals and a small airfield directly North of the CTR.
Various highways cross the CTR or run close to it and the city of Saarbrücken is partially located within the CTR. Part of the CTR is located in French airspace alongside a small TMZ without a frequency monitoring requirement.
There are three VFR routes for entering and exiting the CTR, made up of a total three compulsory reporting points and two optional reporting points with one VFR holding North and South of the field, respectively
##### Reporting points
| **Reporting point** | **Location** |
| **Echo 1** | highway intersection A6 & A8 |
| **Echo 2** | highway A6 exit Rohrbach |
| **November 1** | highway A8 exit Friedrichsthal |
| **November 2** | Rentrisch village |
| **Sierra** | Sitterswald village |
Labels for all reporting points can be displayed in EuroScope via a TopSky plugin map shortcut: Alt + V
##### Heliports & other airfields
The hospital heliport of the **Saarbrücken Klinikum** is located within the CTR, just North of the extended centerline, and requires pilots to contact DRT for clearance.
Additionally, the hospital heliports of **Neunkirchen Staedt Klinikum** and **Homburg Saar Uniklinik** as well as the small grass field of **Bexbach** (EDRX) are located just North of the CTR.
**Zweibrücken** (EDRZ), which has IFR procedures and thus an RMZ and AFIS, is located just West of the CTR.
Labels for all heliports can be displayed in EuroScope via a TopSky plugin map shortcut: Alt + H
# Radar
Langen ACC sector Pfalz is responsible for the airspace around EDDR, also including the AFIS field EDRZ and the US military field ETAR, as well as presequencing traffic into various airports adjacent to the sector. In the absense of EDFH\_EIF\_APP, this station also covers the Eifel (EIF) sector, which is responsible for Frankfurth Han(EDFH), Spangdahlem (ETAD) and Büchel (ETSB) top-down.Additionally, controllers will occasionally see low level enroute traffic cross the airspace.
| **Station** | **ID** | **Login** | **Frequency** | **Remarks** |
| **Pfalz** | PFA | EDDR\_PFA\_APP | 129.675 | -- |
### Sectorization
#### Sector PFA
Sector Pfalz (PFA) is part of Langen ACC EBG 5, whose sectors Eifel (EIF) and Kirn (KIR) it borders to the North.
**Toward the North and East**, the sector borders various other Langen ACC sectors. Located **South of the sector** is French airspace with Strasbourg APP and various LFEE ACC sectors and **in the West** it covers EBBU ACC sectors over Luxembourg.
In addition, the MIL APP position Ramstein GCA is located within the sector.
Sector PFA consists of **various subsectors with differing vertical boundaries**. For the detailed sectorization, please refer to the [sector page](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/edgg-langen-radar/page/pfa-pfalz-eddr-pfa-app "Langen ACC sector PFA (VATGER Knowledgebase)").
#### Ramstein GCA
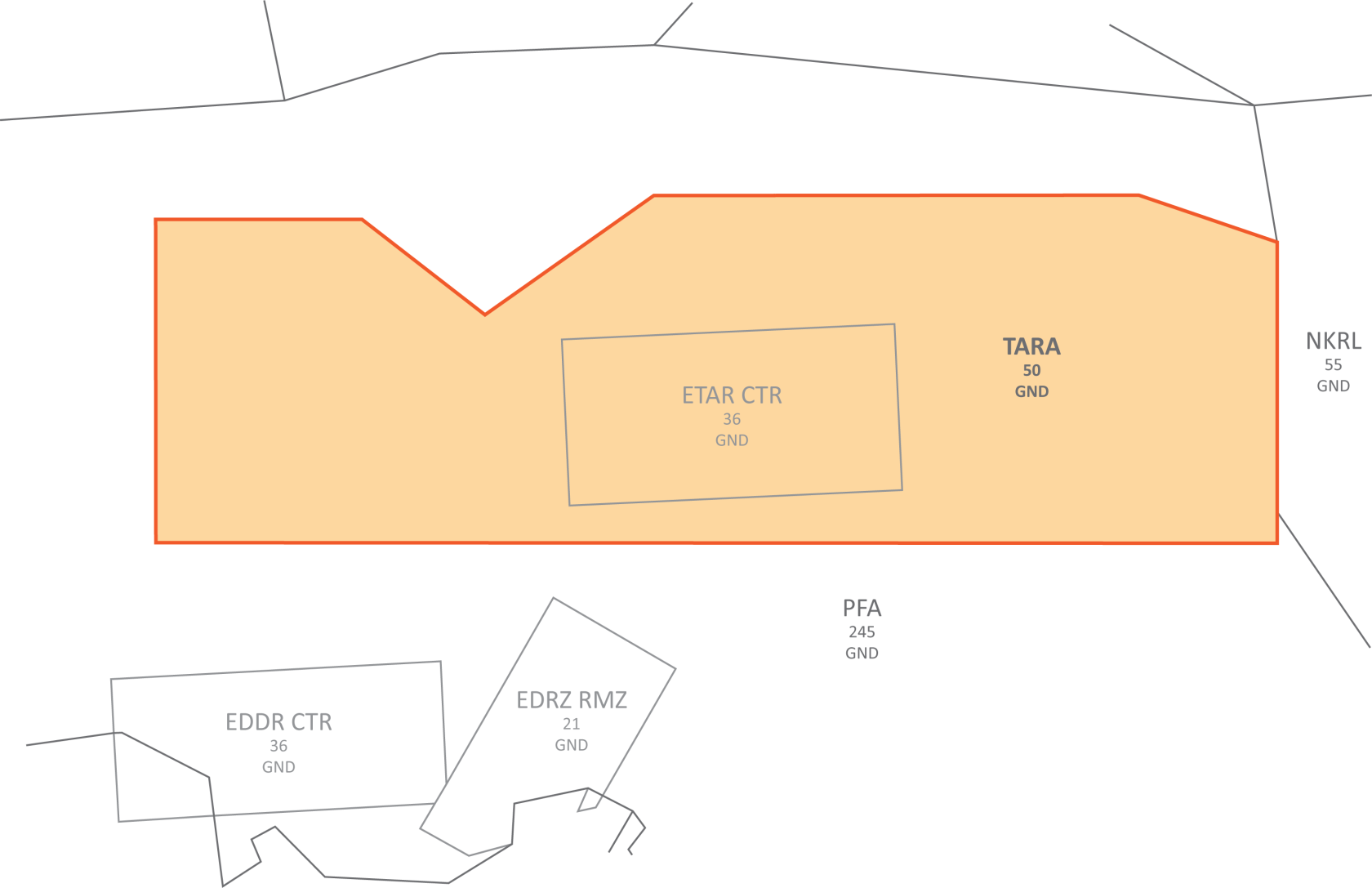Ramstein GCA covers the area around ETAR **up to 5000ft**.
Sector **PFA is responsible for maintaining full radar separation** (i.e. 3NM laterally and 1000ft vertically) to the border of this airspace. Various EDDR and EDRZ procedures infringe on this separation, thus **requiring individual coordination of each affected movement**. Additionally, unless otherwise coordinated, IFR departures from ETAR will only have been cleared to the final waypoint of the SID and their clearance limit thus has to be changed to the destination.
For more detailed information on Ramstein GCA, please refer to the [ETAR SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/approach-3Bo "ETAR SOP APP (VATGER Knowledgebase)").
### Airspace
With the exception of the two D-CTRs EDDR and ETAR, the RMZ EDRZ, and a small section of the TMZ EDFH as well as the TMZ EDDR in delegated French airspace, the entire airspace of sector PFA is **class E below FL100 and class C above FL100**.
#### Airports
There are **multiple airports of direct relevance** to sector PFA, though they all usually see only low traffic levels.
##### EDDR & EDRZ & ETAR
EDDR, EDRZ, and ETAR are the three IFR-capable airports within sector PFA.
**EDDR** is a controlled airport with usually very limited IFR and VFR traffic.
**EDRZ** is an uncontrolled AFIS field with IFR procedures that usually sees similarly low IFR and VFR traffic levels.
**ETAR** is one of the largest and busiest military airports in Germany and the headquarters for the US Air Force in Europe and Africa as well as NATO's Allied Air Command, but on VATSIM it usually sees very low traffic levels.
Procedures for these airports, especially EDDR and EDRZ can **conflict with each other**. If necessary, controllers covering sector PFA should ask underlying Tower controllers to hold departures for release until the risk of conflict is gone.
##### EDFH
**EDFH** is a controlled airport located in neighboring sector EIF; some of its in- and outbound traffic passes through sector PFA.
##### EDFM & EDRY
**EDFM** is a controlled airport and **EDRY** is an uncontrolled AFIS field with IFR approach procedures; both airports are located in neighboring sector NKRL and some of their in- and outbound traffic passes through sector PFA.
##### ELLX
**ELLX** is a controlled airport located in neighboring Luxembourg; some of its inbound traffic passes through sector PFA.
#### Restricted airspace
Langen ACC EBG 5 is one of Germany's main areas of military air traffic activity, which can have a **significant impact on usual operations**.
VATGER currently doesn't require controllers to respect real world area activations - thus, controllers who wish to simulate real world area activations must coordinate this with neighboring sectors where necessary.
Similarly, controllers are allowed to reject area reservations by a VSOA by informing them via the [area booking thread](https://board.vatsim-germany.org/threads/area-booking-vatger.67465/ "Area Booking Thread (VATGER forums)").
Areas currently active in the real world will automatically be displayed with 15 minutes advance notice through the TopSky plugin TSA function, including actual lateral and vertical limits.
Similarly, areas reserved by a VSOA can be manually activated through the TopSky plugin TSA menu.
##### NLFS
ED-R150, also known as the NLFS, is a series of **corridors used for low altitude MIL jet night operations**. A small part of it is located within sector PFA, as depicted on the left.
Only certain segments of the NLFS will be active at any given time, depending on the exact mission to be flown by the pilots and all traffic within the NLFS will operate under MVFR.
Due to the **significant impact on operations at the airports within sector PFA**, VSOAs are currently restricted from using segment GE1-JE1 and it is highly recommended that controllers don't approve its use as well.
As with any other area reservation by a VSOA, controllers may reject reservations of NLFS segments within their airspace by informing the VSOA via the [area booking thread](https://board.vatsim-germany.org/threads/area-booking-vatger.67465/ "Area Booking Thread (VATGER forums)").
The NLFS, including waypoint labels and segment levels, can be displayed via the TopSky plugin map function: Military -> NLFS
#### VFR airspace
A number of PJEs (parachuting drop zones) and glider sectors are located at least partially within the PFA sector.
**Full radar separation** (i.e. 3 NM laterally and 1000ft vertically) has to be maintained to PJEs from approval to drop until 5 minutes after the last jumper jumped; **1 NM lateral and 500ft vertical separation** has to be maintained to glider sectors while they are active.
These VFR airspaces are currently not implemented in the FIR Langen package, but included in this SOP as the related pilot procedures are publicly available to pilots.
##### PJEs
| **PJE** | **Level** | **Airfield** | **Remarks** |
| **Bad Dürkheim** | GND - FL100
| EDRF | managed primarily by PFA, but requires approval by NKRL due to airspace |
| **Lachen-Speyerdorf** | EDRL | managed primarily by PFA, but requires approval by NKRL due to airspace |
| **Saarlouis** | EDRJ | -- |
| **Schweighofen** | EDRO | managed primarily by PFA, but requires approval by STG due to airspace |
| **Zweibrücken** | EDRZ | -- |
##### Glider sectors
| **Sector** | **Min./Max. level** | **Remarks** |
| **Local sectors** |
| Local sectors are only available for specific airfields and activation can only be requested by the respective airfield operator. Pilots are required to monitor that airfield's frequency to stay informed about any changes to the status of the respective sector. |
| **Baumholder-West** | 1500ft - FL95 | managed primarily by PFA, but requires approval by EIF due to airspace
associated airfield: Idar-Oberstein (EDRG) |
| **Idar-Oberstein** | 4500ft - FL75
| managed primarily by EIF, but requires approval by PFA due to airspace
associated airfield: Idar-Oberstein (EDRG) |
| **Wave gliding sectors** |
| Activation of wave gliding sectors can be requested by any pilot through Langen Information. Pilots are required to monitor the applicable FIS frequency to stay informed about any changes to the status of the respective sector. |
| **Haardt** | FL100 - FL195 | managed primarily by PFA, but requires approval by STG due to airspace |
# EDFH - Frankfurt-Hahn Airport
# Overview
Frankfurt-Hahn is located around 100 km West of the city of Frankfurt/Main and known for its low-cost and cargo traffic.
**Frankfurt-Hahn is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. GND and TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. The Eifel sector (APP) can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
**Training:** Controllers with an S2 rating can staff APP during their training (active EDFH\_EIF\_APP solo endorsement required).
### Frankfurt-Hahn ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| AFH
| EDFH\_ATIS
| 136.355
| --
| --
|
| **Ground**
| FHG
| EDFH\_GND
| 121.980
| --
| unrestricted: [EDFH CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=64 "EDFH Tower Course (VATGER Moodle)")
|
| **Tower**
| FHT
| EDFH\_TWR
| 119.655
| --
| unrestricted: [EDFH CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=64 "EDFH Tower Course (VATGER Moodle)")
|
| **Eifel sector**
| EIF
| EDFH\_EIF\_APP
| 125.600
| --
| unrestricted: no course
|
### Quickview
[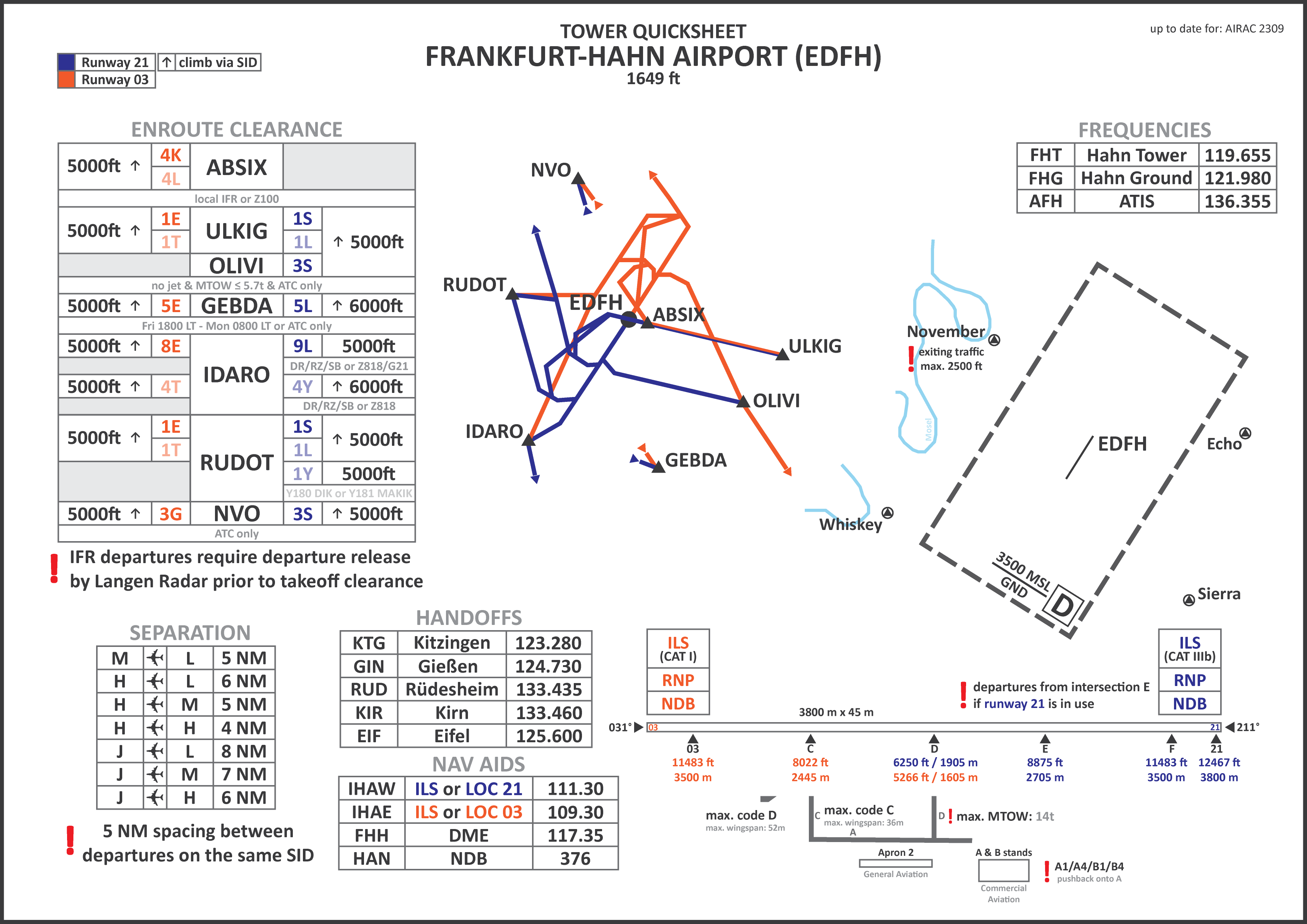](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/ZQNdcHGSLr369kz)*click on the image to open the printable Quicksheet*
# Ground
Hahn Ground is responsible for startup and enroute clearance and all aircraft movements at the airport.
### SID Assignment
For RWY 03 SIDs with designator E/K should be used primarily (highest climbrate required). For RWY 21 SIDs with designator S should be used.
| **SID** | **Restriction** |
| **ABSIX** | only local IFR and flights via Z100 (NON-RNAV) |
| **IDARO #Y** | only flights to EDDR, EDRZ, EDSB or via Z818 |
| **NVO**
*Nörvenich*
| by ATC only |
| **OLIVI** | by ATC only, Non-Jet up to 5,7 t MTOW |
| **RUDOT #Y** | only via Y180 DIK or Y181 MAKIK (NON-RNAV) |
| **IDARO #L** | only flights to EDDR, EDRZ, EDSB or via Z818, G21 (NON-RNAV) |
### Ground Movement
Outbound traffic at Positions **311, 314, 321, and 324** has to be pushed on taxiway A with facing NE or SW. For gate assigment the Groundradar Plugin should be used.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/edfh-pushback.jpg)*Pushback from stand 311 at Hahn Airport*
During 21 operations, medium and light type traffic should be guided to the runway via E whenever possible. The TORA of 2700m should be enough for most of this traffic. The pilot should be informed about that on time.
### Taxiway Restrictions
There are multiple taxiway restrictions that need to be considered:
- TWY A between TWY D and E for aircraft up to category C (wingspan below 36 m - A321/B739) only
- TWY D cannot be used by aircraft exceeding 14.000 kg MTOW (only available for registration D-Cxxx and smaller)
# Tower
**Approaches:** For both runways ILS (RWY 21 CAT III, RWY 03 CAT I), RNP and NDB approaches are available.
### IFR Departures
Departing IFR traffic switches to Radar (APP) frequency without separate instruction, immediately when airborne. Make sure the correct frequency is set inside the ATIS.
All departures shall be separated by radar separation or wake turbulence separation, whichever is greater. Departures flying the same SID shall be spaced by at least 5 NM when the following aircraft overflies the departure end of runway.
### WTC Heavy Aircraft
**Outbound Traffic:** Traffic with WTC Heavy can only enter the runway via F or E. When RWY 03 is in use, this traffic has to enter RWY 21 via E and need to do a backtrack at the end of the runway. If more spacing between inbound traffic is required due to this, it has to be coordinated with the Arrival Sector.
**Inbound Traffic:** A backtrack is also required for Heavies landing on RWY 21 who need to vacate via E. The "turnpad south" between taxiway C and B2 may only be used for aircraft up to CAT D (B764/MD11). To prevent that Heavies will vacate via C it might be necessary to tell the pilot before issuing the landing clearance or shortly after landing, that a backtrack will be required.
*Backtack for Heavies at Hahn Airport*
### VFR Traffic
The control zone in Hahn extends from ground to 3500ft AMSL. VFR traffic exiting the control zone via reporting point NOVEMBER must stay at or below 2500 ft, for all other reporting points maximum is 3500 ft.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/b7pgrafik.png)*Controlzone Frankfurt/Hahn - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
### Auto-Handoff
Frankfurt/Hahn utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach/center controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP/CTR **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# Arrival - Sector Eifel
Responsible for all arrivals and departures into Frankfurt/Hahn is Langen Sector Eifel (EIF).
This sector provides ATC service for all IFR traffic with origin or destination EDFH as well as for the military airports ETAD (Spangdahlem) and ETSB (Büchel). For each RWY ILS, NDB and RNP approaches are available. Only the ILS for RWY 21 is desinged for CAT III approaches, all the other approaches are CAT I only.
**Heavies:** For 21 operations inbound with WTC Heavy need to do a backtrack to vacate the runway. Therefore a target spacing of around 12 NM behind a heavy is recommended.
Usually transitions are used, directs may be coordinated with Center. Inbounds via OLGIL and OLIVI should stay clear of the arrival area of Frankfurt if not released by Frankfurt Arrival.
The MVA within the sector is between 3000ft and 5000ft MSL (see Euroscope for details). MIL charts are available via [MILAIS](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "Military AIP Germany") (GEMIL FLIP VAD).
[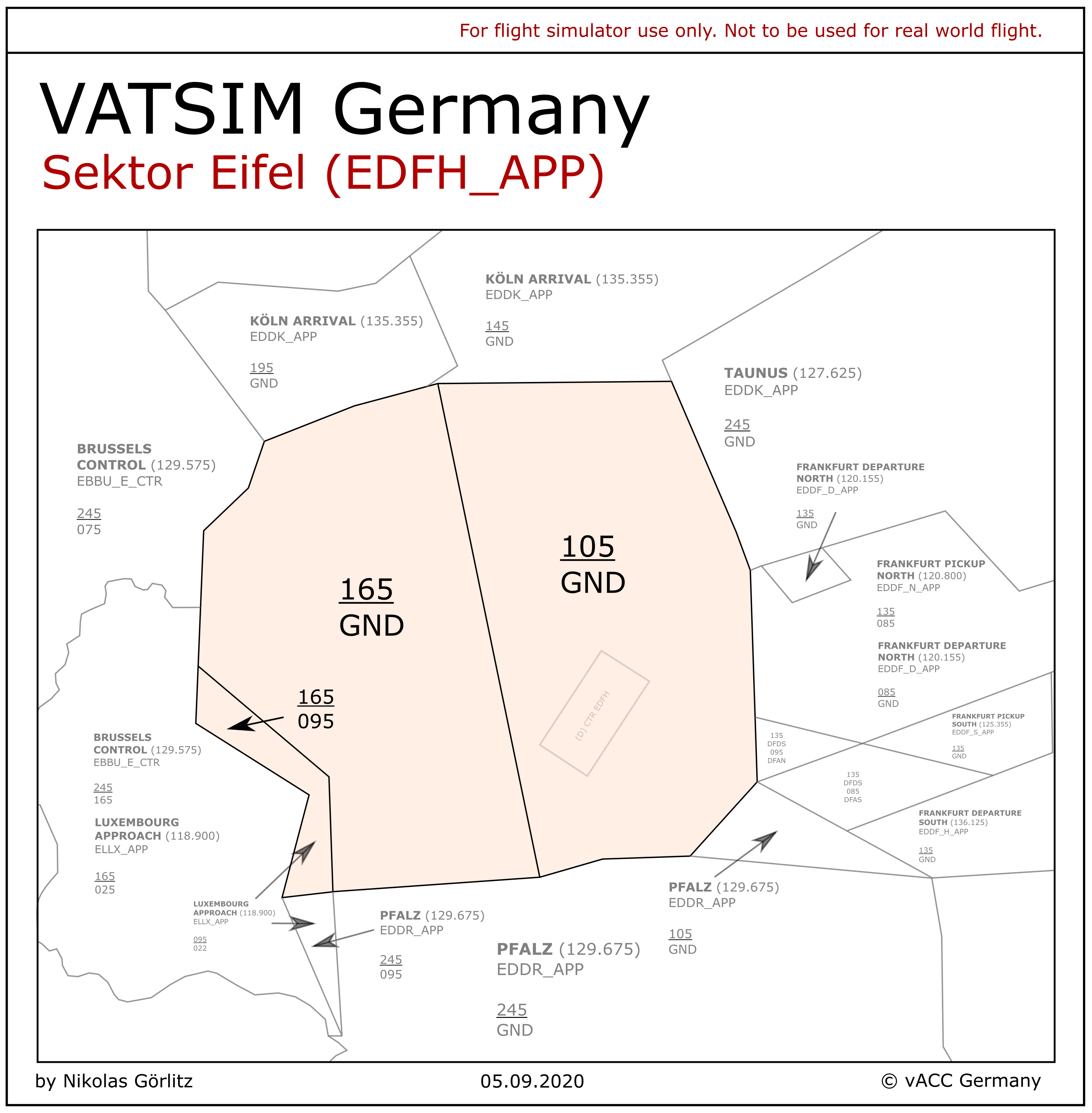](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/l62grafik.png)
*Langen Radar Sector Eifel*
### Military approach positions
Both military airports below the EIF sector, ETAD and ETSB, have their own approach positions. While these positions are online, they are delegated parts of EIF's airspace.
##### Spangdahlem GCA (TADA)
[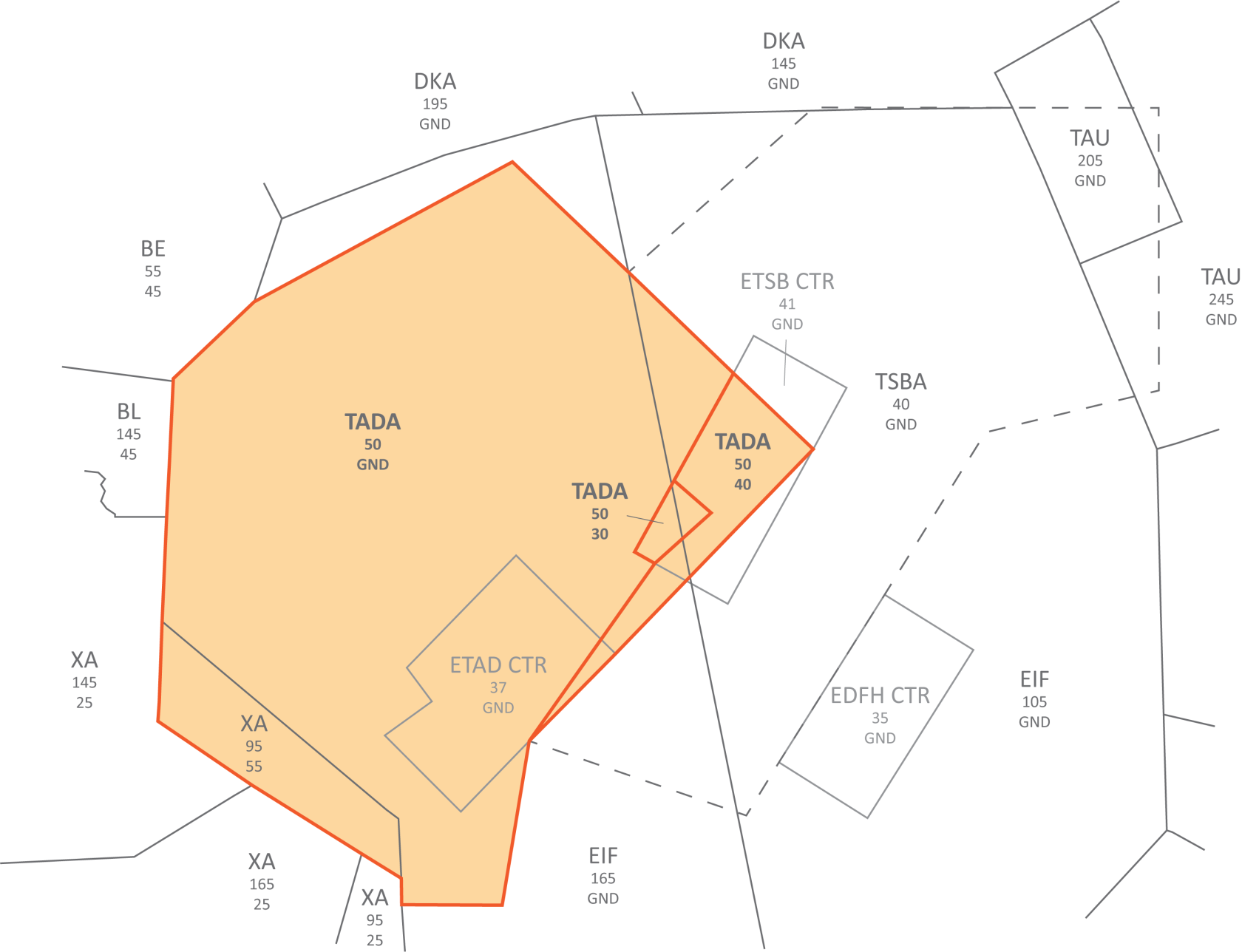](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etad.png)
Spangdahlem GCA covers about half of the Western part of the EIF sector up to 5000ft. Langen Radar is responsible for maintaining full vertical separation to the sector, i.e. **EIF may not clear traffic above the sector below 6000ft**.
ETAD inbounds shall always be coordinated individually, but **usually a DCT to SPA at 5000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
If any position at ETAD is staffed, they will issue **the last point of the cleared SID as the clearance limit**. Thus, ETAD outbounds shall receive an enroute clearance for the rest of their route by Langen Radar.
> **RCH15**: Langen Radar, Reach 15, 3900ft, climbing 5000ft. **Langen Radar**: Reach 15, Langen Radar, identified, climb FL160, cleared to Virginia Beach via flight planned route.
> **RCH15**: Reach 15, climbing FL160, cleared to Virginia Beach via flight planned route.
If a departing aircraft requests or requires an omnidirectional departure, Spangdahlem GCA will coordinate this with EIF.
##### Büchel Radar (TSBA)
[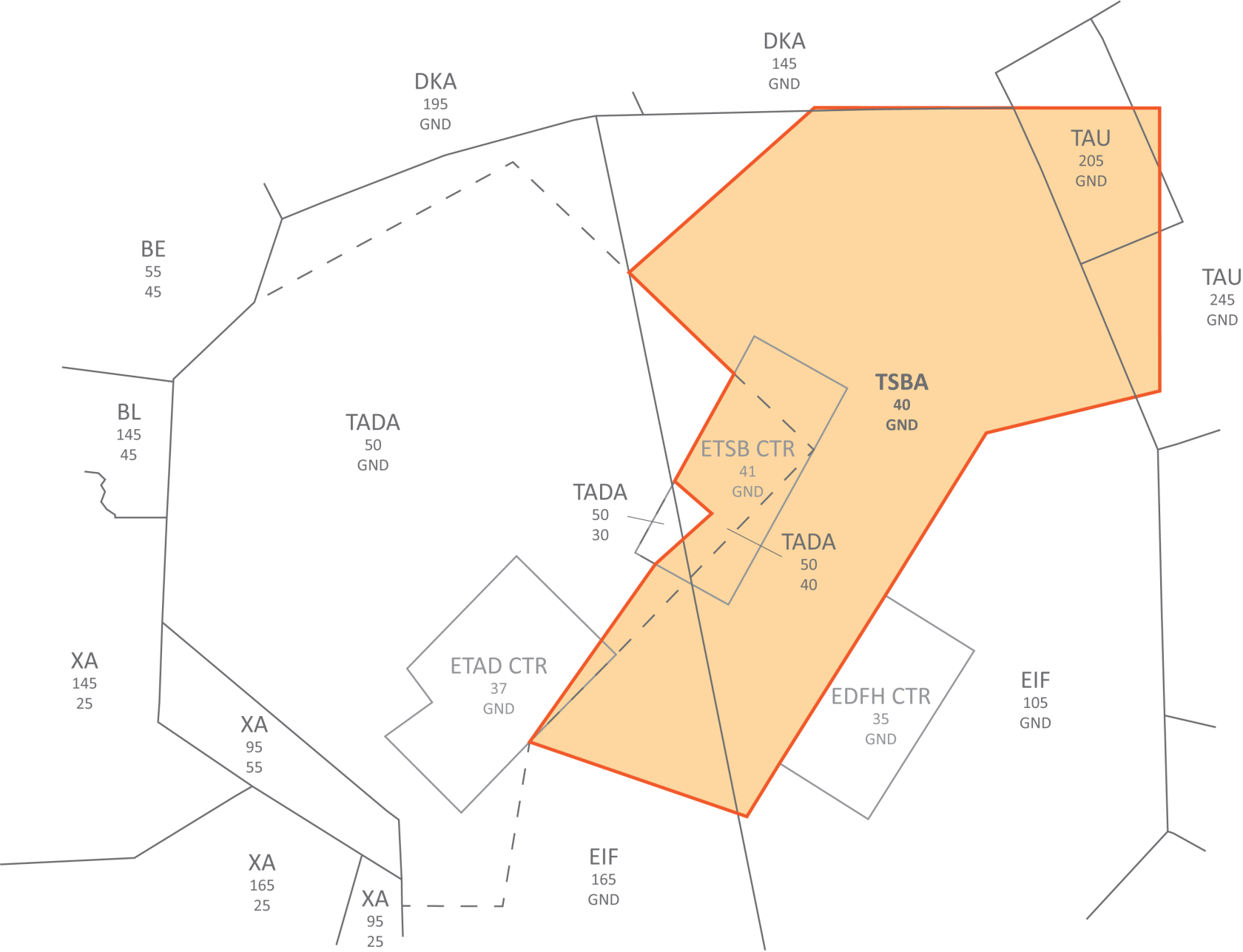](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etsb.png)
Büchel Radar covers about half of the Eastern part of the EIF sector up to 4000ft. Langen Radar is responsible for maintaining full vertical separation to the sector, i.e. **EIF may not clear traffic above the sector below 5000ft**.
ETSB inbounds shall always be coordinated individually, but **usually a DCT to BUE at 4000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
ETSB outbounds shall always be coordinated individually, but **usually a DCT to the first waypoint is the best solution**.
### Handoff
**Departing Traffic:** Outbounds via NVO, ABSIX, ULKIG, OLIVI and GEBDA is handed over to CTR climbing FL100. Outbounds via RUDOT, IDARO with RFL higher than FL160 will be handed over climbing to FL160.
**Arriving traffic:** Inbounds via ROLIS (on arrival or via Z658 EMGOD) and RASVO (Q760) will enter the sector at FL100. Traffic from Brussels via ARCHKY L607 ROPUV is handed over at FL170 and should cross the border at FL150 or below. OLGIL, OLIVI inbounds are already cleared for the transition by Center. Traffic via OLIVI and will be handed over at FL110, traffic via OLGIL at FL140.
Inbounds to ETAD from Brussels via BETEX Z110 BITBU are handed over FL110 at BETEX.
**Crossing Traffic:** Inbounds to ELLX will enter the sector descending to FL110 and need to be handed over at FL90 or lower if coordinated otherwise. They also have to be cleared for the appropriate arrival.
# EDFM - Mannheim City Airport
# Overview
**Mannheim City is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. The Neckar Low sector (APP) can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
### ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| AFM
| EDFM\_ATIS
| 132.415
| --
| --
|
| **Tower**
| FMT
| EDFM\_TWR
| 129.780
| --
| unrestricted: [EDFM CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=63 "Unrestricted courses (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Neckar Low sector**
| NKRL
| EDFM\_NKL\_APP
| 129.355
| --
| unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/F9cyGYKZQnag2y9)*click on the image to open the printable Quicksheet*
# Tower
The Mannheim CTR(HX) is a class D airspace from ground to 2000 ft MSL.
[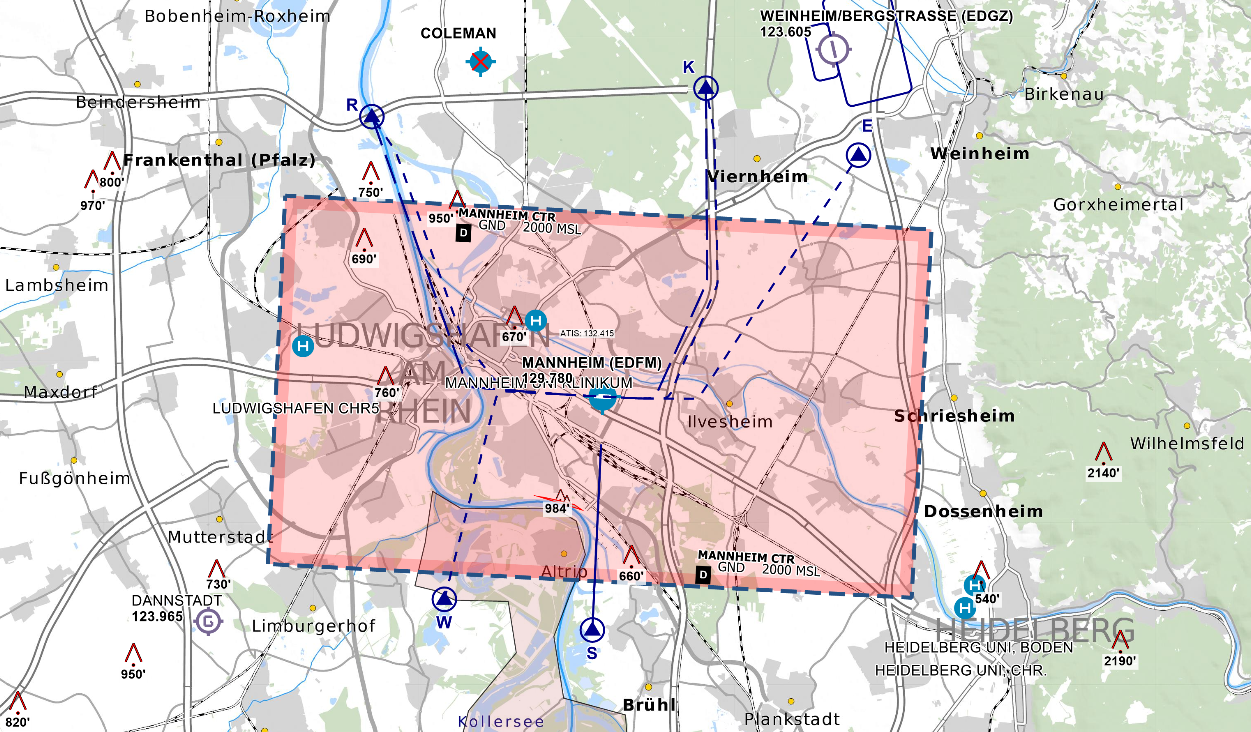](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/FqUgrafik.png)*CTR Mannheim/City - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
### Authorized aircraft
Due to the small size of Mannheim/City, there are restrictions on which aircraft types can be flown at the airport:
- Airplanes up to [10.000 kg MTOW](https://contentzone.eurocontrol.int/aircraftperformance/default.aspx "Eurocontrol Performance Database")
- Donier 328-100 (**D328**)
- Dash 8-100 and 300 (**DH8A, DH8C**)
- ATR 42-500 (**AT45**)
- Falcon 50, 2000, 900 EX/DX (**FA50, F2TH, F900**)
- Challenger 300 (**CL30**)
- Cessna 680 (**C680**)
- Embraer Legacy 450, 500 (**E450, E500**)
Pilots flying unsuitably large aircraft (e.g. A320/B737) should be reminded about the small size of the airport and its short runway length. However, pilots flying aircraft that are not part of the above list, but **similar in size and performance** (e.g. C700) can usually still be accepted in the VATSIM environment.
Additionally, the **grass runway** can only accommodate aircraft up to [5.700 kg MTOW](https://contentzone.eurocontrol.int/aircraftperformance/default.aspx "Eurocontrol Performance Database") (all German aircraft registrations except D-Axxx, D-Bxxx, and D-Cxxx).
### Parking Positions
Preferred parking for Airlines are the two taxi-out positions in front of the Terminal. Other aircraft can be parked either at the positions 1-5, the hangars or at the grass area. For refueling the gas station east of taxiway A is used.
### IFR Procedures
Instrument approach procedures are only available for runway 27: a localizer approach and an RNP approach. Due to its lower minima and higher lateral precision, the localizer approach is preferred.
##### Departure Spacing
Two aircraft on the same SID require a minimum spacing of 5 NM.
##### Visual circling
Since the instrument approach procedures are only available for runway 27, IFR arrivals need to fly a **visual circling maneuver** during 09 operations. This maneuver is **only allowed South of the airport**.
To **ensure separation between inbounds and outbounds**, a takeoff clearance for a 09 departure can only be issued once the inbound has passed abeam the threshold of runway 27.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-05/edfm-visual-circling.jpg)
To **remind pilots that they need to fly a visual circling**, they should be asked to report breaking off or when reaching the right downwind.
> **ATC**: JMP902, report breaking off.
>
> **ATC**: JMP902, report right downwind.
In the event of a go around, the pilot is expected to rejoin the right downwind and from there join the published missed approach procedure. However, since many pilots on VATSIM will be unfamiliar with the details of visual circling procedures, they should be told what to do:
> **ATC**: JMP902, join right downwind runway 09.
And once the aircraft is on right downwind runway 09:
> **ATC**: JMP902, follow the published missed approach procedure.
### VFR Procedures
##### Traffic circuits
Due to noise abatement, the **Southern traffic circuit should be used whenever possible**. The Northern traffic circuit should only be used if the Southern one is unavailable. Additionally, VFR aircraft are expected to avoid overflying the cities of Mannheim and Ludwigshafen as well as the surrounding villages.
##### Reporting point
| **Reporting point**
| **Use**
| **Location**
|
| **R**
| **Exit** to the NW *(27 ops)*
**Entry** from the NW *(09 ops)*
| highway A6 bridge over the Rhine river
|
| **K**
| **Exit** to the N *(09 ops)*
**Entry** from the N *(27 ops)*
| highway intersection A6 and A67
|
| **E**
| **Exit** to the NE *(09 ops)*
| highway intersection A5 and A659
|
| **W**
| **Exit** to the SW *(27 ops)*
| between lakes North of Waldsee
|
| **S**
| **Exit** to the S
**Entry** from the S *(27 ops)*
| between Brühl and Rhine river |
### Auto-Handoff
Mannheim utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach/center controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP/CTR **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# Arrival Sector Neckar Low
The sector Neckar Low (NKRL) is **responsible for all Mannheim/City (EDFM) and Speyer (EDRY) departures and arrivals** from GND up to FL55/FL75/FL115. Usually, this sector is combined with other Langen sectors.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-09/edfm-nkrl.png)
*Sector Neckar Low*
### Approaches
#### Mannheim
Mannheim/City only has instrument approaches for runway 27. Both the LOC and RNP approach have a **non-standard 3.7° glide path**.
During 09 operations, arrivals need to fly a **visual circling procedure** south of the airport. The clearance for the visual circling has to be **part of the approach clearance**.
> **ATC**: JMP902, cleared localizer approach runway 27, followed by circling runway 09.
Alternatively, **upon coordination with Tower**, pilots can be cleared for a straight-in visual approach into runway 09.
#### Speyer
Speyer has RNP approaches for both operating directions. Generally, the **RNP Z approach shall be used**; the **RNP Y is available on pilot request** for pilots wanting to utilize LPV minima. Apart from the minima, the approaches are identical.
**Speyer does not have instrument departure procedures**; all IFR flights from Speyer must depart VFR and pick up IFR once in the air.
# EDLN - Mönchengladbach Airport
# Overview
Mönchengladbach is a small airport in Western Germany. Traffic mostly consists of general aviation VFR flights as well as private jets and business charters. The maintenance center located in the Northern part of the airport also attracts maintenance flights for various smaller aircraft.
**Mönchengladbach is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. GND and TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. Further information on the radar stations can be found in the [EDDL SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/entwurfe/chapter/eddl-old "EDDL SOP (VATGER Knowledgebase)").
### Aircraft size
Mönchengladbach is **too small for most passenger aircraft**, even though there are no specific type restrictions.
Pilots flying unsuitably large aircraft (e.g. A320, B737, ...) **should be reminded of the small size of the airport and its short runway length** but may not be denied service if they decide to continue the flight as planned regardless.
### Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ALN
| EDLN\_ATIS
| 121.815
| fictional frequency, real ATIS on MHV VOR
| --
|
| **Ground**
| LNG
| EDLN\_GND
| 121.930
| --
| unrestricted: [EDLN CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=81 "Course EDLN Tower (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Tower**
| LNT
| EDLN\_TWR
| 120.455
| --
| unrestricted: [EDLN CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=81 "Course EDLN Tower (VATGER moodle)")
|
| Arrival EDDL
(Feeder)
| DLAT
| EDDL\_F\_APP
| 128.655
| airborne frequency during 13 operations at EDLN and 05 operations at EDDL if DLAT is staffed
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/division/endorsements/tier-1 "Tier 1 Endorsement List (VATEUD Core)")
|
| Approach EDDL
| DLA
| EDDL\_APP
| 128.555
| airborne frequency during 05 operations at EDDL if DLA or PADH is staffed except when DLAT is the applicable airborne frequency
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/division/endorsements/tier-1 "Tier 1 Endorsement List (VATEUD Core)") |
| Departure EDDL
| DLD
| EDDL\_APP
| 121.355
| airborne frequency during 23 operations at EDDL if DLA or PADH is staffed
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/division/endorsements/tier-1 "Tier 1 Endorsement List (VATEUD Core)") |
### Quickview
[](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/kbk2k9aT6nZDNMe "EDLN Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Ground
Mönchengladbach Ground is responsible for all enroute and startup clearances at the airport as well as ground movements within the Ground AoR.
### Enroute clearance
##### SID restrictions
##### Airborne frequency
Mönchengladbach utilizes an **auto-handoff for all IFR departures** whereby pilots are required to switch to the airborne frequency immediately when airborne. As the airborne frequency changes with the operating direction and staffing at EDDL, it **shall be given together with the enroute clearance**. The possible airborne frequencies are 121.355 (DLD), 128.555 (DLA), and 128.655 (DLAT). An explanation of when which frequency is in use can be found in the [overview](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/overview-yAy "EDLN SOP Overview").
Phraseology example
> **ATC**: Sylt Air 730G, cleared to Palma de Mallorca, MODRU9M departure, flight planned route, climb to altitude 2000ft, airborne frequency is Langen Radar on 128.555, squawk 2014.
> **Pilot**: Cleared to Palma de Mallorca, MODRU9M departure, flight planned route, climb to altitude 2000ft, airborne frequency Langen Radar on 128.555, squawk 2014, Sylt Air 730G.
Phraseology example
> **ATC**: Sylt Air 730G, revised airborne frequency is Düsseldorf Arrival on 128.655, wind 090 degrees 3 knots, runway 13, cleared for takeoff.
> **Pilot**: Revised airborne frequency Düsseldorf Arrival on 128.655, runway 13, cleared for takeoff, Sylt Air 730G.
| **Reporting point**
| **Use**
| **Location**
|
| **G**
| **Exit** to the SW
*(13 ops)*
**Entry** from the SW
*(31 ops)*
| industrial district Giesenkirchen-Nord
|
| **K1**
| **Exit** to the N
*(31 ops)*
**Entry** from the N
*(13 ops)*
| quarry lake Kempen
|
| **K2** | **Exit** to the N
*(31 ops)* **Entry** from the N
*(13 ops)* | roundabout NW of St. Tönis |
| **M** | **Exit** to the N
*(13 ops)* **Entry** from the N
*(31 ops)* | DHL distribution center Krefeld |
| **E** | **Entry** from the SW
*(13 ops)*
| highway A61 exit Wickrath
|
| **W** | **Exit & Entry** from the West
| highway intersection A52/A61
|
##### Recommended traffic circuit
Mönchengladbach has a recommended traffic circuit in the North and the South. These circuits are not published in the AIP and **pilots should thus not be expected to follow them**. Additionally, ATC instructions always overrule the recommended traffic circuit.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/edln-circuits.png)
*the recommended circuit is at 1200ft AMSL in the Northeast and 1100ft AMSL in the Southwest; the downwind for both circuits is not perfectly parallel to the runway*
# EDLP - Paderborn/Lippstadt Airport
# Overview
Traffic at Paderborn/Lippstadt is usually characterized by GA (VFR) traffic and holiday flights, mixed with some scheduled flights.
**Paderborn/Lippstadt is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. GND and TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. The Paderborn Low sector (APP) can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher.
**Training:** Controllers with an S2 rating can staff APP during their training (active EDLP\_PAL\_APP solo endorsement required).
### Paderborn/Lippstadt ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ALP
| EDLP\_ATIS
| 125.730
| --
| --
|
| **Ground**
| LPG
| EDLP\_GND
| 121.930
| --
| unrestricted: [EDLP CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=75 "Unrestricted courses (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Tower**
| LPT
| EDLP\_TWR
| 133.380
| --
| unrestricted: [EDLP CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=75 "Unrestricted courses (VATGER moodle)") |
| **Paderborn Low sector**
| PADL
| EDLP\_PAL\_APP
| 125.225
| airborne frequency if PADL, HMM, or PADH is staffed
| unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[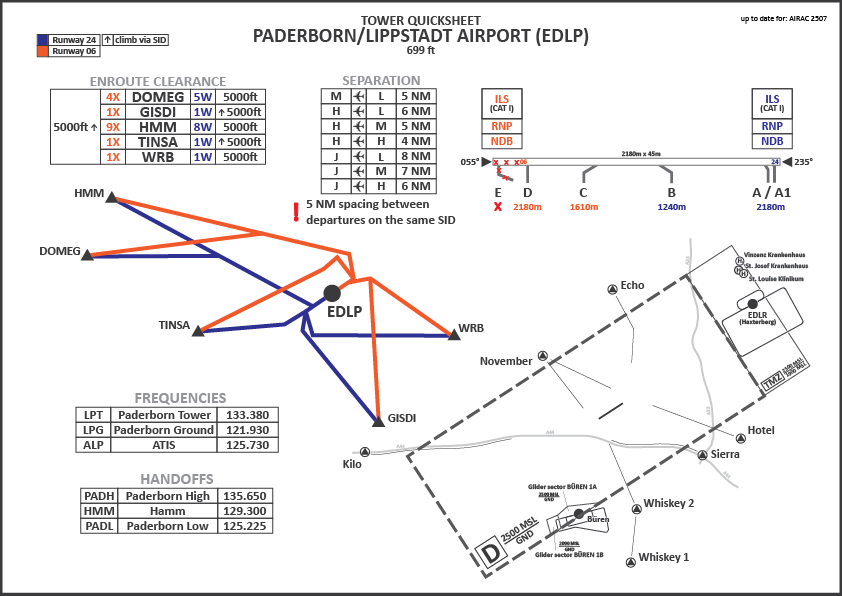](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/EDQytoTcR5zWHqZ "EDLP Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Ground
Paderborn Ground is responsible for startup and enroute clearance and all aircraft movements at the airport.
### Departure Routes
Paderborn has a quite simple structure for departure routes. There are no specific restrictions to keep in mind, except some climb restrictions, which make the "Climb via SID 5.000ft" phrase, with the initial climb in the IFR clearance necessary. The affected SIDs, are listed below and marked as **\*↑**:
| **SID**
| **RWY 06** | **RWY 24** |
|---|
| **DOMEG** | 4X\*↑ | 5W |
| **GISDI** | 1X\*↑ | 1W\*↑ |
| **HMM**
*Hamm*
| 9X\*↑ | 8W |
| **TINSA** | 1X\*↑ | 1W\*↑ |
| **WRB**
*Warburg*
| 1X\*↑ | 1W |
**Vectored Departures:** If pilots are unable to fly a standard instrument departure (even an older version of the current SID), a vectored departure can be coordinated between Ground and Radar.
Primary **runway heading** and an initial climb of **5000ft** should be used. Other coordinations are always possible.
### Parking Positions
Positions 4 - 6 are terminal positions and are prefered for jets. Stand 2A can be used for aircraft category heavy.
Only stands 1A, 1B and 7A - 7C are taxi out positions but are rarely used. All other positions require a pushback.
The **GAT** are is located at the western part of the airport.
### Taxiways
Taxiway **F** can only be used by light type aircraft.
Taxiways **A** and **A1** can be used as bypass area if light type aircraft are not ready for departure or require a runup.
# Tower
Paderborn Tower is responsible for all aircraft within the control zone and at the active runway.
**Runway in use:** There is no prefered operation direction at Paderborn.
**Approaches:** For both runways ILS (CAT I), RNP and NDB approaches are available.
### Control Zone
The control zone of Paderborn reaches up to 2500 ft AMSL.
*[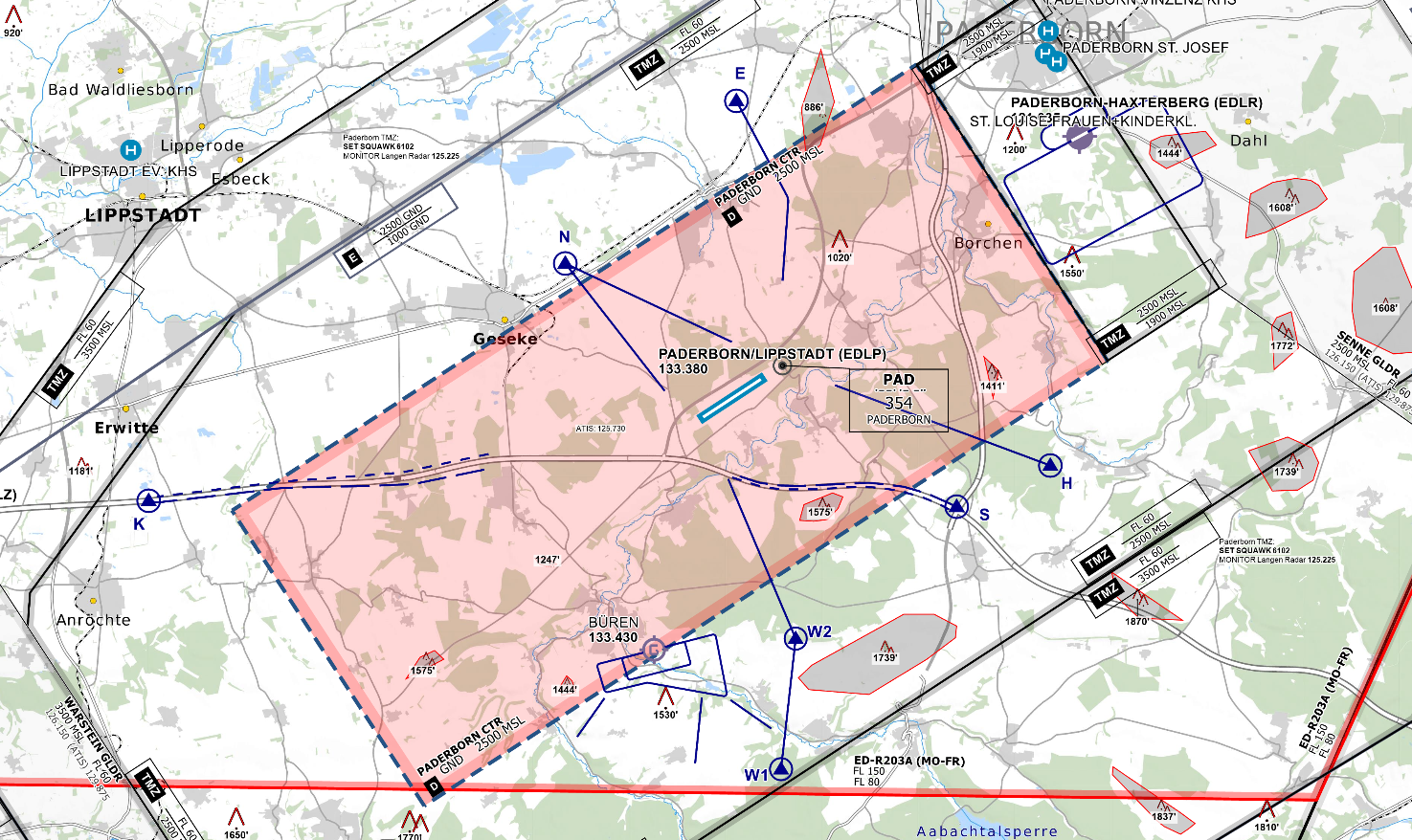](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-12/padctr.png)
Paderborn/Lippstadt Control Zone (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
VFR traffic entering or leaving the CTR via **SIERRA** need to cross the reporting point between 2200 and 2500 ft MSL.
**TMZ:** Outside the control zone is a TMZ where all VFR aircraft have to set transponder code 6102.
**Paderborn-Haxterberg:** The airfield Paderborn-Haxterberg EDLR is located north-east close to the border of the CTR. Traffic within the traffic pattern have to stay clear of the control zone and are independant.
**Helicopter:** As there are no helipads available at Paderborn, all departures and arrivals of helicopters have to take place at the active runway, followed/preceeded by airtaxi.
### Auto-Handoff
Paderborn utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach/center controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP/CTR **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# Arrival - Sector Paderborn Low
Paderborn Low is a small sector and most of the time this sector and sector Hamm are staffed by the same controller. Main duties for PADL is the arriving and departing traffic out of Dortmund EDLW and Paderborn/Lippstadt EDLP, next to some VFR or training flights. Except some inbounds to Cologne there is usually no transferring traffic within this sector.
[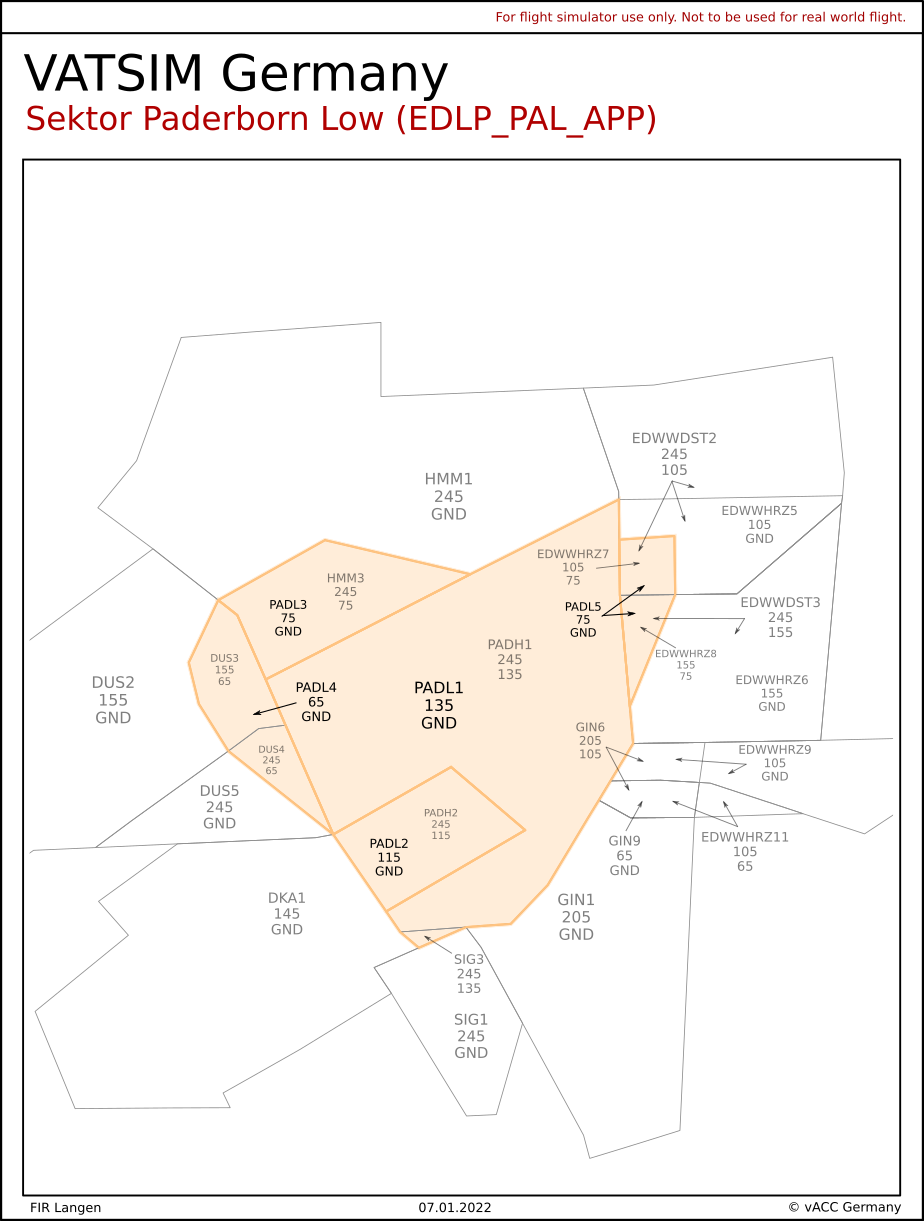](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2023-02/padl.png)
*Langen Sector Paderborn Low PADL*
### Dortmund Area
The Dortmund Area is located west of Dortmund airport. It is designed for inbound traffic on runway 06 or outbound traffic of runway 24 at Dortmund airport. It reaches from Ground up to FL65. Above this level Düsseldorf arrival is responsible. All in- and outbounds to Dortmund always need to stay below FL60 if not released by Düsseldorf. All Düsseldorf inbound on the other hand always have to stay above FL70 if not coordinated otherwise.
### Traffic Flows
There are no major traffic flows expect departing and arriving traffic for Dortmund and Paderborn and some inbounds to Cologne.
**Paderborn High PADH:** The sector above Paderborn Low is Paderborn High (PADH) that is usually staffed by a different controller. PADH is primary responsible for presequencing inbounds to Düsseldorf and Cologne via ADEMI - DOMUX and KOPAG.
**In- and Outbounds Düsseldorf:** Inbounds to Düsseldorf are released by PADL to DLA for descend to FL100 and turns. Lower levels always have to be coordinated between PADL and DLA! Dortmund outbounds via GMH will cross below.
Outbounds Düsseldorf via **GMH Z841** with RFL **below FL130** will enter the sector PADL for a short time. Due to the airway crossing the lowered part of Paderborn High, **coordination** with PADH is always required for all flights above FL90!
**Inbound Cologne:** Inbounds to Cologne will enter the sector Paderborn Low descending inbound to **ERNEP**. PADL will send this traffic descending to Köln Arrival. Inbounds via **KOPAG** usually stay clear of PADL. If runway 24 is used for landings traffic might be handed over from PADH to PADL at FL120 for further descend to **FL80** at KOPAG. Coordination between DKA, PADL and PADH is always required! It's also possible to release this traffic for PADH without handoff to PADL.
### Handoff Levels
All levels for inbound, outbound and transferring traffic for sectors HMM and PADL are available at the [**Quicksheet**](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/beHDp2W3RET57c7 "HMM/PADL Quicksheet"). All levels that are not listed need to be coordinated individually!
### VFR Traffic
In real life the sector is known for a lot of VFR and training flights due to many flight schools located in this area.
**FIS:** All VFR traffic that are provided with Flight Information Service should get Squawk 7742 (FDL).
**TMZ:** VFR traffic within the Paderborn and Dortmund TMZ is expected to set squawk 6102 (TW) and maintain listening watch on 125.225.
### Restricted Area
There are several ED-Rs within the eastern part of sectors PADL and HMM. The military **ED-R 203A** "Münsterland" reaches from **FL80 up to FL150**. Above this is the **ED-R 203B** between **FL150 to FL200**. Both ED-Rs are regular active. Additionally ED-R 162 "Lanta Paderborn" is located within the mentioned ED-Rs reaching from 3.500 ft AMSL up to FL125. All restricted areas are automatically activated in Euroscope according the real world airspace use plan. When active, all flights should stay outside the active ED-Rs.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/edgg-padl-hmm-edr203.png)*ED-R 203A from FL80 to FL150 (red area) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
### Holdings
As there are just two small airports within the sector and almost no transit traffic, holdings are rarely used. If they are required or for training purpose there are published holdings available at **PAD** NDB (055° R | 3000ft - FL140) and **ADEMI** (284° L | FL60 - FL240).
# EDLV - Niederrhein Airport
# Overview
Niederrhein is a small airport at Germany's border with the Netherlands. It hosts primarily Ryanair flights to and from various destinations; additionally, due to its history as a military air base, it still has some basic military infrastructure and thus sees occasional military flights.
**Niederrhein is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. Further information on the radar stations can be found in the [EDDL SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/entwurfe/chapter/eddl-old "EDDL SOP (VATGER Knowledgebase)").
### Niederrhein ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ALV
| EDLV\_ATIS
| 124.455
| --
| --
|
| **Tower**
| LVT
| EDLV\_TWR
| 129.405
| --
| unrestricted: [EDLV CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=82 "Course EDLV Tower (VATGER moodle)")
|
| Bottrop sector
| BOT
| EDDL\_BOT\_APP
| 119.110
| airborne frequency if BOT, DLD, DLA, or PADH is staffed
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/division/endorsements/tier-1 "Tier 1 Endorsement List (VATEUD Core)") |
### Quickview
[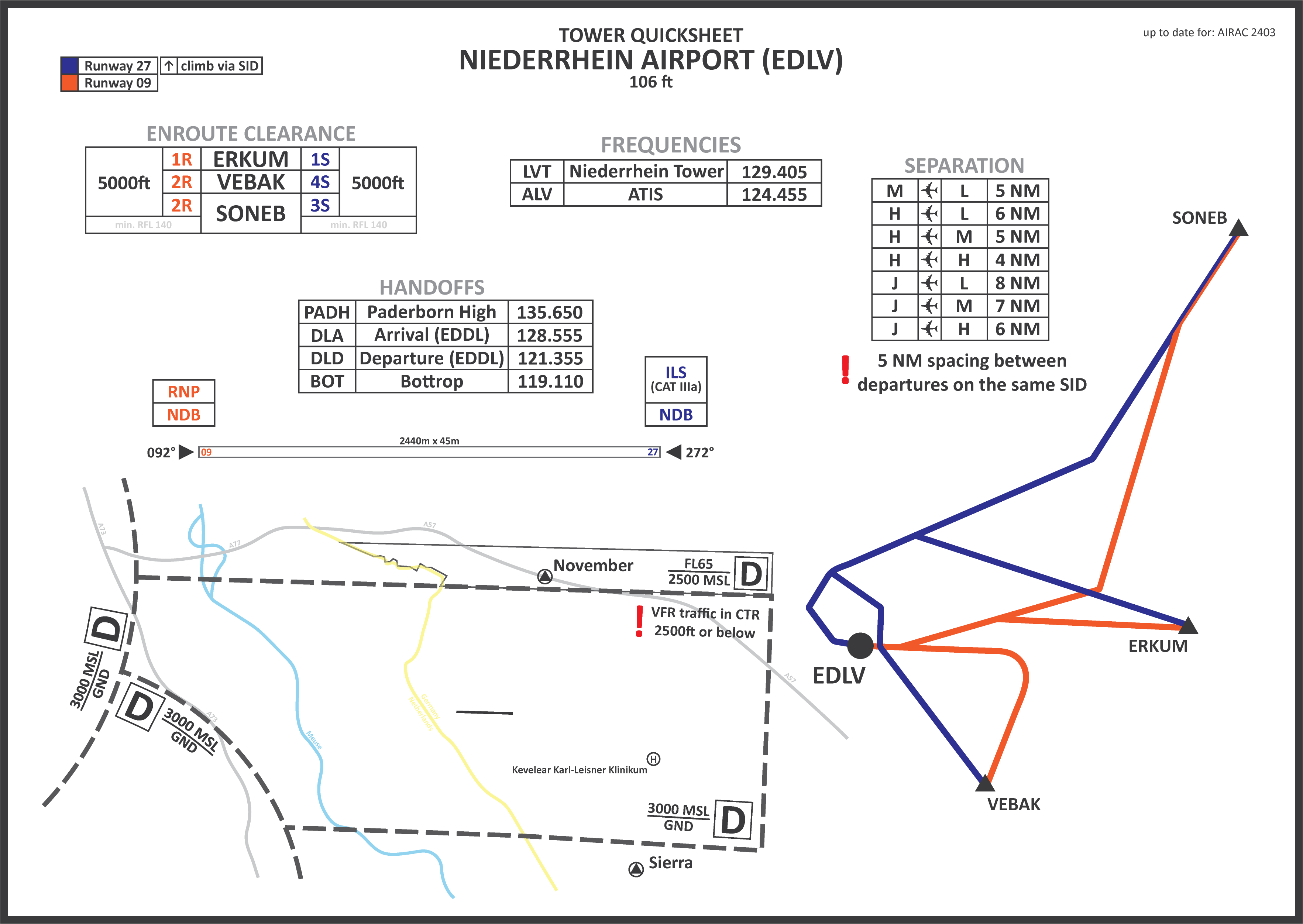](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/xoJia9xnsiQx5pk "EDLV Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Tower
Niederrhein/Weeze Airport is located on German territory, directly on the border with the Netherlands. To the west, the control zones of the Dutch airports De Peel (EHDP) and Volkel (EHVK) border directly on Niederrhein.
The tower is responsible for all traffic at the airport and within the control zone, including startup and enroute clearances as well as all ground movements.
### Enroute clearance
##### SID restrictions
### Airspace
##### Overview
[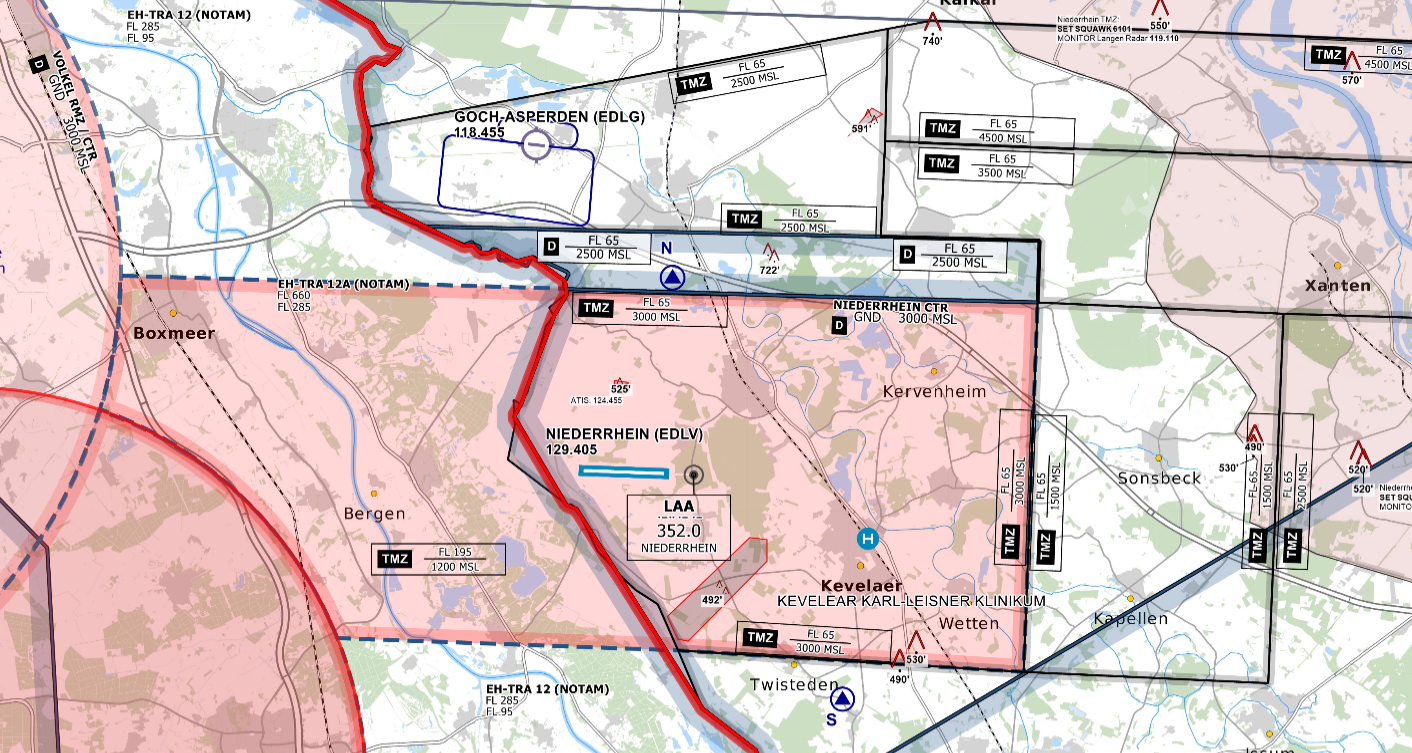](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/edlv-ctr.png)*Niederrhein CTR - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
##### CTR
The Western half of the airport's CTR is over Dutch territory and directly borders the CTRs of the Dutch military airfields Volkel and De Peel.
VFR traffic can only enter and exit the CTR over German territory, primarily via reporting points N and S. The maximum altitude for entering and exiting the CTR is 2500ft AMSL. Direct transitions between the CTRs of Niederrhein and Volkel or De Peel are possible after coordination with the responsible Dutch controller.
##### TMZ
The CTR is surrounded by a TMZ in which VFR pilots must squawk 6101 and monitor the frequency of the responsible radar controller.
### Helicopters
All helicopters must take off or land on the active runway at the airport. This is followed or preceded by hovering to/from the target position at the airport.
### Direction of Operation
Operating direction 27 is preferred up to a tailwind component of 5 KT. In addition, this is the only runway for which an ILS approach is available.
##### Opposite departures
In close consultation with the responsible radar controller, departures against the current operating direction are also possible in Niederrhein. This procedure is **mainly used during 27 operations with a slight tailwind**.
### Taxiway restrictions
Taxiways **B** and **C** may only be used by aircraft up to **max. code C** (B739/A321) after landing to leave the runway. **No intersection departures** are permitted in Niederrhein!
### Parking positions
All parking positions in Niederrhein are designed for **max. code C** **aircraft** (B739/A321). All larger aircraft block both the taxiway behind the position and the neighbouring positions. If, in exceptional cases, an aircraft larger than code C should land, the taxiway between positions 1 to 6 can be used for parking. Until then, only positions 7 to 9 can be used for other traffic! Pushbacks are required at all parking positions.
GA Terminals 1 and 2 can be used for **general aviation** aircraft.
### Auto-handoff
Weeze utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach/center controller**. Make sure to set the correct airborne frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP/CTR **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# EDLW - Dortmund Airport
# Overview
Traffic at Dortmund is usually characterized by low cost and VFR flights, mixed with some holiday destinations. One specialty at the airport are the nose out parking positions where arriving traffic is pushed backwards into the stand.
**Dortmund is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. GND and TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**. Further information on the Paderborn Low sector can be found in the [EDLP SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/chapter/edlp-paderbornlippstadt-airport "EDLP SOP (VATGER Knowledgebase)").
### Dortmund ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ALW
| EDLW\_ATIS
| 125.130
| --
| --
|
| **Ground**
| LWG
| EDLW\_GND
| 121.830
| --
| unrestricted: [EDLW CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=55 "Unrestricted courses (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Tower**
| LWT
| EDLW\_TWR
| 134.180
| --
| unrestricted: [EDLW CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=55 "Unrestricted courses (VATGER moodle)") |
| **Paderborn Low sector**
| PADL
| EDLP\_PAL\_APP
| 125.225
| airborne frequency if PADL, HMM, or PADH is staffed
| unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[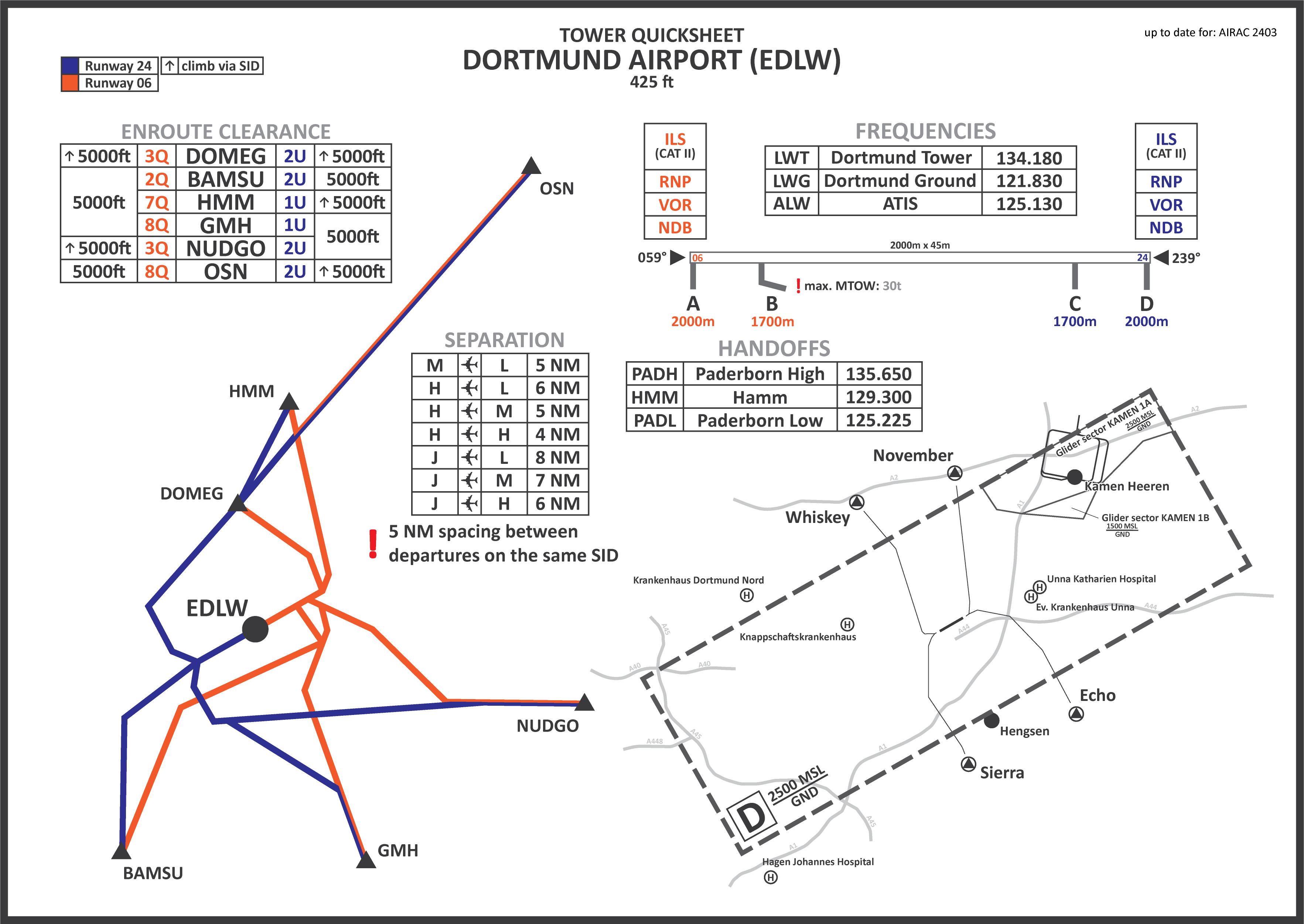](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/C8CqBNRDSifNDSt "EDLW Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Ground
Dortmund Ground is responsible for startup and enroute clearance and all aircraft movements at the airport.
### Departure Routes
Dortmund has a quiet simple structure for departure routes. There are no specific restrictions to keep in mind, except some climb restrictions, which make the "Climb via SID 5.000ft" phrase, with the initial climb in the IFR clearance necessary. The affected SIDs, are listed below and marked as **\*↑**:
| **SID** | **Runway** |
|
| **06** | **24** |
| **BAMSU** | **2Q** | **2U** |
| **DOMEG** | **3Q\*↑** | **2U\*↑** |
| **OSN** | **8Q** | **2U\*↑** |
| **GMH** | **8Q** | **1U** |
| **NUDGO** | **3Q\*↑** | **2U** |
| **HMM** | **7Q** | **1U\*↑** |
**Vectored Departures:** In the event that a pilot does not have a departure route available for Dortmund (also not an older route), a vectored departure can be offered to the pilot in close coordination with the responsible radar controller. Especially in 24 operations, it is imperative to ensure that the aircraft does not enter the Düsseldorf Arrival sector.
The following instructions shall be used:
> **RWY 06**: EWG123, cleared to Berlin, on RWY-Heading climb 5.000ft.....
>
> **RWY 24**: EWG123, cleared to Berlin, on RWY-Heading climb 5.000ft, when passing 3.000ft, turn right heading 030......
### Parking Positions
Stands 0 - 2 are apron positions with bus boarding/deboarding. Only stands 3 and 4 are equiped with a jetway that is able to connect to the aircraft.
**Nose In Positions:** Positions 5 - 12 can be used nose in (towards the terminal) or [nose out](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GxxuduCQoLE "Dortmund Airport - Nose Out Stand") (towards the taxiway). For nose in position there is no difference to any other positions, the aircraft can taxi in the normal way and a pushback is requrired to leave the stand. That is the **recommended procedure** as pilots might not be able to push in the gate.
**Nose Out Positions:** On pilots request these positions can be used nose out, and the aircraft has to taxi from A coming on the yellow line in front of the stand. The aircraft has to hold abeam the next stand (hold abeam stand 6 to be pushed into stand 5). After shutting down the engines the aircraft is then pushed into the stand with the tail close to the terminal building. All of these stands are walk in positions for the passengers, there is no jetway to connect to the aircraft.
> EWG123, taxi via A and the yellow line, hold abeam stand 6, expect push in procedure for stand 5.
To leave a nose out stand there is no pushback required and the aircraft can leave it with own power. If you are unsure of the facing before pushback you may ask the pilot.
Nose Out parking is only available for X-Plane pilots and with MSFS Pushback tools (Toolbar Pushback and the PMDG 737 tug)! GSX will not support the push into the stand.
The **GAT** is located at the west side of the airport.
### Taxiway Restrictions
Taxiway **B** can only be used for aircraft with a MTOW **less than 30 tons** (e.g. DH8D).
Most of the landings on runway 24 has to vacate via taxiway A. On Vatsim it might be helpful to inform the pilot about that. Take in mind that it will take longer to vacate the runway at the end and the spacing for outbound traffic might be adjusted if necessary.
# Tower
Dortmund Tower is responsible for all aircraft within the control zone and at the active runway.
**Approaches:** For both runways ILS (CAT II), RNP, VOR and NDB approaches are available.
### Control Zone
The control zone of Dortmund reaches up to 2500 ft AMSL.
| **24 Operations**
| **06 Operations**
|
| **VFR Entry:** N and E
**VFR Exit:** W and S
| **VFR Entry:** W and S
**VFR Exit:** N and E
|
*[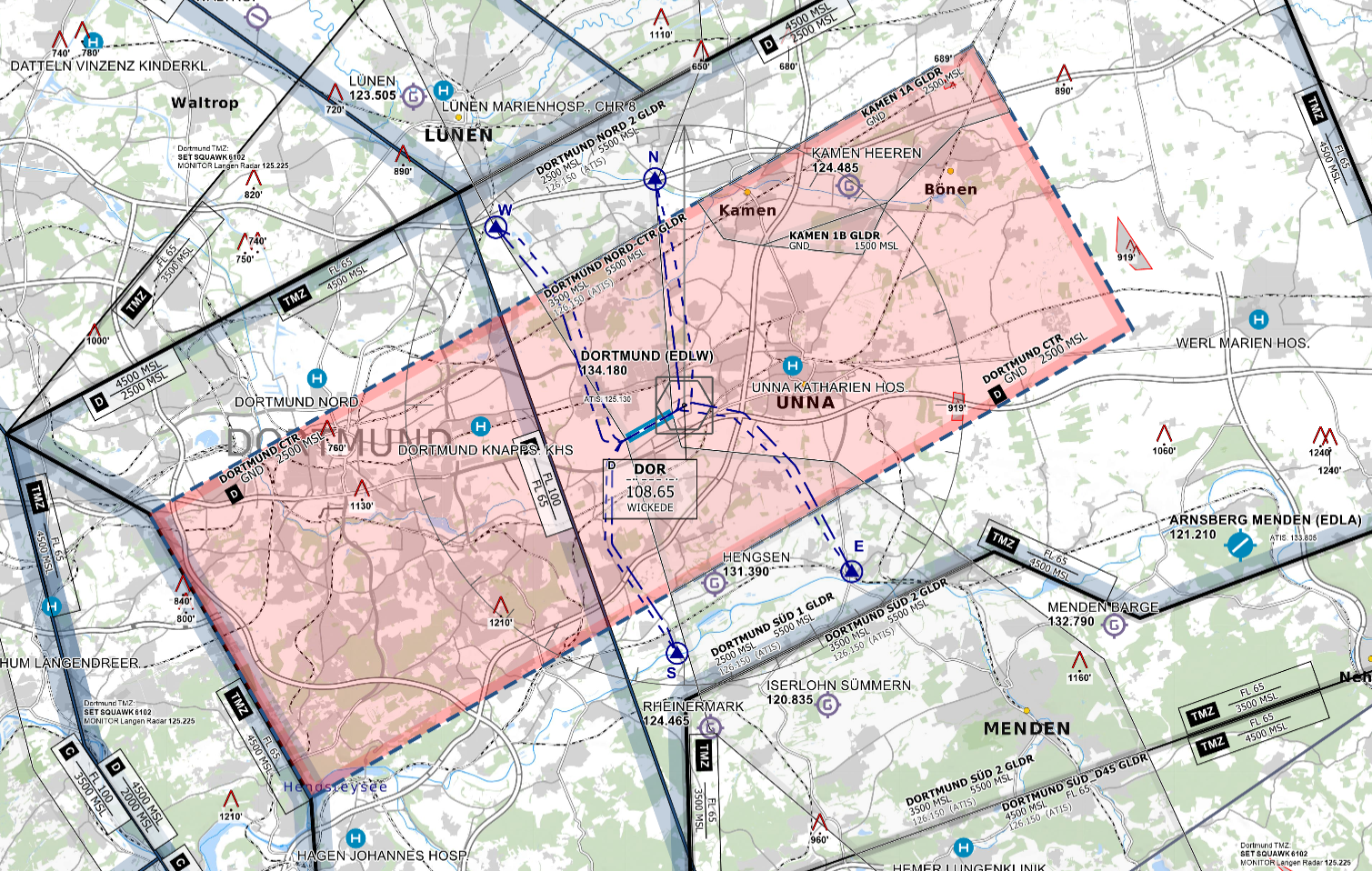](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/edlw-ctr.png) Dortmund Control Zone (D-CTR) - © [openflightmaps.org](https://www.openflightmaps.org/)*
**TMZ:** Outside the control zone is a TMZ where all VFR aircraft must set transponder code 6102.
**Helicopter:** The Helipad west of the GAT can be used for all helicopter landings and departures.
### Direction of Operation
Operating direction 24 is preferred up to a tailwind component of 5 KT.
### Auto Handoff
Dortmund utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach/center controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP/CTR **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# EDSB - Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden
# Overview
**Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. All positions can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**.
### Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ASB
| EDSB\_ATIS
| 121.280
| --
| --
|
| **Ground**
| SBG
| EDSB\_GND
| 121.830
| --
| unrestricted: [EDSB CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=66 "Unrestricted courses (VATGER moodle)")
|
| **Tower**
| SBT
| EDSB\_TWR
| 134.105
| --
| unrestricted: [EDSB CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=66 "Unrestricted courses (VATGER moodle)") |
All aerodrome stations at Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden use the **callsign "Baden"**, e.g. "Baden Tower".
### Quickview
[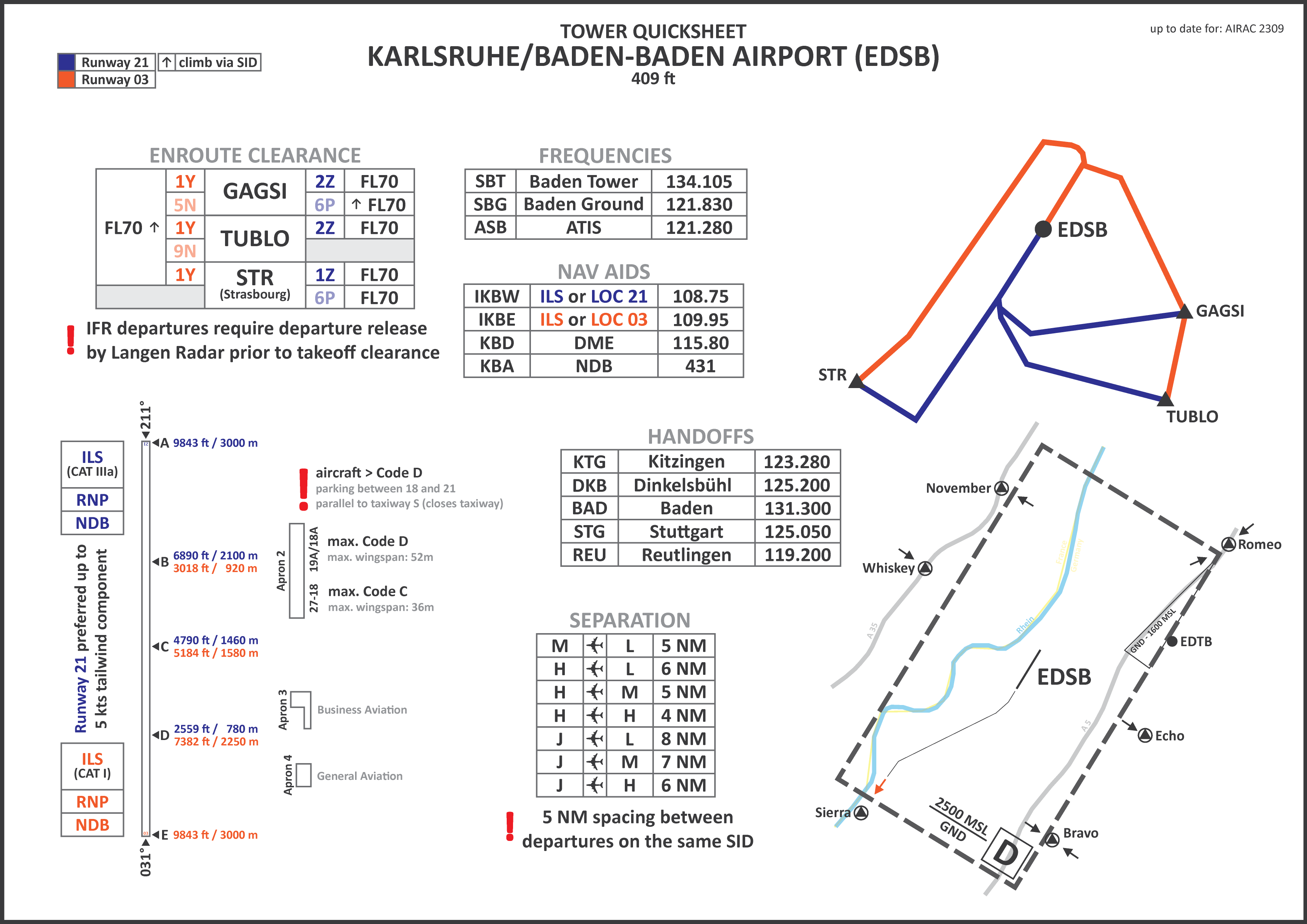](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/kPWY3njkYjJcNqH)*click on the image to open the printable Quicksheet*
# Ground and Tower
### SID Assignment
Usually the RNAV SID (Designator Y and Z) should be used primarily. Non-RNAV capable aircraft will get SIDs with Designator N or P.
### Ground
Baden Ground is responsible for startup and enroute clearance and all aircraft movements at the airport.
#### Parking Position
All positions at EDSB are taxi-out positions, no pushback is required. Positions 18 - 27 are only for Code C aircraft (max. B739/A321), Positions 18A and 19A can be used up to Code D (B764). Bigger aircraft can park between Positions 18 and 21, parallel to the taxiway, that is closed as long as this traffic is parked there. Aprons 4 is close to the GAT used for GA traffic, Apron 3 should be used for Buisness GA traffic.
### Prefered Runway
RWY 21 is preferred for usage up to a tailwind component of 5 knots.
**Approaches:** For both runways ILS (RWY 21 CAT III, RWY 03 CAT I), RNP and NDB approaches are available.
### VFR Traffic
Karlsruhe CTR is a class D airspace from ground to 2500 ft MSL.
**Leaving CTR** via the following routings: Bravo, Echo, November, Romeo or Sierra (S only RWY 21)
**Entering CTR** via the following routings: Bravo, Romeo or Whiskey
**Traffic Pattern:** Traffic Pattern east of the airport for traffic > 5,7 t MTOW (German aircraft registration D-Cxxx, D-Bxxx, D-Axxx) are only authorized at minimum 2000ft MSL and should not cross the highway (A5).
**Baden-Oos EDTB:** Traffic in the pattern, approaching or departing Baden-Oos airfield does not need to contact Karlsruhe Tower. This traffic has to stay below 1600ft MSL.
### IFR Departures
Departing IFR traffic switches to departure frequency without a separate instruction, immediately when airborne.
All departures shall be separated by radar separation or wake turbulence separation, whichever is greater. Departures flying the same SID shall be spaced by at least 5NM when the following aircraft overflies the departure end of runway.
### Auto-Handoff
Karlsruhe utilizes an auto-handoff procedure for IFR departures where **Tower will not hand off outbounds to the approach controller**. Make sure to set the correct departure frequency in the ATIS.
Outbounds should contact APP **immediately when airborne** unless explicitly told to remain on Tower frequency.
# Arrival
The primary arrival sector for Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden is Strasbourg Approach (LFST\_APP). If Strabourg is not online, Stuttgart Arrival (STG) is responsible for all arrivals and departures.
There are ILS, RNP and NDB approaches available for each runway, while the ILS RWY 21 is the only one that can be used during LVO.
### Low Visibillity Operations (LVO)
RWY 21 is certified for CATII/III, RWY 03 for CAT I only.
# EDTL - Lahr
# Overview
Lahr is a small airport in Southwestern Germany. It sees primarily cargo flights for the adjoining industrial districts which host numerous major international companies and charter operations or private flights often carrying passengers from or to the nearby Europa-Park Rust. Its history as a military airport and the resulting infrastructure make it suitable for government and some military flights as well; NATO uses it as a reserve airfield.
**Lahr is an unrestricted airport** and **part of the [S1 minor program](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/langen-fir-edgg-cw9/page/s1-training "EDGG S1 minor program")**. TWR can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher who have passed the **required moodle courses**.
### Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **Tower**
| TLT
| EDTL\_TWR
| 125.180
| --
| unrestricted: [EDTL CBT](https://moodle.vatsim-germany.org/course/view.php?id=83 "Course EDTL Tower (VATGER moodle)")
|
### Quickview
[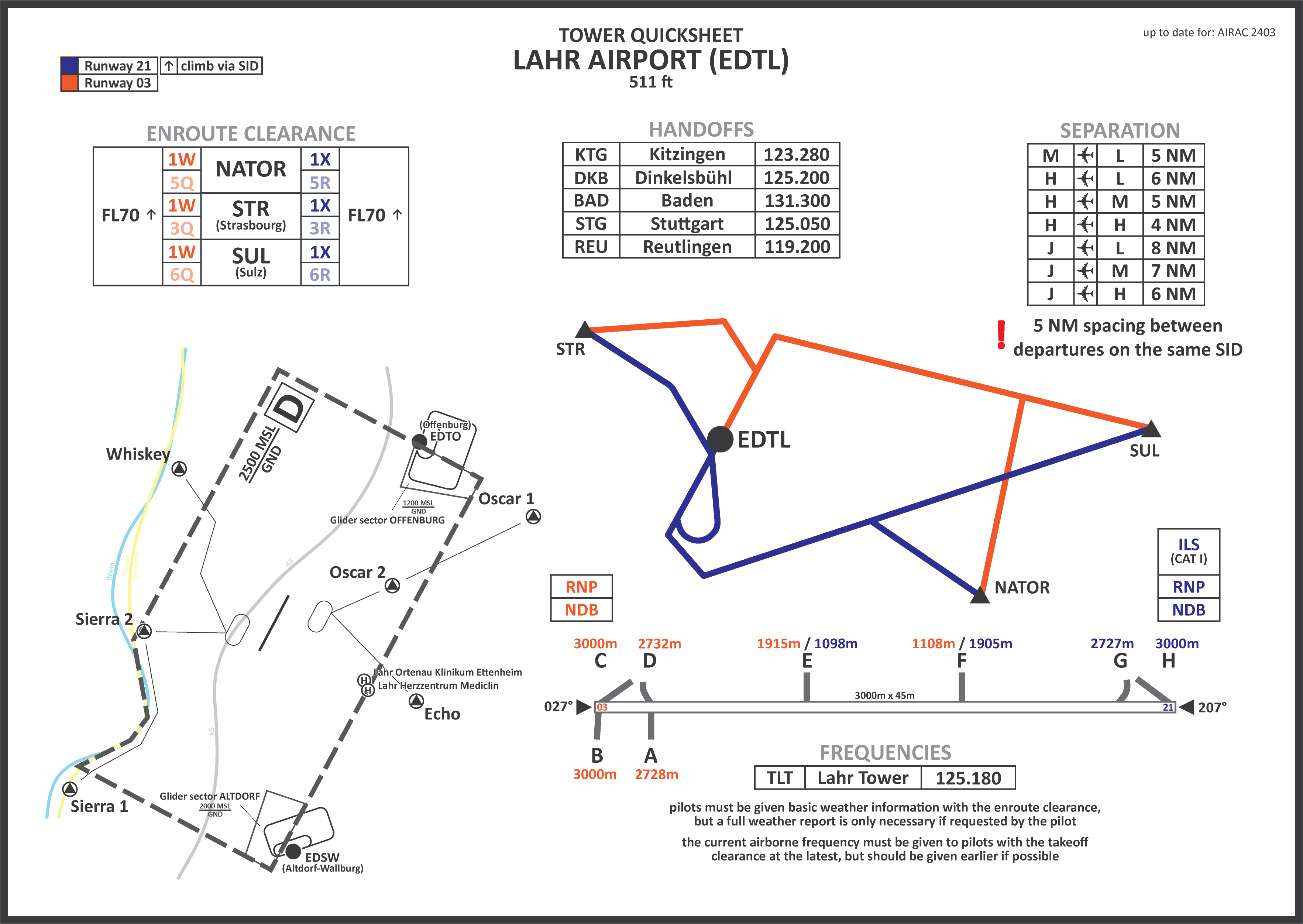](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/Bm4HQXHFMfkWRft "EDTL Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Tower
Lahr Tower is responsible for all enroute and startup clearances, ground and runway movements, and traffic within the Lahr CTR.
### Enroute Clearance
##### SID assignment
W- and X-SIDs should be used for all RNAV1-capable aircraft. Other aircraft shall always be cleared on Q- and R-SIDs.
##### Weather information
As Lahr has no ATIS, **pilots shall always be given basic weather information with their enroute clearance** or - if requested by the pilot - a full weather report. Pilots are only required to read back the QNH from the weather report.
Phraseology examples
> **Pilot**: Lahr Tower, Avanti Air 130H, request enroute clearance.
> **ATC**: Avanti Air 130H, Lahr Tower, cleared to London Stansted, Strasbourg 1W departure, flight planned route, climb via SID to FL70, squawk 2016, wind 310 degrees 3 knots, QNH1021.
> **Pilot**: Avanti Air 130H, cleared to London Stansted, Strasbourg 1W departure, flight planned route, climb via SID to FL70, squawk 2016, QNH1021.
> **Pilot**: Lahr Tower, Avanti Air 130H, request enroute clearance and weather information.
> **ATC**: Avanti Air 130H, Lahr Tower, cleared to London Stansted, Strasbourg 1W departure, flight planned route, climb via SID to FL70, squawk 2016, wind 310 degrees 3 knots, visibility 10 kilometers, clouds few at 4000ft scattered at 4800ft, temperature 08, dew point 07, QNH1021.
> **Pilot**: Avanti Air 130H, cleared to London Stansted, Strasbourg 1W departure, flight planned route, climb via SID to FL70, squawk 2016, QNH1021.
Phraseology examples
> **ATC:** Avanti Air 130H, Lahr Tower, cleared to London Stansted, Strasbourg 1W departure, flight planned route, climb via SID to FL70, revised airborne frequency is Langen Radar on 125.050, squawk 2016, wind 310 degrees 3 knots, QNH1021. **Pilot:** Avanti Air 130H, cleared to London Stansted, Strasbourg 1W departure, flight planned route, climb via SID to FL70, revised airborne frequency is Langen Radar on 125.050, squawk 2016, QNH1021.
> **ATC**: Avanti Air 130H, revised airborne frequency is Langen Radar on 125.050, wind 310 degrees 3 knots, runway 03, cleared for takeoff.
> **Pilot**: Avanti Air 130H, revised airborne frequency is Langen Radar on 125.050, runway 03, cleared for takeoff.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
|
| **Echo**
| B415 between Kuhbach and Reichenbach
|
| **Oscar 1**
| B33 exit Gengenbach
|
| **Oscar 2**
| fields between Oberschopfheim and Oberweier
|
| **Sierra 1**
| Rhine river mouth Dornskopf
|
| **Sierra 2**
| Rhine passing Nonnenweier
|
| **Whiskey**
| quarry lake Meißenheim |
##### Offenburg (EDTO)
Offenburg's runway and traffic circuit are located partially within the Lahr CTR. Pilots flying at Offenburg require an individual clearance to enter the CTR. If Offenburg Radio is staffed, the **radio operator may request the Offenburg sector to be opened** in which case this part of the Lahr CTR reverts to airspace class G and E, respectively, and pilots are allowed to operate inside this sector without acquiring an individual clearance to enter the Lahr CTR.
##### Altdorf-Wallburg (EDSW)
Altdorf-Wallburg's traffic circuit is partially located within the Lahr CTR. Pilots in the published traffic circuit at Altdorf-Wallburg require an individual clearance to enter the CTR. If Altdorf Radio is staffed, the **radio operator may request the Altdorf sector to be opened** in which case this part of the Lahr CTR reverts to airspace class G and E, respectively, and pilots are allowed to operate inside this sector without acquiring an individual clearance to enter the Lahr CTR.
# ETAD - Spangdahlem Airbase
# Overview
Spangdahlem is a United States Air Force base in Spangdahlem. It is home to the 52nd Fighter Wing and thus hosts a large number of F-16 jet fighter aircraft, but also serves as a a hub for the air mobility command and has facilities for military cargo and personnel transport flights.
Due to Spangdahlem being an American airfield, **controllers may use FAA procedures and phraseology** if they are familiar with them, but are not required to do so.
As Spangdahlem is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the GEMIL FLIP US DoD in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Spangdahlem is an unrestricted airport**. Clearance and Ground can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. The GCA position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher. However, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
### Spangdahlem ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ATAD
| ETAD\_ATIS
| 135.310
| --
| --
|
| **Clearance**
| TADC
| ETAD\_DEL
| 120.905
| relief station, American procedures, military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Ground**
| TADG
| ETAD\_GND
| 121.865
| American procedures, military station | unrestricted: no course |
| **Tower**
| TADT
| ETAD\_TWR
| 122.200
| American procedures, military station | unrestricted: no course |
| **GCA**
| TADA
| ETAD\_APP
| 129.475
| American procedures, military station | unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[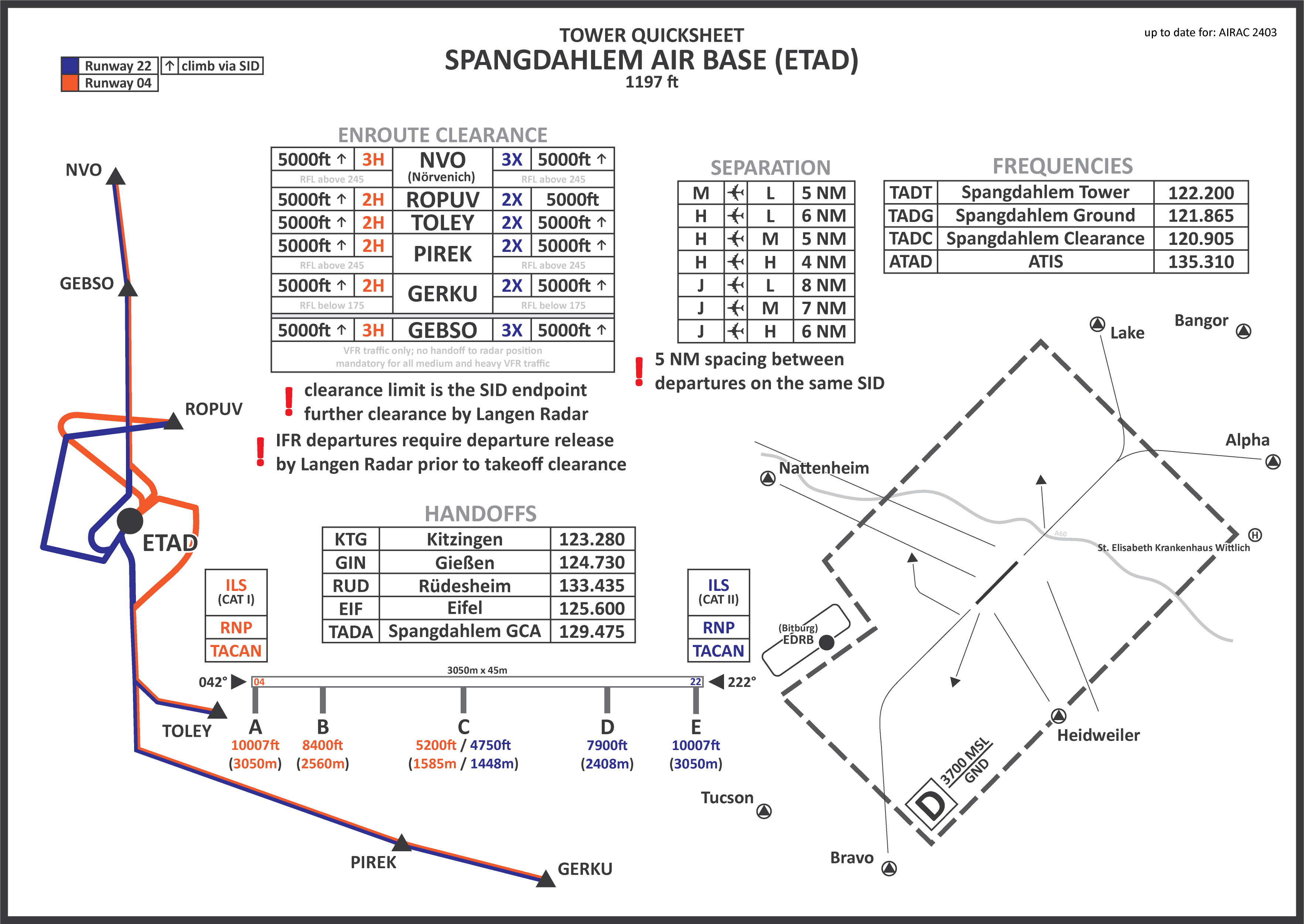](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/xEPQBew3baw8McT "ETAD Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Clearance
Spangdahlem Clearance is responsible for enroute and startup clearances for all departing IFR aircraft. It is primarily opened as a relief station when workload for Spangdahlem Ground is too high to work both positions at the same time.
### Enroute clearance
##### Clearance limit
The **clearance limit for all IFR departures is the last waypoint of the SID** or first waypoint on the flight plan. Further enroute clearance will be given by the civilian radar controller in-flight. Thus, the phrase "flight planned route" shall not be used.
##### Departure frequency
Pilots shall always be informed of the departure frequency during the enroute clearance.
##### SID assignment
The **use of SIDs is mandatory** during all operations. However, if Spangdahlem GCA is separately staffed, omnidirectional departures are also available for all aircraft.
**Non-TACAN equipped aircraft** must use the applicable ROPUV departure. A reroute may be necessary depending on the filed route.
##### Omnidirectional departure
Aircraft given an omnidirectional departure shall be instructed to expect vectors to their initial waypoint. The actual departure heading will later be coordinated by Tower and Approach shortly before departure. Clearance for an omnidirectional departure is **subject to approval by Spangdahlem GCA** and **only available when Spangdahlem GCA is separately staffed**.
> **Spangdahlem Clearance**: Duke 31, cleared to RUPOV via radar vectors out of runway 22, climb to altitude 5000ft, departure frequency 129.475, squawk 1000, expect further clearance by Langen Radar.
##### GEBSO departures
GEBSO departures are only available for aircraft on a Z flight plan or on request for VFR aircraft. Additionally, Medium and Heavy VFR GAT flights are required to leave the CTR via a GEBSO departure.
IFR aircraft filing via GEBSO shall be rerouted.
### IFR pattern
The radar pattern is **only available when Spangdahlem GCA is separately staffed** and requires approval by Spangdahlem GCA. The precise clearance for the IFR pattern **must be coordinated with Spangdahlem GCA**. Tower shall be informed of any aircraft that has been cleared for a radar pattern, e.g. through a remark in the scratchpad.
> **Iceman 1**: Spangdahlem Clearance, Iceman 1, request clearance for radar patterns. **Spangdahlem Clearance**: Iceman 1, Spangdahlem Clearance, standby.
>
> **TADC**: GCA, Clearance.
> **TADA**: Go ahead.
> **TADC**: Iceman 1, F16, requesting radar patterns.
> **TADA**: Approved at 4000ft.
> **TADC**: Approved at 4000ft.
>
> **Spangdahlem Clearance**: Iceman 1, clearance available, report ready to copy. **Iceman 1**: Ready to copy, Iceman 1.
> **Spangdahlem Clearance**: Iceman 1, cleared to Spangdahlem via radar vectors, climb to 4000ft, departure frequency 129.475, squawk 2024.
> **Iceman 1**: Cleared to Spangdahlem via vectors, climb to 4000ft, departure frequency 129.475, squawk 2024, Iceman 1.
# Ground
Spangdahlem Ground is responsible for all ground movements at the airport.
### Parking positions
Cargo and personnel transport flights park on the Southeastern side of the airport, other traffic uses the Northwestern side.
The **hard shelters** are used by fighter jets.
**Ramps 1 thru 4** are used for helicopters, training aircraft, and similar traffic.
**Ramp 5** is used for all cargo and personnel transport flights except for those transporting hazardous cargo which shall instead use **Ramp 6**. Additionally, all aircraft with a wingspan >41m always have to use Ramp 5 or 6.
### Ground movements
All outbound aircraft can be expected to call in ready for taxi. **Pushbacks are not needed** at any parking position in Spangdahlem.
##### Hot Pits
There are three hot pits on the Northwestern side of the airport. These are used for on-the-fly refueling of fighter jets between missions. They are only used on pilot request or as per a prior mission briefing.
##### Arm/Dearm Pads
There are Arming/Dearming pads near the holding points on the Northwestern side of the airport. These are used by fighter jets and other aircraft equipped or to be equipped with active ammunition and/or warheads. Like the hot pits, they are only used on pilot request or as per a prior mission briefing.
##### Intersection departures
Intersection departures are available for all aircraft from C and D during 22 operations and B and C during 04 operations. Pilots being given an intersection departure shall always be informed of the TORA for the intersection. All taxi clearances to intersections **must be approved by Spangdahlem Tower**.
> **Spangdahlem Ground**: Duke 31, taxi to holding point runway 22, intersection Delta, via Charlie, Papa, Delta, TORA 7900ft.
# Tower
Spangdahlem Tower is responsible for all traffic on the runway and within the CTR of the airport.
### General
##### Operating direction
The preferred operating direction below 5 knots tailwind component is runway 22.
During a runway change, Spangdahlem Tower is responsible for informing both military and civilian radar controllers of the change.
##### Runway crossing
Runway crossings are principally the responsibility of Spangdahlem Tower. However, after coordination, aircraft may remain on the Ground frequency for their runway crossing.
##### Low visibility operations
Spangdahlem Airbase uses different LVO minima than German civilian airfields. LVO has to be implemented at or below the following values:
- ceiling: 200ft
- visibility: 800m
- RVR: 550m
During LVO, only runway 22 is available with approaches up to CAT II.
### IFR traffic
#### Departure procedures
##### Release & handoff
A **departure release for all IFR departures** shall be obtained from Spangdahlem GCA.
Departures shall be handed off to Spangdahlem GCA as soon as possible.
##### Omnidirectional departure
Traffic cleared for a radar vectored departure shall be cleared for the following default headings with their takeoff clearance unless otherwise coordinated with Spangdahlem GCA:
- runway 04: left turn heading 330
- runway 22: right turn heading 330
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Duke 31, turn right heading 330, wind 230 degrees, 12 knots, runway 22, cleared for takeoff.
#### Radar pattern
The radar pattern is always located Northwest of the airport with at an altitude of 4000ft or 5000ft AMSL. This pattern is only available on explicit pilot request and when Spangdahlem GCA is separately staffed. Spangdahlem Tower shall instruct the pilot to climb out straight ahead during 04 operations or with an initial heading of 210 during 22 operations and initiate a handoff to Spangdahlem GCA as soon as possible.
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, turn left heading 210, wind 230 degrees, 12 knots, runway 22, cleared for takeoff.
> **Iceman 1**: Turning left heading 210 for radar pattern, runway 22, cleared for takeoff, Iceman 1.
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, contact departure.
### VFR traffic
#### Departure procedures
##### General
Unless otherwise instructed, **pilots may leave the Tower frequency on their own once clear of the Spangdahlem CTR**. Pilots are not required to use one of the reporting points to exit the CTR and may instead request a departure to a cardinal direction.
Unrestricted takeoffs, i.e. high angle climb after takeoff, are possible for all fighter jet aircraft during VMC with approval by Spangdahlem Tower. The standard maximum climb level during an unrestricted takeoff is FL95, but pilots may request a higher level which then has to be coordinated with Langen Radar.
##### 04 operations
During 04 operations, all departures are required to climb straight ahead until exiting the CTR laterally or vertically.
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, climb straight ahead until clear of the CTR, wind 020 degrees, 7 knots, runway 04, cleared for takeoff.
##### 22 operations
Northbound departures shall be instructed to turn right to heading 280 when airborne to avoid local villages; traffic may proceed on course once passing abeam the departure end of the runway.
Southbound departures shall be instructed to turn left to heading 210 when airborne to avoid local villages; traffic may proceed on course once passing abeam the departure end of the runway..
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, turn right heading 280, after passing abeam departure end of runway proceed on course, wind 230 degrees, 12 knots, runway 22, cleared for takeoff.
#### Arrival procedures
##### General
Arriving aircraft are required to contact Spangdahlem Tower no later than 10 NM prior to reaching the planned entry point. Pilots are required to enter the CTR via one of the published reporting or military entry points; the latter are **only available for military fighter jet traffic**.
While military entry points are publicly available, **pilots should be expected to not be aware of them** and will most likely request entry via one of the reporting points.
##### Fighter jet approaches
When entering via military entry points Alpha, Bravo, or Lake, pilots will continue to final and shall be instructed to report initial between 3 and 5 NM final at 2700ft. These arrivals will perform an overhead approach maneuver. If necessary, Tower shall sequence traffic by instructing early or late breaks.
Aircraft may request radar vectoring guidance toward the initial.
> **Iceman 1**: Iceman 1, overhead Alpha, 3000ft. **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, roger, report 3 mile initial at 2700ft.
> **Iceman 1**: Wilco, Iceman 1.
> **Iceman 1**: 3 mile initial, 2700ft, Iceman 1.
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, make an early break.
> **Iceman 1**: Making early break, Iceman 1.
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, report base with intentions.
> **Iceman 1**: Wilco, Iceman 1.
> **Iceman 1**: Base, gear down, for full stop, Iceman 1.
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, wind 230 degrees, 12 knots, runway 22, cleared to land.
> **Iceman 1**: Runway 22, cleared to land, Iceman 1.
Controllers are reminded that fighter jets will **fly at high speeds of ca. 300 KIAS** until breaking off.
##### Tactical fighter jet recovery
Tactical recovery approaches via Bangor or Tucson are subject to approval by Spangdahlem Tower and only possible during VMC. There are two recovery procedures: **Rhino recovery** and **Thud recovery**. During both procedures, regardless of operating direction, pilots will cross the respective **entry point between FL80 and FL95 at ca. 400 KIAS**.
For the **Rhino recovery**, pilots will execute a **descending turn Southeast and within 3 NM of the runway** - pilots should be expected to complete the descend within one orbit.
For the **Thud recovery**, pilots will execute a straight in approach.
> **Iceman 1**: Spangdahlem Tower, Iceman 1, 10 miles North of Bangor, FL95, for tactical arrival. **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, roger, report Bangor.
> **Iceman 1**: Bangor, FL85, for Rhino arrival, full stop, Iceman 1. **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, roger, report base.
> **Iceman 1**: Wilco, Iceman 1. **Iceman 1:** Base, gear down, Iceman 1. **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, wind 230 degrees, 12 knots, runway 22, cleared to land.
> **Iceman 1**: Runway 22, cleared to land, Iceman 1
#### Traffic pattern
The standard traffic pattern is always located Southeast of the airport with a maximum altitude of 2700ft AMSL. Spangdahlem Tower shall always inform pilots of these restriction.
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: Iceman 1, join right hand traffic pattern runway 04, not above 2700ft, wind 020 degrees, 7 knots, runway 04, cleared for takeoff.
#### Reporting points
There are two reporting points for civilian aircraft around the Spangdahlem CTR, both of which are mandatory reporting points. Additionally, there are five military entry points.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
| **Remark**
|
| **Heidweiler**
| village of Heidweiler
| --
|
| **Nattenheim**
| A60/B51 intersection, abeam village of Nattenheim
| --
|
| **Alpha** | highway A1 parking lot Flußbach
| military entry during 22 operations
|
| **Bravo** | Kordel village
| military entry during 04 operations
|
| **Lake** | lake Meerfelder Maar
| military entry during 22 operations
|
| **Bangor** | Wallscheid village
| tactical approach entry during 22 operations
|
| **Tucson** | Eisenach village
| tactical approach entry during 04 operations
|
#### Other procedures
##### SVFR procedures
SVFR is not approved for fixed wing aircraft. Rotary wing aircraft may be cleared for SVFR operations at or below 2000ft; higher levels are only available after coordination with Büchel Radar or, if Büchel Radar is not separately staffed, by Langen Radar.
Spangdahlem Tower shall assign squawk 4210 to SVFR aircraft.
##### NVFR procedures
If Büchel Radar is separately staffed, all Night VFR operations require approval by Büchel Radar.
Night VFR traffic shall be instructed to squawk 4215.
##### Overflights
Aircraft only crossing the CTR shall be instructed to remain at or above 1000ft AGL (2200ft AMSL).
> **Spangdahlem Tower**: D-ETAD, enter CTR via Nattenheim, thereafter proceed to Heidweiler, not below 2200ft.
#### Bitburg (EDRB)
Bitburg airfield is located East of Spangdahlem Airbase. All operations at this airfield take place outside of the Spangdahlem CTR except for parachuting. The Bitburg PJE is partially located within the Spangdahlem CTR. During parachuting operations in the Bitburg PJE, IFR operations at Spangdahlem are prohibited and all VFR operations must take place Southeast of Spangdahlem's runway.
Spangdahlem GCA or Langen Radar will notify Spangdahlem Tower when parachuting operations in the Bitburg PJE begin and conclude.
# Approach
Spangdahlem GCA is responsible for all airborne traffic within the Spangdahlem approach sector.
Spangdahlem GCA shall **always inform the controllers of EDGG sector Eifel**, **EBBU sectors ELS and LUS**, **ELLX APP**,and **military approach sector Büchel** when opening and closing the position.
### Airspace
The airspace controlled by Spangdahlem GCA is class E which is lowered to 1000ft AGL in the majority of the area of responsibility with a small section of class E lowered to 1700ft AGL in the Southeast.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etad.png)
##### Airspace boundary
Spangdahlem GCA may use the entire vertical range of the sector. Langen Radar is responsible for maintaining full vertical separation to the sector border.
### Departure procedures
##### Omnidirectional departure
Aircraft on an omnidirectional departure will depart on **runway heading during 04 operations** and on **heading 210 during 22 operations**. Clearance for such an omnidirectional departure is only possible when Spangdahlem GCA is separately staffed and approval for this type of departure will be requested by Spangdahlem GCA. If the omnidirectional departure goes to a waypoint other than ROPUV, Spangdahlem GCA has to acquire **approval by Langen Radar** before releasing the omnidirectional departure clearance.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC or Büchel Radar
Handoffs for departures shall always take place **before the sector boundary or the final waypoint of the SID**, whichever is earlier on a published departure procedure. Deviations or radar vectored departures (except for radar vectored departures to ROPUV) must always be coordinated individually.
### Arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC or Büchel Radar
Handoffs for arrivals shall always be **coordinated individually** and then take place as agreed. Spangdahlem GCA should, whenever possible, approach civilian ATC/Büchel Radar with a proposal for the handoff ahead of time, but **usually a DCT to SPA at 5000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
If an aircraft will fly a instrument approach procedure via an IAF, Spangdahlem GCA has to either obtain an early handoff and release to clear the aircraft for the published procedure or instruct Langen Radar to clear the procedure before initiating the handoff.
##### 04 operations arrival coordination
During 04 operations, it is not possible to vector arrivals onto the final approach of any instrument approach procedure while maintaining the required 2.5 NM separation to the sector border. Additionally, if an arriving aircraft is flying an instrument approach procedure via an IAF, they will briefly cross the Luxembourg Approach sector.
Due to this, **any IFR arrival for runway 04 is subject to coordination with Luxembourg Approach**. Depending on this position's workload and/or traffic situation, controllers shall be prepared to hold such traffic or organize an opposite direction landing on runway 22.
### Radar pattern
The radar pattern is always located Northwest of the airport at an altitude of 4000ft or 5000ft AMSL and will be conducted entirely through radar vectors. This pattern is only available on explicit pilot request and when Spangdahlem GCA is separately staffed. Spangdahlem Tower will instruct the pilot to climb out straight ahead during 04 operations or with an initial heading of 210 during 22 operations and initiate a handoff to Spangdahlem GCA as soon as possible.
Spangdahlem Clearance will request approval for a radar pattern clearance from Spangdahlem GCA. During this coordination, Spangdahlem GCA shall assign the pattern altitude.
# ETAR - Ramstein Airbase
# Overview
Ramstein is a United States Air Force base near Kaiserslautern. It is the headquarters of the American Air Forces in Europe and Africa as well as the NATO Allied Air Command. It serves as a base for the 86th Airlift Wing and the 435th Air Ground Operations Wing, but regularly hosts aircraft of over 30 other squadrons. It is the most important American military installation in Europe.
Most traffic at the airfield is of logistical and training nature, but it can also serve combat traffic like fighter jets.
Due to Ramstein being an American airfield, **controllers may use FAA procedures and phraseology** if they are familiar with them, but are not required to do so.
As Ramstein is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the GEMIL FLIP US DoD in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Ramstein is an unrestricted airport**. The Ground position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. The GCA position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher. However, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
### Ramstein ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ATAR
| ETAR\_ATIS
| 127.185
| --
| --
|
| **Ground**
| TARG
| ETAR\_GND
| 121.775
| American procedures, military station | unrestricted: no course |
| **Tower**
| TART
| ETAR\_TWR
| 133.205
| American procedures, military station | unrestricted: no course |
| **GCA**
| TARA
| ETAR\_APP
| 124.280
| American procedures, military station | unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[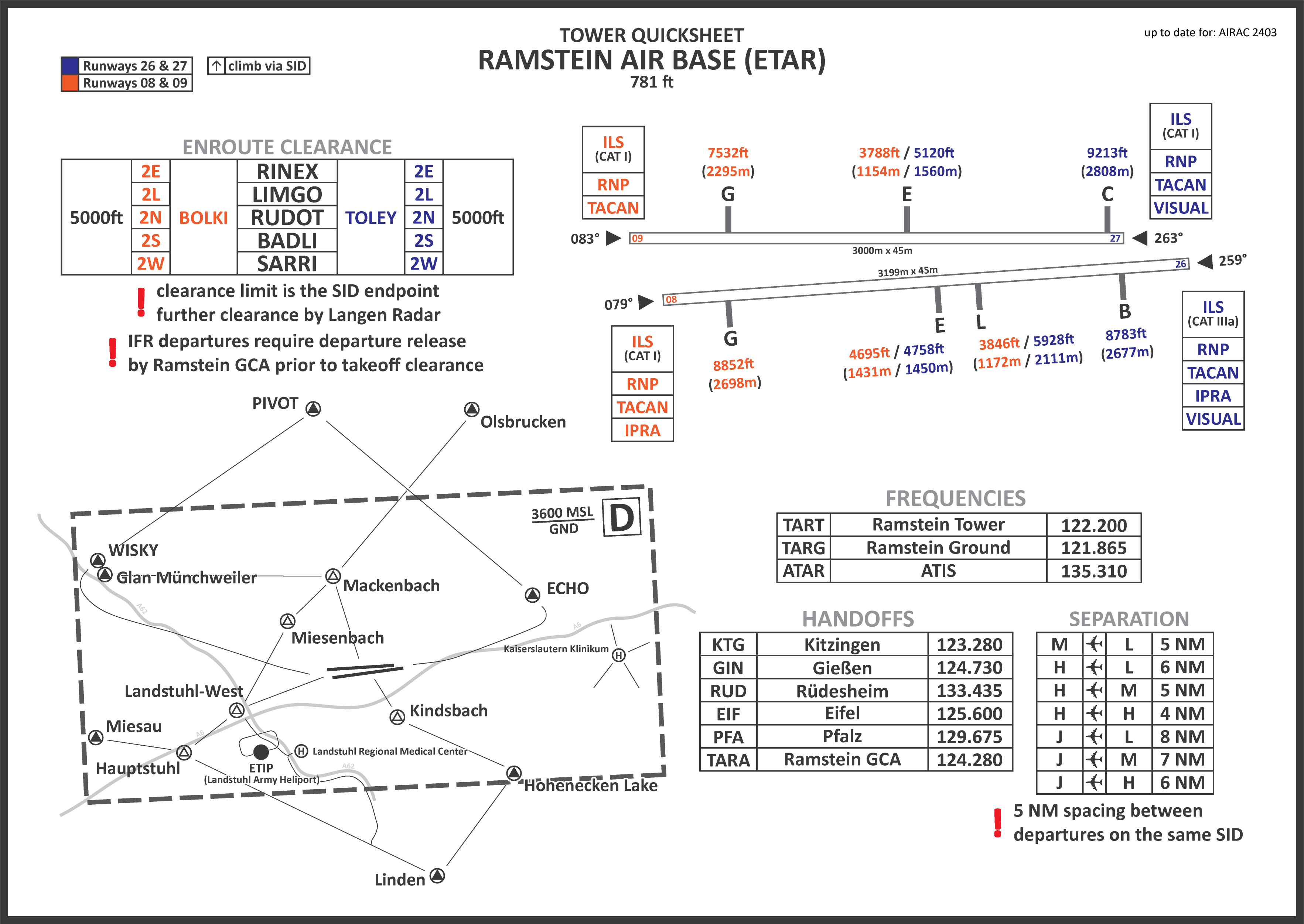](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/tqPimr3aR8y2XNm "ETAR Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Ground
Ramstein Ground is responsible for all enroute and startup clearances as well as ground movements at the airport with the exception of the taxiways between the runways.
### Enroute clearance
##### Clearance limit
The **clearance limit for all IFR departures is the last waypoint of the SID** or first waypoint on the flight plan. Further enroute clearance will be given by the civilian radar controller in-flight. Thus, the phrase "flight planned route" shall not be used.
##### Departure frequency
Pilots shall always be informed of the departure frequency during the enroute clearance.
> **Ramstein Ground**: Giant 8119, cleared to LIMGO via TOLEY 2 departure, runway 26, climb to altitude 5000ft, departure frequency 124.280, squawk 2024, expect further clearance by Langen Radar.
##### SID assignment
The **use of SIDs is mandatory** during all operations. Omnidirectional departures are not possible.
##### Radar pattern
The radar pattern is **only available when Ramstein GCA is separately staffed** and requires approval by Ramstein GCA. The precise level clearance for the IFR pattern **must be coordinated with Ramstien GCA**. Tower shall be informed of any aircraft that has been cleared for a radar pattern, e.g. through a remark in the scratchpad.
> **Clue 1**: Ramstein Ground, Clue 1, request clearance for radar patterns. **Ramstein Ground**: Clue 1, Ramstein Ground, standby.
>
> **TARG**: GCA, Ground.
> **TARA**: Go ahead.
> **TARG**: Clue 1, C-21, requesting radar patterns.
> **TARA**: Approved at 5000ft.
> **TARG**: Approved at 5000ft.
>
> **Ramstein Ground**: Clue 1, clearance available, report ready to copy. **Clue 1**: Ready to copy, Clue 1.
> **Ramstein Ground**: Clue 1, cleared to Ramstein via radar vectors, climb to 5000ft, departure frequency 124.280, squawk 2024.
> **Clue 1**: Cleared to Ramstein via vectors, climb to 5000ft, departure frequency 124.280, squawk 2024, Clue 1.
### Ground operations
##### Hot refueling
Hot refueling takes place primarily on the HOT pads on Ramp 1. If all Ramp 1 HOT pads are in use, the Ramp 5 stands south of TWY F may also be used for hot refueling.
##### Arming/dearming
Arming and dearming operations take place primarily on TWYs A and K. If there is no more space on either of these TWYs, TWY G Center will be used for arming and dearming.
##### Intersection departures
Intersection departures are available for all aircraft from C and D during 22 operations and B and C during 04 operations. Pilots being given an intersection departure shall always be informed of the TORA for the intersection. All taxi clearances to intersections **must be approved by Ramstein Tower**.
> **Ramstein Ground**: Clue 1, taxi to holding point runway 08, intersection Golf, via Golf, TORA 8852ft.
# Tower
Ramstein Tower is responsible for all traffic on the runways and within the CTR of the airport as well as taxiing traffic on the taxiways between the runways.
### General
##### Runway in use
Ramstein generally operates using runway 08/26 for departures, arrivals, and pattern traffic while **runway 09/27 is used for taxiing**.
The operating direction below 5kt tailwind shall always be 26/27.
During a runway change, Ramstein Tower is responsible for informing both military and civilian radar controllers of the change.
##### Opposite direction operations
Opposite direction operations are **only available on pilot request** and as long as no other traffic will experience delays. Opposite arrivals have to be approved by Ramstein Tower while opposite departures have to be approved by Ramstein GCA.
> **TART**: GCA, Tower.
> **TARA**: Go ahead.
> **TART**: Request opposite direction departure, Giant 8119, Boeing 747-400, runway 08.
> **TARA**: Opposite direction departure runway 08 approved.
An **opposite arrival** must have touched down before an arrival to the current operating direction reaches 10 NM final.
An **opposite departure** must be airborne and have turned away from the extended centerline before an arrival to the current operating direction reaches 10 NM final. If the opposite departure is operating under VFR, they **shall be explicitly instructed to turn right or left** as required when airborne.
##### Runway crossing
Runway crossings are principally the responsibility of Ramstein Tower. However, after coordination, aircraft may remain on the Ground frequency for their runway crossing.
Additionally, clearances to cross both runways are not possible. Before clearing an aircraft to cross the next runway, it must have fully cleared the previous one.
##### Low visibility operations
Ramstein Airbase differentiates between CAT I, CAT II, and CAT III low visibility operations.
**CAT I operations** are in effect when the ceiling is less than 800ft and/or the visibility is less than 2 SM (3200m).
During CAT I operations, the critical area of the ILS has to be clear once an arriving aircraft is within 2 NM final.
**CAT II operations** are in effect when the ceiling is less than 200ft, the visibility is less than 800, or the RVR is less than 550m.
During CAT II operations, the activity of CAT II operations shall be broadcast in the ATIS and the critical area of the ILS has to be clear once an arriving aircraft is within 2 NM final.
**CAT III operations** are in effect when the ceiling is less than 100ft or the RVR is less than 300m.
During CAT III operations, the activity of CAT III operations shall be broadcast in the ATIS, spacing between two arrivals shall be no less than 10 NM, and departing traffic shall be rolling before the next arrival reaches 10 NM final.
### IFR traffic
#### Departure procedures
##### Release & handoff
A **departure release for all IFR departures** shall be obtained from Ramstein GCA.
Departures shall be handed off to Ramstein GCA as soon as possible.
#### Arrival procedures
The primary approach procedure is the ILS. Other approach procedures must be explicitly requested by the pilot. Additionally, the Autobahn 6 visual approach to runway 26/27 is only available when Ramstein GCA is separately staffed.
##### Go around procedure
If an aircraft **goes around further away from the runway than 6 NM final**, they shall be instructed to climb straight ahead to 5000ft and handed off to Ramstein GCA.
If an aircraft **goes around within 6 NM final**, they shall be instructed to climb straight ahead to 5000ft and during 08/09 operations they shall additionally be informed of the minimum climb gradient of 250ft per NM.
> **Clue 1**: Clue 1, going around.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, roger, fly runway heading, climb to 5000ft, climb gradient 250ft per mile.
When Ramstein GCA is not separately staffed, **pilots shall always be instructed to perform the published missed approach procedure**.
#### Radar pattern
The radar pattern is always located North of the airport at an altitude of 4000ft or 5000ft AMSL. This pattern is **only available on explicit pilot request and when Ramstein GCA is separately staffed**. Ramstein Tower shall instruct the pilot to climb out straight ahead to the coordinated pattern altitude and initiate a **handoff to Ramstein GCA no later than 3 NM beyond the departure end** of the runway. Additionally, during 08/09 operations, pilots shall be informed of the minimum climb gradient of 250ft per NM.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, fly runway heading, climb to 5000ft, climb gradient 250ft per mile, wind 060 degrees, 9 knots, runway 08, cleared for takeoff.
> **Clue 1**: Roger, runway heading to 5000ft, runway 26, cleared for takeoff, Clue 1.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, contact departure.
### VFR traffic
#### Departure procedures
##### General
Helicopter pilots are required to exit the CTR on one of the **published helicopter routes**, while other traffic has to exit the CTR via the VFR departure pattern.
During **08/09 operations**, aircraft shall be instructed to continue on runway heading until passing 1.5 DME RMS and then turn right heading 170 or until passing 3 DME RMS and then turn left heading 360 until clear of the CTR depending on requested departure direction.
During **26/27 operations**, aircraft shall be instructed to continue on runway heading until passing 2 DME RMS and then turn right heading 290 or 360 until clear of the CTR depending on requested departure direction.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, after departure continue on runway heading until passing 3 DME Ramstein, then turn left heading 360, report leaving class D airspace, wind 300 degrees, 4 knots, runway 26, cleared for takeoff.
##### Fighter jet departures
Departing fighter jets have to exit the CTR via the VFR departure pattern as well but **shall be instructed to climb to 4000ft or above**.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, after departure continue on runway heading until passing 2 DME Ramstein, then turn right heading 290, climb to 4000ft or above, report leaving class D airspace, wind 060 degrees, 9 knots, runway 08, cleared for takeoff.
#### Arrival procedures
##### General
Arriving aircraft are required to contact Ramstein Tower prior to entering the CTR and obtain clearance for entry into the CTR. Helicopter pilots are required to enter the CTR on one of the **published helicopter routes**, while other traffic has to enter the CTR either from a cardinal direction or via the military reporting point. Additionally, all VFR traffic must be at 3000ft AMSL or below when entering the CTR
While military entry point and initials are publicly available, **pilots should be expected to not be aware of them** and will most likely request entry via a cardinal direction.
##### Overhead approach
Aircraft entering via PIVOT for an **overhead approach** will continue to WISKY or ECHO and shall be instructed to report WISKY/ECHO at 3000ft. The break-off always has to be right-hand at 2500ft. If necessary, Tower shall sequence traffic by instructing early or late breaks.
> **Clue 1**: Clue 1, overhead PIVOT, 3000ft, for overhead pattern. **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, roger, report ECHO at 3000ft.
> **Clue 1**: Wilco, Clue 1.
> **Clue 1**: ECHO, 3000ft, Clue 1.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, break to the right at 2500ft, report base with intentions.
> **Clue 1**: Breaking to the right at 2500ft, wilco, Clue 1.
> **Clue 1**: Base, gear down, for full stop, Clue 1.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, wind 300 degrees, 4 knots, runway 26, cleared to land.
> **Clue 1**: Runway 26, cleared to land, Clue 1.
Controllers are reminded that during an overhead approach, aircraft, especially fighter jets, will **fly at high speeds of up to 300 KIAS** until breaking off.
##### High speed downwind
The high speed downwind is **only available on pilot request**. Pilots will enter via PIVOT and then proceed to WISKY (26/27 operations) or ECHO (08/09 operations) to cross both points at 3000ft and join the downwind from there.
During 08/09 operations, only the Southern high speed downwind is available. When passing ECHO, pilots shall be instructed to turn to a suggested heading of 240 and descend to 2000ft to enter a right hand downwind.
During 26/27 operations, aircraft entering the Northern high speed downwind shall be instructed to join a right hand downwind from WISKY and descend to 2000ft; aircraft entering the Southern high speed downwind shall be instructed to turn to a suggested heading of 110 and descend to 2000ft to enter a left hand downwind.
> **Clue 1**: Clue 1, overhead PIVOT, 3000ft, for high speed downwind. **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, roger, report WISKY at 3000ft.
> **Clue 1**: Wilco, Clue 1.
> **Clue 1**: WISKY, 3000ft, Clue 1.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, turn left to suggested heading 110 to join downwind runway 26, descend to 2000ft, report base with intentions.
> **Clue 1**: Heading 110 to join downwind runway 26, descending to 2000ft, wilco, Clue 1.
> **Clue 1**: Base, gear down, for full stop, Clue 1.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, wind 300 degrees, 4 knots, runway 26, cleared to land.
> **Clue 1**: Runway 26, cleared to land, Clue 1.
#### Traffic pattern
##### Closed inside traffic pattern
The standard inside traffic pattern, which is contained within the CTR, is always located North of the airport with a maximum altitude of 2000ft AMSL. Ramstein Tower shall always inform pilots of these restriction. Additionally, the inside pattern is **only available during 26/27 operations**.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, join right hand inside pattern runway 08, not above 2000ft, wind 060 degrees, 9 knots, runway 08, cleared for takeoff.
##### Closed outside traffic pattern
The standard outside traffic pattern, during which the aircraft shortly leave the CTR, is always located North of the airport with a maximum altitude of 3000ft AMSL. Additionally, pilots in the outside pattern are required to route WISKY PIVOT ECHO during 08/09 operations and ECHO PIVOT WISKY during 26/27 operations. Ramstein Tower shall always inform pilots of these restriction and may **only use this pattern on explicit pilot request**.
As this is the only pattern available during 08/09 operations, pilots requesting VFR patterns should be pointed towards the appropriate documentation for the outside pattern or, if Ramstein GCA is online, be recommended to opt for the radar pattern.
> **Clue 1**: Ramstein Tower, Clue 1, at Golf South, request outside pattern, ready for departure. **Ramstein Tower**: Clue 1, join right hand outside pattern runway 08 via WISKY, PIVOT, and ECHO, at 3000ft, wind 060 degrees, 9 knots, runway 08, cleared for takeoff.
#### Helicopter procedures
Helicopters at Ramstein may be cleared for take-off and landing on either runway as well as any taxiway. Departure from or landing on the ramps is not possible.
##### Helicopter routes
Helicopters can enter and exit the CTR via reporting points Olsbrucken, Glan Münchweiler, Miesau, and Linden. Ramstein Tower will instruct pilots depart/approach the airport via Mackenbach, Landstuhl West, or Kindsbach. The airport connection points and CTR entry/exit points shall be connected through the published routes.
##### Landstuhl Heliport (ETIP)
Helicopters operating locally at Landstuhl Heliport at or below 100ft AGL (ca. 1200ft AMSL) are not required to contact Ramstein Tower. Departing traffic has to contact Ramstein Tower prior to departure for clearance to enter the CTR; however, their takeoff is on own discretion and they shall thus not be given a takeoff clearance. Likewise, arriving traffic shall not be given a landing clearance.
##### Landstuhl Hospital
Helicopters operating locally at Landstuhl Hospital at or below 100ft AGL (ca. 1200ft AMSL) are not required to contact Ramstein Tower.
Departing traffic has to contact Ramstein Tower prior to departure for clearance to enter the CTR; however, their takeoff is on own discretion and they shall thus not be given a takeoff clearance. After departure, helicopters shall be instructed to proceed to Landstuhl West and then to leave the CTR along the published helicopter routes
Arriving traffic shall not be given a landing clearance as landings are on own discretion. When arriving from the North, these helicopters shall be routed to Landstuhl West and from there follow Autobahn 62 at or above 500ft AGL toward the hospital; when arriving from the South, they may enter the CTR along Autobahn 62 at or above 500ft AGL toward the hospital.
> **Medevac 86**: Ramstein Tower, Medevac 86.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Medevac 86, Ramstein Tower, go ahead.
> **Medevac 86**: Medevac 86, 2 minutes North of Olsbrucken, destination Landstuhl Hospital.
> **Ramstein Tower**: Medevac 86, enter class D via Olsbrucken, Mackenbach, Miesenbach, Landstuhl West, thereafter follow Autobahn 62 to Landstuhl hospital, not below 500ft AGL.
> **Medevac 86**: Enter via Olsbrucken, Mackenbach, Miesenbach, Landstuhl, and Autobahn 62, not below 500ft AGL, Medevac 86.
#### Reporting points
There are thirteen reporting points around the Ramstein CTR, some of which are non-compulsory reporting points.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
| **Remark**
|
| **Olsbrucken** | Olsbrücken village | helicopters only
CTR entry from/exit to the North |
| **Glan Münchweiler** | Glan-Münchweiler village | helicopters only
CTR entry from/exit to the West
|
| **Mackenbach** | Mackenbach village | helicopters only
non-compulsory reporting point
|
| **Miesenbach** | Miesenbach village | helicopters only
non-compulsory reporting point
|
| **Landstuhl West** | highway intersection A6 and A62 | helicopters only
non-compulsory reporting point
|
| **Kindsbach** | Kindsbach village | helicopters only
non-compulsory reporting point
|
| **Miesau** | Miesau village | helicopters only
CTR entry from/exit to the West
|
| **Hauptstuhl**
| Hauptstuhl village
| helicopters only
non-compulsory reporting point
|
| **Hohenecken Lake**
| Gelterswoog lake
| helicopters only |
| **Linden**
| Linden village
| helicopters only
CTR entry from/exit to the South and East
|
| **PIVOT**
| Jettenbach quarry
| fixed wing only
military reporting point
CTR entry/exit
|
| **WISKY**
| intersection B423 and A62
| fixed wing only
military reporting point
|
| **ECHO**
| intersection L367 and B270
| fixed wing only
military reporting point
|
#### Other procedures
##### Low approaches with lined up traffic
Low approaches may be authorized with traffic lined up on the runway. In these cases, Ramstein Tower shall instruct the approaching aircraft to overfly the runway not below 1300ft (light and medium traffic) or 1800ft (heavy traffic).
##### SVFR procedures
SVFR is not approved for fixed wing aircraft. Rotary wing aircraft may be cleared for SVFR operations if they can remain clear of clouds.
# Approach
Ramstein GCA is responsible for all airborne traffic within the Ramstein approach sector.
Ramstein GCA shall **always inform the controller of EDGG sectors Pfalz and Neckar Low** when opening and closing the position.
### Airspace
The airspace controlled by Ramstein GCA is class E which is lowered to 1000ft AGL in the majority of the area of responsibility with a small section of class E lowered to 1700ft AGL in the West.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etar.png)
##### Airspace boundary
Ramstein GCA may use the entire sector up until the border except for the border with Langen Radar sector Neckar Low to which half lateral separation shall be kept. Langen Radar sector Pfalz is responsible for maintaining full lateral and vertical separation to the sector border.
##### EDDR/EDRZ departures
EDDR and EDRZ departures via TOMPI which climb at a very low rate may not clear the Ramstein approach sector. In these cases, Langen Radar will request an airspace crossing which shall be approved as soon as possible.
##### EDRZ arrivals
During 21 operations at EDRZ, all IFR approaches will have to cross the Ramstein approach sector. In these cases, Langen Radar will request an airspace crossing which shall be approved as soon as possible.
### Departure procedures
##### Departure release
When Ramstein Tower requests a departure release for an aircraft that will not remain in the local pattern, Ramstein GCA has to **obtain a further departure release for this aircraft from Langen Radar**.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC
Handoffs for departures shall always take place **before the sector boundary or before reaching BOLKI or TOLEY**, whichever is earlier.
### Arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC
Handoffs for arrivals shall always be **coordinated individually** and then take place as agreed. Ramstein GCA should, whenever possible, approach civilian ATC with a proposal for the handoff ahead of time, but **usually a DCT to XIDOD** (26/27 operations)**, MAPIG** (08/09 operations)**, or RMS** (either direction) **at 5000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
### Radar pattern
The radar pattern is always located North of the airport at an altitude of 4000ft or 5000ft AMSL and will be conducted entirely through radar vectors. This pattern is **only available on explicit pilot request and when Ramstein GCA is separately staffed**. Ramstein Tower will instruct the pilot to climb out straight ahead to the coordinated pattern altitude and initiate a handoff to Ramstein GCA within 3 NM of the departure end of the runway.
Ramstein Ground will request approval for a radar pattern clearance from Ramstein GCA. During this coordination, Ramstein GCA shall assign the pattern altitude.
# ETHF - Fritzlar Airbase
# Overview
Fritzlar is a Bundeswehr base in Fritzlar. Originally a Luftwaffe base during World War II, after the end of the war it was first under American and then under French control before being returned to the German military in 1956. It primarily hosts helicopters from Transporthubschrauberregiment 10, Transporthubschrauberregiment 30, and Kampfhubschrauberregiment 36, but its 1043m hard surface runway can also support smaller fixed wing aircraft. Additionally, an army ambulance regiment is stationed at the airport which attracts medevac and other medical flights as well.
As Fritzlar is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the MIL AIP, GEMIL FLIP VAD, and CENOR FLIP in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Fritzlar is an unrestricted airport**. The Ground position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. The radar position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher. However, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
### Fritzlar ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **Ground**
| THFG
| ETHF\_GND
| 131.450
| fictional frequency, military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Tower**
| THFT
| ETHF\_TWR
| 128.830
| fictional frequency, military station
| unrestricted: no course |
| **Arrival**
| THFA
| ETHF\_APP
| 120.865
| military station
| unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[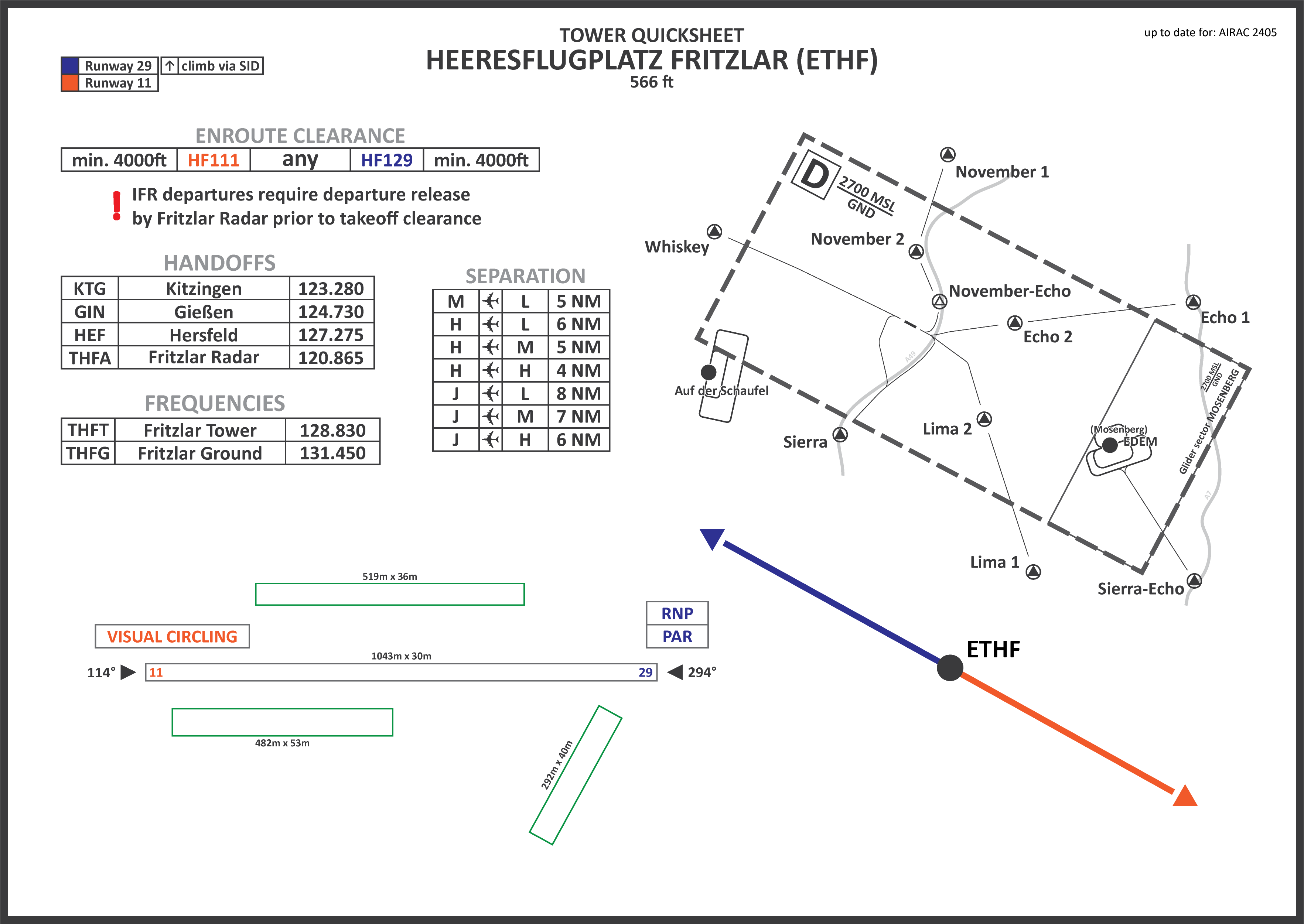](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/DeARCtYiBcxz6X5 "ETHF Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Ground
Fritzlar Ground is responsible for all enroute and startup clearances as well as ground movements at the airport.
### Enroute clearances
All enroute clearances must be **coordinated with Fritzlar Radar**. The clearance will be given by Fritzlar Radar to be **relayed to the pilot** by Fritzlar Ground. Usually, pilots are first given their startup and taxi clearance and the enroute clearance is coordinated while the aircraft is on its way to the runway to be **given at the holding point shortly before departure**. If Fritzlar Radar is offline, the enroute clearance has to be coordinated with the appropriate civilian radar controller.
Further information on clearances to be given can be found in the [ETHF Approach SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/approach-EY2 "ETHF Approach SOP").
### Startup
All IFR and VFR aircraft at Fritzlar require a startup clearance from Fritzlar Ground.
# Tower
Fritzlar Tower is responsible for all traffic on the runway, helipad, and grass lanes as well as traffic within the CTR of the airport.
### General
##### Operating direction
As only runway 30 has instrument approaches, it is the preferred runway whenever conditions permit.
##### Runway crossing
Runway crossings are principally the responsibility of Fritzlar Tower. However, after coordination, aircraft may remain on the Ground frequency for their runway crossing.
##### Grass lanes
The grass lanes (as well as the helipad) may all be **used in parallel** to the hard surface runway and other grass lanes. They are generally only used for helicopter traffic.
### Non-line taxi
After coordination with Fritzlar Ground, helicopters may be cleared directly to the departure runway or parking position without using the taxiways. This non-line taxi **shall always take place on the Tower frequency**, thus outbound non-line taxi has to be handed over from Ground to Tower for the taxi clearance. Non-line taxi is **not available for fixed wing aircraft**.
> **Fritzlar Tower**: Colibri 36, air-taxi direct to holding point runway 30.
### IFR traffic
All IFR traffic shall use the hard surface runway. The grass lanes and the helipad are only available for VFR traffic.
##### Departures
A **departure release for all IFR departures** shall be obtained from Fritzlar Radar.
Departures shall be handed off to Fritzlar Radar as soon as possible.
##### Arrivals
As only runway 30 has instrument procedures, a **circling approach South of the airport is required for all IFR inbounds during 12 operations**.
During activity of the Mosenberg sector, **IFR arrivals will enter this sector during their descent**. In this situation, the IFR arrival shall be informed about possible VFR traffic in the vicinity of Mosenberg and Fritzlar Tower shall inform Mosenberg Radio of all IFR inbounds. If VFR traffic within the Mosenberg traffic circuits complies with the circuit altitude of 2000ft AMSL and IFR inbounds don't descend below the normal glide profile, **no conflicts should arise**.
For IFR arrivals on a PAR approach, a landing clearance shall be relayed to Fritzlar Radar. Depending on the traffic situation, **Tower may instruct Fritzlar Radar to hand these arrivals directly off to Ground**.
### VFR traffic
##### Noise abatement
Traffic should avoid overflying the town of Fritzlar directly North of the airfield below 2000ft. Due to this, the **Southern traffic circuit shall be used whenever possible**.
##### Reporting points
There are ten reporting points around the Fritzlar CTR, all of which except for November Echo are mandatory reporting points. Additionally, reporting point **Sierra Echo is only used for traffic approaching or departing Mosenberg (EDEM)** and should generally be the entry/exit point for traffic at this airfield.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
| **Remark**
|
| **Echo 1**
| A7/B253 intersection
| --
|
| **Echo 2**
| B254 exit between town of Wabern and fresh concrete quarry Wabern
| --
|
| **Lima 1**
| Lützelwig village
| --
|
| **Lima 2**
| railroad crossing South of Uttershausen
| --
|
| **November 1**
| Gleichen village
| --
|
| **November 2**
| A49/L3150 intersection
| --
|
| **November Echo**
| A49 Eder bridge
| non-compulsory reporting point
|
| **Sierra**
| A49/B3 intersection
| --
|
| **Sierra Echo**
| A7/B323 intersection
| reporting point for EDEM only |
| **Whiskey**
| Anraff village
| --
|
##### Mosenberg (EDEM)
Mosenberg's runway and traffic circuits are located within the Fritzlar CTR. Pilots flying at Mosenberg require an individual clearance to enter the CTR and operate at the airfield. If Mosenberg Radio is staffed, the **radio operator may request the Mosenberg sector to be opened** in which case this part of the Fritzlar CTR reverts to airspace class G and E, respectively, and pilots are allowed to operate inside this sector without acquiring an individual clearance to enter the Lahr CTR. However, **inbound aircraft are still required to make the initial call to Fritzlar Tower** even when the Mosenberg sector is active and shall be handed off to Mosenberg Radio as soon as possible; vice versa, Mosenberg Radio is required to inform Fritzlar Tower about any outbound aircraft. During high traffic operations at Fritzlar, it is recommended not to open the Mosenberg sector and if necessary prevent traffic at the airfield entirely. Aircraft departing from or arriving at Mosenberg should always **route via reporting point Sierra Echo**.
##### Auf der Schaufel
Auf der Schaufel is an airfield for ultralight aircraft. It's traffic circuit extends into the Fritzlar CTR. **Pilots flying at Auf der Schaufel require an individual clearance to enter the CTR**. There is no separate sector that can be opened and due to a lack of an ICAO code for the airfield, Auf der Schaufel Radio cannot be staffed on VATSIM.
# Approach
Fritzlar Radar is responsible for all airborne traffic within the Fritzlar approach sector as well as coordinating all enroute clearances for IFR departures out of Fritzlar airport.
Fritzlar Radar shall **always inform the controllers of EDGG sectors Hersfeld and Gießen as well as the controller of EDWW sector Harz** when opening and closing the position.
### Airspace
The airspace controlled by Fritzlar Radar is class E which is lowered to 1000ft AGL in the entire area of responsibility.
[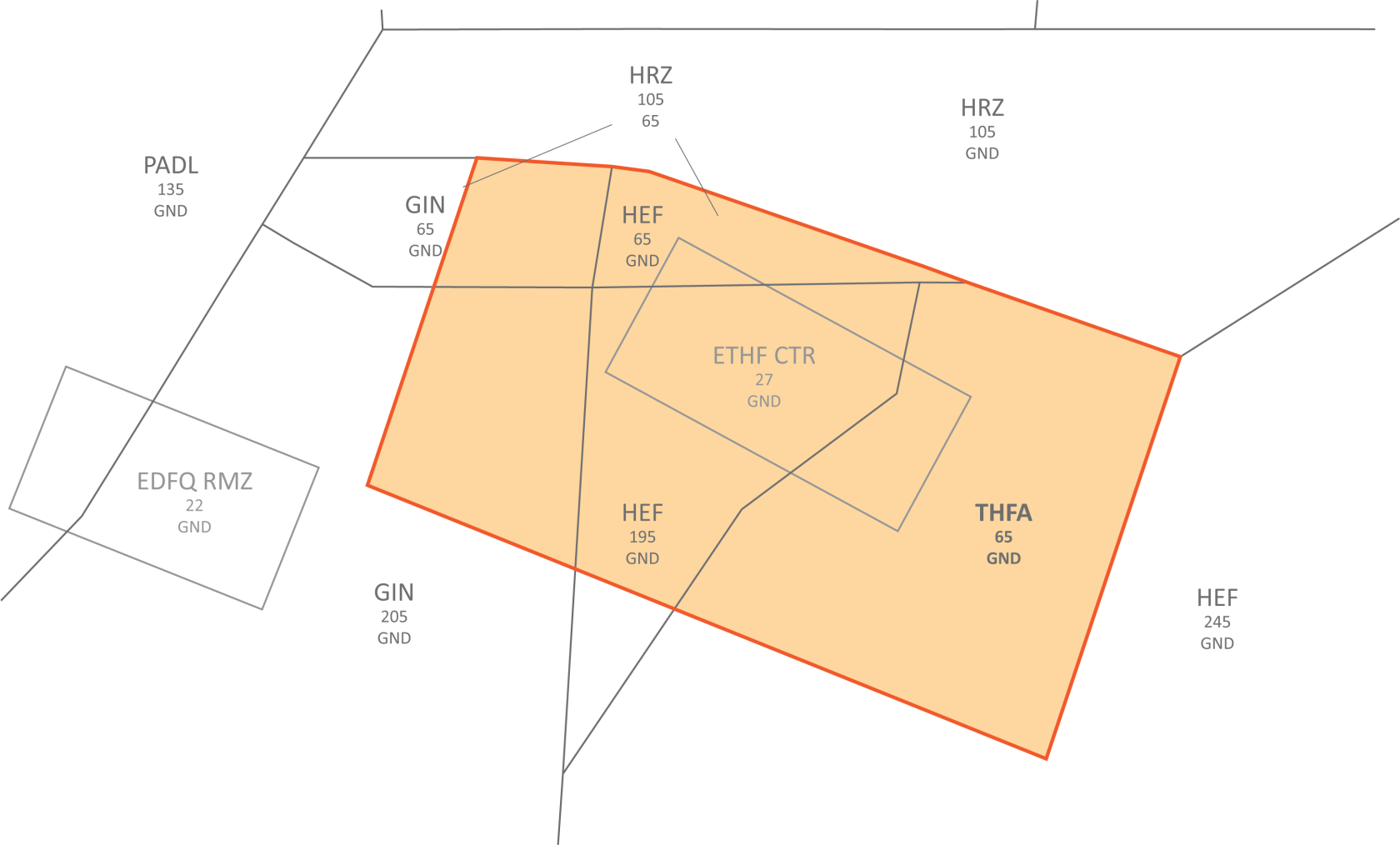](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/ethf.png)
### Departure procedures
##### Enroute clearances
Enroute clearances must **always be coordinated with all concerned adjacent sectors**. Exact routings to the first fix in the flight plan must be adapted to the individual traffic situation but **usually a DCT to the first waypoint is the best solution**. The initial climb shall always be at least 4000ft and should not exceed FL60. Higher initial flight levels must be coordinated with all concerned sectors. All IFR departures shall use the applicable OID for the departure runway.
The enroute clearance will be requested by Fritzlar Ground and has to be communicated to Fritzlar Ground once it has been coordinated. Fritzlar Ground will then relay the clearance to the pilot.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC
Handoffs for departures shall always be **coordinated individually** (preferably while coordinating the enroute clearance) and then take place as agreed.
### Arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC
Handoffs for arrivals shall always be **coordinated individually** and then take place as agreed. Fritzlar Radar should, whenever possible, approach civilian ATC with a proposal for the handoff ahead of time, but **usually a DCT to the respective IAF** (from the South: RANIN, from the North: KEMAD) **at 5000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
##### Approach
Fritzlar only has instrument approach procedures for runway 30. Thus, a **circling approach is required during 12 operations**.
The **RNP approach should be used primarily**; however, there is also a PAR approach available.
Since **Fritzlar Precision is currently not implemented on VATSIM**, PAR approaches can only be conducted if traffic levels permit - if necessary, Fritzlar Radar can coordinate with civilian ATC to keep other inbound traffic outside of the airspace while a PAR approach is taking place; whether this is possible, however, depends on the current workload of civilian ATC.
# ETHN - Niederstetten Airbase
# Overview
Niederstetten is a Bundeswehr base in Niederstetten with mixed military and civilian use. The airport was built during World War II as a temporary field and abandoned after the end of the war; however, when the post-war Luftwaffe was formed, the rudimentary infrastructure was built out to a permanent airfield which was improved even further in recent years, including a runway extension. While traffic consists primarily of helicopters of the Transporthubschrauberregiment 30, including multiple SAR helicopters, the airport is also used by civilian general and business aviation traffic.
As Niederstetten is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the MIL AIP, GEMIL FLIP VAD, and CENOR FLIP in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Niederstetten is an unrestricted airport**. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. The radar position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher. However, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
### Niederstetten ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **Tower**
| THNT
| ETHN\_TWR
| 134.205
| military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Arrival**
| THNA
| ETHN\_APP
| 127.190
| military station
| unrestricted: no course |
All stations at Niederstetten use the **callsign "Stetten"**, e.g. "Stetten Radar".
### Quickview
[](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/WE8DXSQkaF4R43x "ETHN Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Tower
Stetten Tower is responsible for all movements at the airport and within the CTR as well as all enroute and startup clearances.
### General
##### Enroute clearances
All enroute clearances must be **coordinated with Stetten Radar**. The clearance will be given by Stetten Radar to be **relayed to the pilot** by Stetten Tower. Usually, pilots are first given their startup and taxi clearance and the enroute clearance is coordinated while the aircraft is on its way to the runway to be **given at the holding point shortly before departure**. If Stetten Radar is offline, the enroute clearance has to be coordinated with the appropriate civilian radar controller.
Further information on clearances to be given can be found in the [ETHN Approach SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/approach-h5C "ETHN Approach SOP").
##### Civilian apron
Civilian traffic may move without taxi clearance on the civilian apron in the North. These aircraft only need taxi clearance from the fence onward.
### IFR traffic
All IFR traffic shall use the hard surface runway. The grass lanes and the helipad are only available for VFR helicopter traffic.
##### Departures
A **departure release for all IFR departures** shall be obtained from Stetten Radar.
Departures shall be handed off to Stetten Radar as soon as possible.
##### Arrivals
For IFR arrivals on a PAR approach, a landing clearance shall be relayed to Stetten Radar.
### VFR traffic
##### Grass lanes
The grass lanes are only available for VFR helicopter emergency landings.
##### Reporting points
There are seven reporting points around the Niederstetten CTR, all of which except for two are mandatory reporting points.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
| **Remark**
|
| **November 1**
| wind turbines Northeast of Queckbronn | -- |
| **November 2**
| East of Ebertsbronn village | non-compulsory reporting point |
| **Whiskey 1**
| wind turbine West of Rot village | -- |
| **Whiskey 2**
| power lines over B290 | non-compulsory reporting point |
| **Echo**
| Schön village | -- |
| **Hotel**
| Leuzendorf airfield | -- |
| **Sierra**
| forest between B290 and Schrozberg | -- |
# Approach
Stetten Radar is responsible for all airborne traffic within the Stetten approach sector as well as coordinating all enroute clearances for IFR departures out of Niederstetten airport.
Stetten Radar shall **always inform the controllers of EDGG sectors Dinkelsbühl, König, and Stuttgart** as well as **EDMM sector Franken** when opening and closing the position.
### Airspace
The airspace controlled by Stetten Radar is class E which is lowered to 1000ft AGL in the majority of the area of responsibility with small sections of class E lowered to 1700ft AGL in the North and Southeast.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/ethn.png)
### Niederstetten departure procedures
##### Enroute clearances
Enroute clearances must **always be coordinated with all concerned adjacent sectors**. Exact routings to the first fix in the flight plan must be adapted to the individual traffic situation but **usually a DCT to the first waypoint is the best solution**. The initial climb shall always be at least 3500ft and should not exceed 5000ft. Initial flight levels beyond the upper boundary of the Stetten Radar sector must be coordinated with all concerned sectors. All IFR departures shall use the applicable OID for the departure runway.
The enroute clearance will be requested by Stetten Tower and has to be communicated to Stetten Tower once it has been coordinated. Stetten Tower will then relay the clearance to the pilot.
##### Departure release
During 06 operations, Nörvenich Radar shall obtain a further departure release from DKA before granting a departure release to Nörvenich Tower. If possible, Nörvenich Radar should also instruct Nörvenich Tower to hand off departures directly to DKA.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC
Handoffs for departures shall always be **coordinated individually** (preferably while coordinating the enroute clearance) and then take place as agreed, but **usually a handoff at the sector border is the best solution**.
### Niederstetten arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC
Handoffs for arrivals shall always be **coordinated individually** and then take place as agreed. Stetten Radar should, whenever possible, approach civilian ATC with a proposal for the handoff ahead of time, but **usually a DCT to the respective IAF** (07 operations: NIBKO, 25 operations: TIMLO) **at 5000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
##### Approach
Niederstetten has an RNP approach to both runways as well as an ILS approach to runway 25.
During 25 operations, the **ILS approach should be used primarily**; however, there is also a PAR approach available for both runways.
Since **Stetten Precision is currently not implemented on VATSIM**, PAR approaches can only be conducted if traffic levels permit - if necessary, Stetten Radar can coordinate with civilian ATC to keep other inbound traffic outside of the airspace while a PAR approach is taking place; whether this is possible, however, depends on the current workload of civilian ATC.
### Giebelstadt departure procedures
##### Enroute clearances
Pilots shall always be cleared on the applicable SID to their first waypoint depending on the runway in use. The initial climb is always 5000ft via SID.
The enroute clearance will be requested by Giebelstadt Information who will in turn relay the clearance to the pilot.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC
Departures shall be handed off to Langen Radar as soon as possible to enable a continuous climb.
### Giebelstadt arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC
Handoffs for arrivals shall always be **coordinated individually** and then take place as agreed. Stetten Radar should, whenever possible, approach civilian ATC with a proposal for the handoff ahead of time, but **usually a DCT to COSJE at 5000ft or the lowest available flight level is the best solution**.
# ETNG - Geilenkirchen Airbase
# Overview
Geilenkirchen is a NATO base in Geilenkirchen. The airfield was originally built and used by British occupation forces after World War II and later handed over to the German Luftwaffe for a short time before becoming a NATO headquarter and the most important AWACS base in Europe. In addition to the military operations, the aeroclub Geilenkirchen conducts civilian general aviation flights at the airport, albeit primarily outside of the military operating hours.
As Geilenkirchen is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the MIL AIP, GEMIL FLIP VAD, and CENOR FLIP in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Geilenkirchen is an unrestricted airport**. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. The radar position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher, although it is **recommended to hold the EDDL\_APP Tier 1 endorsement** for familiarity with the surrounding airspace. Additionally, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
### Geilenkirchen ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ATNG
| ETNG\_ATIS
| 118.090
| --
| --
|
| **Tower**
| TNGT
| ETNG\_TWR
| 120.055
| military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Arrival**
| TNGA
| ETNG\_APP
| 123.730
| military station
| unrestricted: no course |
| Bottrop sector
| BOT
| EDDL\_BOT\_APP
| 119.110
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDL\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)") |
All stations at Geilenkirchen use the **callsign "Frisbee"**, e.g. "Frisbee Radar".
### Quickview
[](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/ytis2RXLLSKDWTz "ETNG Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Tower
Frisbee Tower is responsible for all movements at the airport and within the CTR as well as all enroute and startup clearances.
### General
##### Operating direction
Whenever traffic levels and weather conditions allow, opposite direction operations should be used with runway 09 as departure runway and 27 as arrival runway.
##### Enroute clearances
All IFR departures shall be cleared for the applicable SID according to the departure runway.
Whenever there is no SID to the first waypoint or the pilot requests an OID for departure, the enroute clearance must be **coordinated with Frisbee Radar**. The clearance will be given by Frisbee Radar to be **relayed to the pilot** by Frisbee Tower. If Frisbee Radar is offline, the enroute clearance has to be coordinated with the appropriate civilian radar controller.
Further information on clearances to be given can be found in the [ETNG Approach SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/approach-xCn "ETNG Approach SOP").
### IFR traffic
All IFR traffic shall use the hard surface runway.
##### Departures
A **departure release for all IFR departures** shall be obtained from Frisbee Radar during 09 operations and from Beek Approach during 27 operations as well as from Bottrop sector regardless of operating direction.
Departures shall be handed off to Frisbee Radar (09 operations) or Beek Approach (27 operations) as soon as possible unless otherwise coordinated.
##### Arrivals
For IFR arrivals on a PAR approach, a landing clearance shall be relayed to Frisbee Radar.
In case of a missed approach, Frisbee Radar (during all operations) and Beek Approach (during 27 operations) shall be informed immediately.
### VFR traffic
##### General
VFR approaches are only possible during 27 operations; VFR departures are only possible during 09 operations.
VFR traffic going around or conducting low approaches/touch and goes shall always be instructed to remain over German territory.
> **Frisbee Tower**: D-ETNG, cleared touch and go runway 27 grass, join right circuit runway 27, remain over German territory.
##### Grass lane
The grass lane may be **used in parallel** to the hard surface runway. It is only available for aircraft with a maximum wingspan of 15m. Traffic circuits for the grass lane shall always take place to the North.
##### Break direction
Overhead breaks shall only take place toward the South.
##### Reporting points
There are seven reporting points around the Geilenkirchen CTR, all of which are mandatory reporting points.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
| **Remark**
|
| **November 1**
| Adolfosee lake | -- |
| **November 2**
| Tripsrath village | -- |
| **Sierra 1**
| Plitschard village | -- |
| **Sierra 2**
| Siepenbusch village | -- |
| **Entry North
Exit North**
| quarry lake Baal | Entry North for military traffic during 27 operations only
Exit North for military traffic during 09 operations only |
| **Entry South
Exit South**
| Blausteinsee lake | Entry South for military traffic during 27 operations only
Exit South for military traffic during 09 operations only |
| **Initial**
| Immendorf village | for military traffic during 09 operations only |
# Approach
Frisbee Radar is responsible for all airborne traffic within the Geilenkirchen approach sector as well as coordinating all enroute clearances for IFR departures out of Geilenkirchen airport.
Frisbee Radar shall **always inform the controllers of EDGG sectors Bottrop, Düsseldorf Arrival, Köln Arrival** as well as **EHAA sector Beek** when opening and closing the position.
### Airspace
The airspace controlled by Frisbee Radar is class E which is lowered to 1000ft AGL in the entire area of responsibility.
[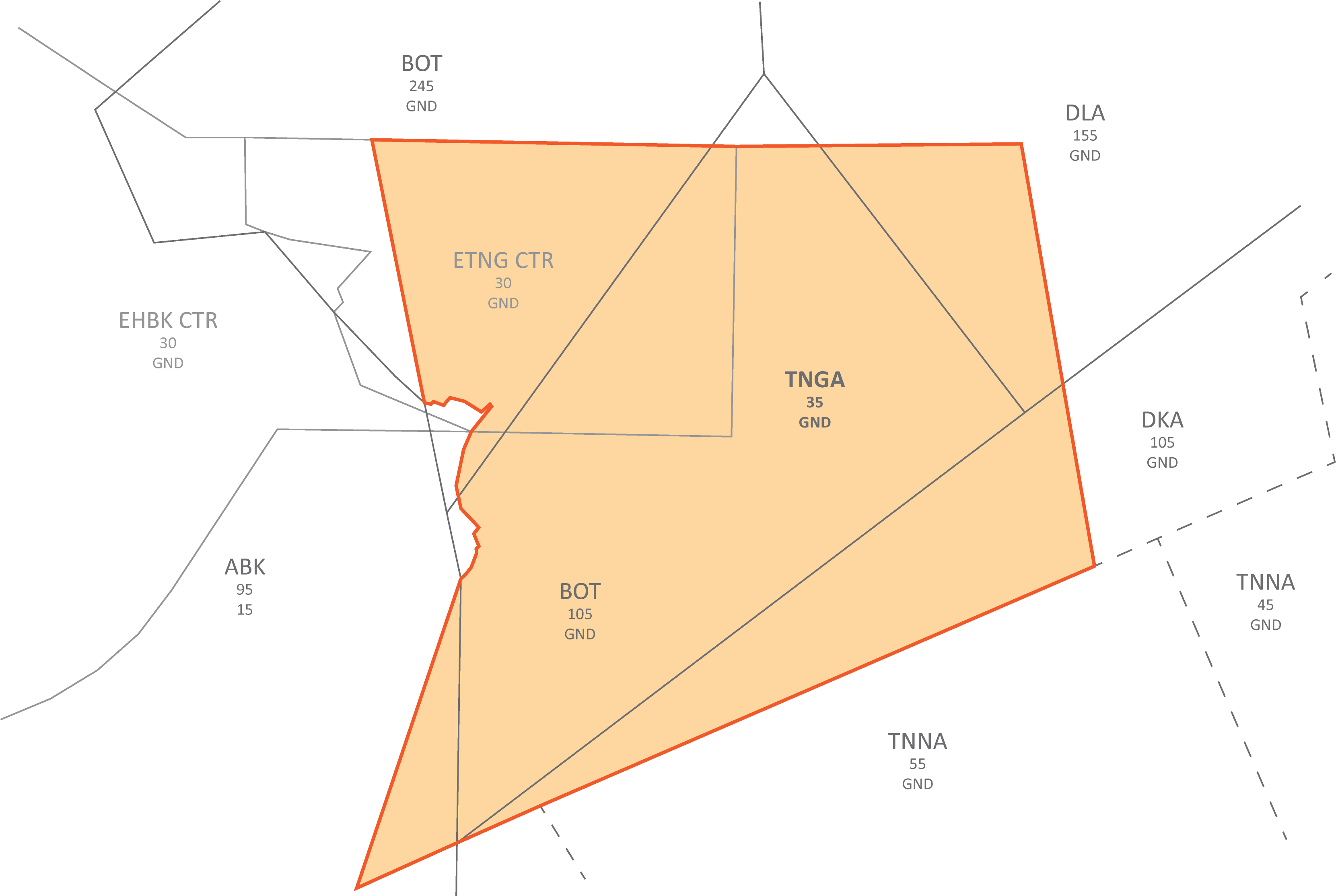](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etng.png)
### Departure procedures
##### Enroute clearances
Enroute clearances for OID departures must **always be coordinated with all concerned adjacent sectors**. Exact routings to the first fix in the flight plan must be adapted to the individual traffic situation but **usually a DCT to the first waypoint is the best solution**. The initial climb shall always be at least 3000ft. Initial flight levels beyond the upper boundary of the Frisbee Radar sector must be coordinated with all concerned sectors.
The enroute clearance for OID departures will be requested by Frisbee Tower and has to be communicated to Frisbee Tower once it has been coordinated. Frisbee Tower will then relay the clearance to the pilot.
For departures from runway 27, the initial climb always has to be coordinated with Beek Approach.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC
All departures on an SID shall be handed off before reaching the sector border and Frisbee Radar shall obtain a release by Bottrop sector for all departures.
Handoffs for OID departures shall always be **coordinated individually** (preferably while coordinating the enroute clearance) and then take place as agreed, but **usually a handoff at the sector border is the best solution**.
##### 27 departures
Departures out of runway 27 will not be sent to Frisbee Radar unless otherwise agreed. The default departure controller for these is Beek Approach.
### Arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC
Handoffs for arrivals shall always be **coordinated individually** and then take place as agreed. Frisbee Radar should, whenever possible, approach civilian ATC with a proposal for the handoff ahead of time, but **usually a DCT to an appropriate IAF or to GIX** **at 4000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
##### Approach
Geilenkirchen has a TACAN and an RNP approach to both runways as well as an ILS to runway 27.
During 27 operations, the **ILS approach should be used primarily**; however, there is also a PAR approach available for both runways.
Since **Frisbee Precision is currently not implemented on VATSIM**, PAR approaches can only be conducted if traffic levels permit - if necessary, Frisbee Radar can coordinate with civilian ATC to keep other inbound traffic outside of the airspace while a PAR approach is taking place; whether this is possible, however, depends on the current workload of civilian ATC.
During 09 operations, arriving traffic will be guided to final approach by Beek Approach and sent directly to Frisbee Tower unless otherwise agreed.
# ETNN - Nörvenich Airbase
# Overview
Nörvenich is a Bundeswehr base in Nörvenich. Originally built as an RAF base after World War II, it was transferred to the German military almost immediately after construction was completed and became the first airport of the newly formed German Luftwaffe. Today, it is home to the Taktische Luftwaffengeschwader 31 and a SAR helicopter from the Transporthubschrauberregiment 30. Additionally, it serves as an alternate for aircraft stationed at Geilenkirchen and Büchel air base.
As Nörvenich is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the MIL AIP, GEMIL FLIP VAD, and CENOR FLIP in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Nörvenich is an unrestricted airport**. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. The radar position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher, although it is **recommended to hold the EDDK\_APP Tier 1 endorsement** for familiarity with the surrounding airspace. Additionally, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
### Nörvenich ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **Tower**
| TNNT
| ETNN\_TWR
| 136.205
| military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Arrival**
| TNNA
| ETNN\_APP
| 129.055
| military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| Arrival (EDDK)
| DKA
| EDDK\_APP
| 135.350
| --
| Tier 1: [EDDK\_APP](https://core.vateud.net/my/endorsements "Your endorsements (VATEUD Core)")
|
### Quickview
[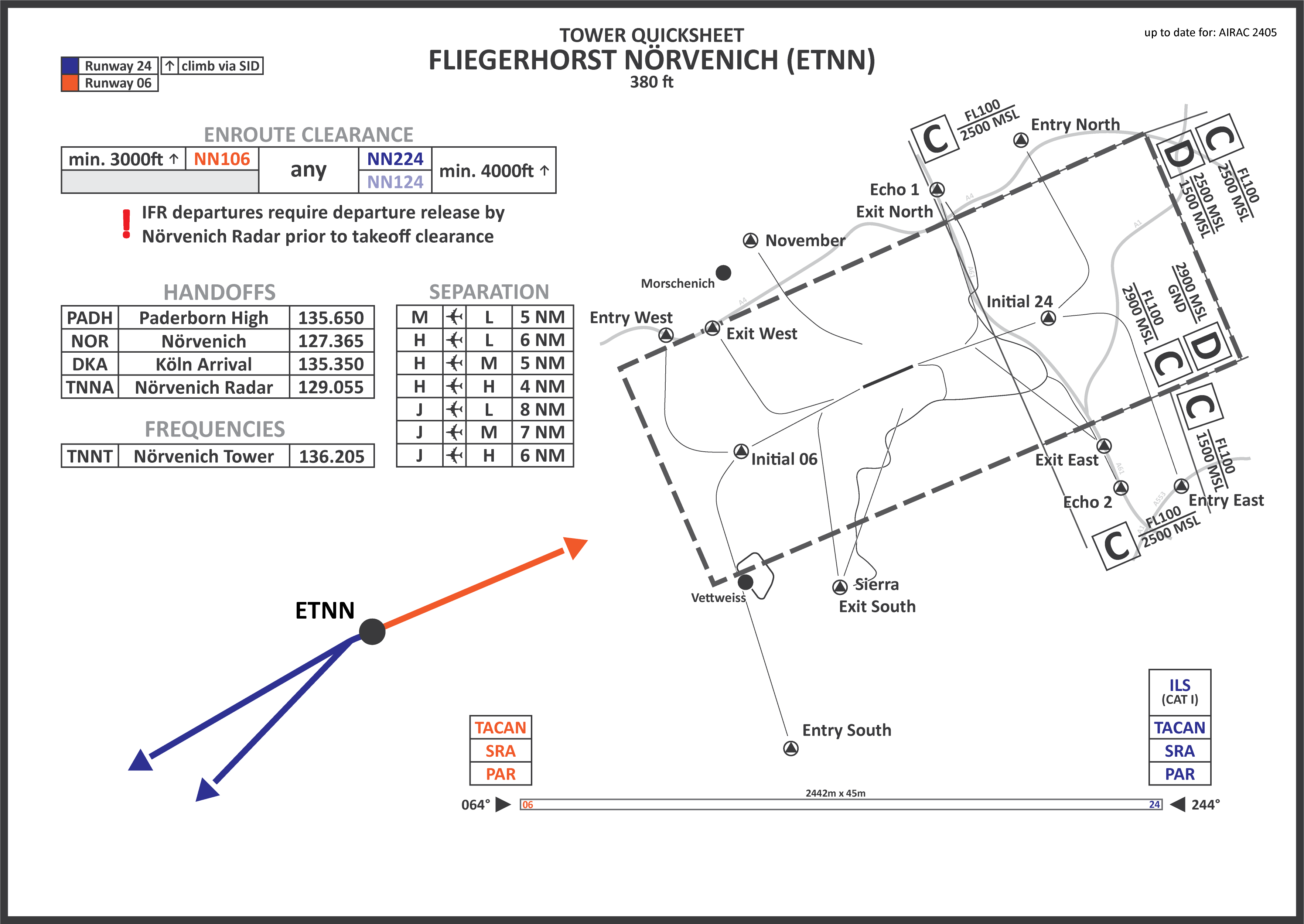](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/ALiGbnrHLn5DckA "ETNN Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Tower
Nörvenich Tower is responsible for all movements at the airport and within the CTR as well as all enroute and startup clearances.
### General
##### Operating direction
The operating direction shall generally decided based on the weather conditions. However, depending on the traffic situation and active runway at EDDK, it may be beneficial for the expeditious flow of traffic to use runway 24 for departures and runway 06 for arrivals, weather permitting.
##### Enroute clearances
All enroute clearances must be **coordinated with Nörvenich Radar**. The clearance will be given by Nörvenich Radar to be **relayed to the pilot** by Nörvenich Tower. Usually, pilots are first given their startup and taxi clearance and the enroute clearance is coordinated while the aircraft is on its way to the runway to be **given at the holding point shortly before departure**. If Nörvenich Radar is offline, the enroute clearance has to be coordinated with the appropriate civilian radar controller.
Further information on clearances to be given can be found in the [ETNN Approach SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/approach-JlS "ETNN Approach SOP").
### IFR traffic
All IFR traffic shall use the hard surface runway. The grass lanes are only available for VFR helicopter traffic.
##### Departures
A **departure release for all IFR departures** shall be obtained from Nörvenich Radar.
Departures shall be handed off to Nörvenich Radar as soon as possible.
##### Arrivals
For IFR arrivals on a PAR approach, a landing clearance shall be relayed to Nörvenich Radar.
In case of a missed approach, Nörvenich Radar and DKA shall be informed immediately.
### VFR traffic
##### Grass lanes
The grass lanes may all be **used in parallel** to the hard surface runway and other grass lanes. They are generally only used for helicopter traffic.
##### Noise abatement
Jet traffic is only permitted in the Northern pattern. Additionally, overhead breaks shall only take place toward the North.
##### Reporting points
There are twelve reporting points around the Nörvenich CTR, all of which are mandatory reporting points.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
| **Remark**
|
| **November**
| forest Hambacher Forst | for non-military or crossing traffic only |
| **Sierra
Exit South**
| roundabout L33 and L264 | Sierra for SAR and non-military or crossing traffic only
Exit South for military traffic during 24 operations only |
| **Echo 1
Exit North**
| rail bridge over A61 | Echo 1 for SAR only
Exit North for military traffic during 06 operations only |
| **Echo 2**
| highway A1 West of Bliesheim | for SAR only |
| **Entry North**
| bridge Horremer Brücke | for military traffic during 24 operations only |
| **Exit East**
| intersection L265 and A1 | for military traffic during 06 operations only |
| **Entry East**
| highway A553 service station Am Alten Hau | for military traffic during 24 operations only |
| **Exit West**
| parallel highway A4 and rail tracks split up | for military traffic during 24 operations only |
| **Entry West**
| intersection L264 and A4 | for military traffic during 06 operations only |
| **Entry South**
| lake Neffelsee | for military traffic during 06 operations only |
| **Initial 06** | farm Eko Farm Nörvenich | for military traffic during 06 operations only; non-cumpolsory |
| **Initial 24** | town center Balkhausen | for military traffic during 24 operations only; non-cumpolsory |
##### Vettweiss
Vettweiss' traffic circuit is located partially within the Nörvenich CTR. Pilots flying at Vettweiss require an individual clearance to enter the CTR.
# Approach
Nörvenich Radar is responsible for all airborne traffic within the Nörvenich approach sector as well as coordinating all enroute clearances for IFR departures out of Nörvenich airport.
Nörvenich Radar shall **always inform the controller of EDGG sector Köln Arrival** when opening and closing the position.
### Airspace
The airspace controlled by Nörvenich Radar is class E which is lowered to 1000ft AGL in the majority of the area of responsibility with a small section of class E starting only from 2500ft AGL in the South. Additionally, within the Eastern sector, parts of the area of responsibility are class C within the Köln/Bonn TMA.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etnn.png)
##### Airspace boundary
Nörvenich Radar may use the entire lateral range of the sector. Langen Radar is responsible for maintaining full lateral separation to the sector border.
### Departure procedures
##### Enroute clearances
Enroute clearances must **always be coordinated with all concerned adjacent sectors**. Exact routings to the first fix in the flight plan must be adapted to the individual traffic situation but **usually a DCT to the first waypoint is the best solution**. The initial climb shall always be at least 3000ft during 06 operations and 4000ft during 24 operations and should not exceed 5000ft. Initial flight levels beyond the upper boundary of the Nörvenich Radar sector must be coordinated with all concerned sectors. All IFR departures shall use the applicable OID for the departure runway; during 24 operations, NN224 shall be used primarily.
The enroute clearance will be requested by Nörvenich Tower and has to be communicated to Nörvenich Tower once it has been coordinated. Nörvenich Tower will then relay the clearance to the pilot.
##### Departure release
Nörvenich Radar shall obtain a further departure release from DKA before granting a departure release to Nörvenich Tower. If possible, Nörvenich Radar should also instruct Nörvenich Tower to hand off departures directly to DKA.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC
Handoffs for departures shall always be **coordinated individually** (preferably while coordinating the enroute clearance) and then take place as agreed, but **usually a handoff at the sector border is the best solution**.
### Arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC
Civilian ATC will hand off traffic from the South inbound IZWOK at FL70 and traffic from the North inbound NVO at 5000ft. All inbounds are fully released.
##### Approach
Nörvenich has a TACAN approach to both runways. Civilian aircraft types will usually not be able to fly TACAN approaches and will thus have to use the ILS 24 with a circling during 06 operations.
During 24 operations, the **ILS approach should be used primarily**; however, there is also a PAR approach available for both runways.
Since **Nörvenich Precision is currently not implemented on VATSIM**, PAR approaches can only be conducted if traffic levels permit - if necessary, Nörvenich Radar can coordinate with civilian ATC to keep other inbound traffic outside of the airspace while a PAR approach is taking place; whether this is possible, however, depends on the current workload of civilian ATC.
Additionally, in order to move traffic onto final approach during 24 operations, Nörvenich Radar needs to activate sector A (the Easternmost sector which is not part of Nörvenich Radar's airspace by default). **Nörvenich Radar shall inform DKA immediately when activating and deactivating sector A** and shall make sure to open the sector only for the absolute minimum amount of time required.
> **TNNA**: DKA, Nörvenich Radar.
> **DKA**: Go ahead.
> **TNNA**: Sector A now active.
> **DKA**: Roger.
> **TNNA**: DKA, Nörvenich Radar.
> **DKA**: Go ahead.
> **TNNA**: Sector A deactivated.
> **DKA**: Roger.
# ETOU - Wiesbaden Airbase
# Overview
Wiesbaden is a United States Army Air Forces base in Wiesbaden. It hosts mainly helicopters and smaller training aircraft (e.g. Beechcraft King Airs), but can also support smaller jetliners. Its location directly next to the the Frankfurt CTR and below the Frankfurt TMA make it a very interesting airport that can require a lot of coordination. Additionally, it has probably the most complex VFR procedures of any controlled airport in Germany.
Due to Wiesbaden being an American airfield, **controllers may use FAA procedures and phraseology** if they are familiar with them, but are not required to do so.
As Wiesbaden is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the GEMIL FLIP US DoD in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Wiesbaden is an unrestricted airport**. The Ground position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S1** rating or higher. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher, although it is **recommended to hold the EDDF\_TWR and EDDF\_APP Tier 1 endorsements** for familiarity with the surrounding airspace. Additionally, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
### Wiesbaden ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remark**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **ATIS**
| ATOU
| ETOU\_ATIS
| 119.030
| --
| --
|
| **Ground**
| TOUG
| ETOU\_GND
| 126.555
| American procedures, military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Tower**
| TOUT
| ETOU\_TWR
| 122.100
| American procedures, military station
| unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[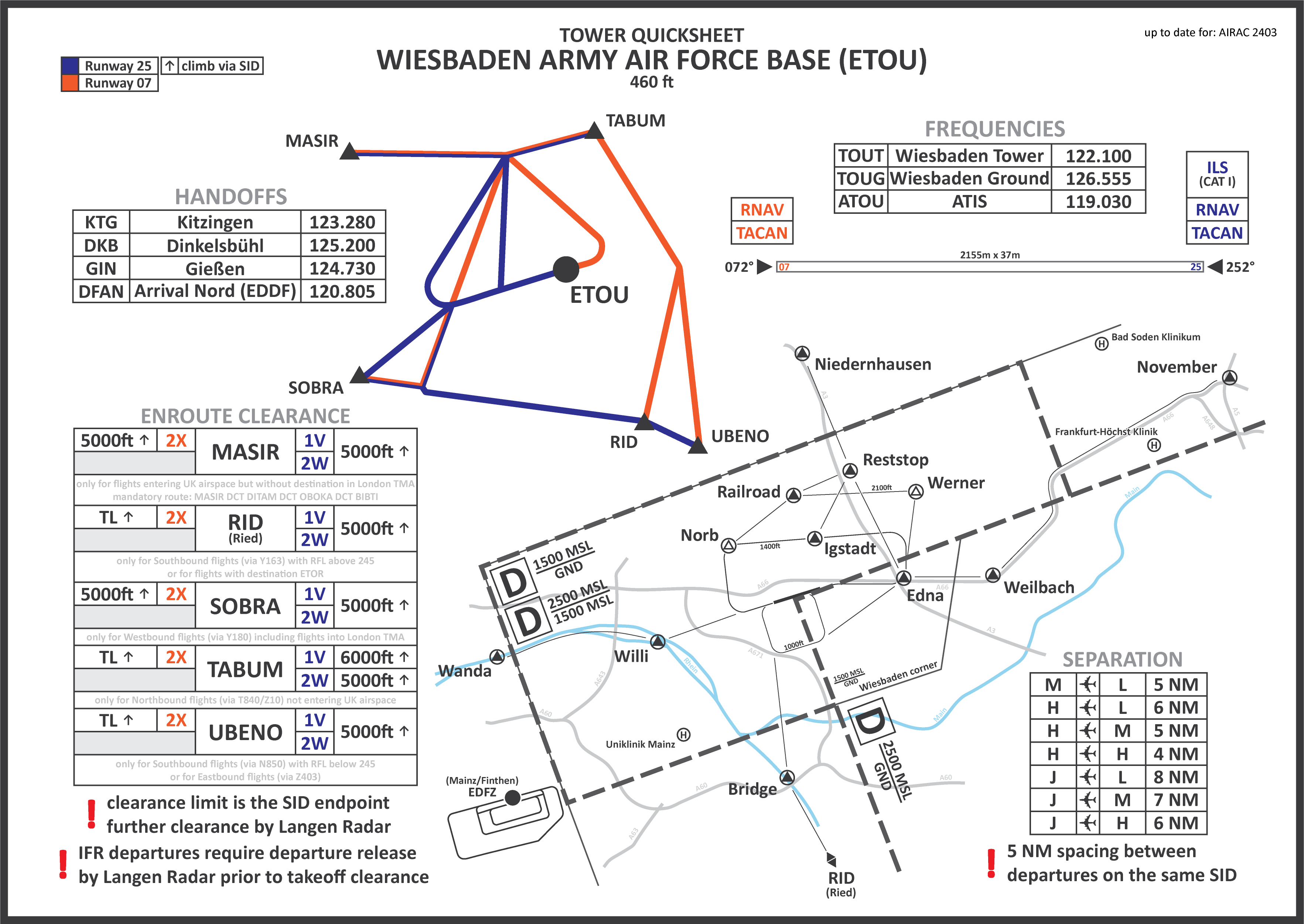](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/yCRGH3zSiRPWirf "ETOU Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Ground
Wiesbaden Ground is responsible for all enroute and startup clearances as well as ground movements at the airport.
### SID assignment
##### 25 operations
SIDs with **designator V should be primarily assigned to all aircraft**. SIDs with designator W require TACAN and should only be assigned on pilot request and/or if the pilot's flight plan indicates that the aircraft is TACAN-equipped.
##### 07 operations
All SIDs out of runway 07 (designator X) require TACAN. Aircraft that are not equipped with TACAN **have to depart VFR and pick up IFR in the air** from Langen Radar. When traffic levels at both Wiesbaden and Frankfurt/Main permit, an **opposite departure out of runway 25 on a V-SID can be coordinated with DFAN**.
##### Restrictions
Due to the complex air traffic environment in the area around Frankfurt/Main, **IFR departures are only possible following the SIDs**. Visual or radar vectored departures are not permitted.
| **Waypoint**
| **Restrictions**
|
| **MASIR**
| only flights **entering British airspace** (except when destination is in London TMA) intending to use **upper airspace** (FL245+) and able to cross BIBTI at or above FL250
**mandatory routing**: MASIR DCT DITAM DCT OBOKA DCT BIBTI
|
| **RID** *Ried*
| only **Southbound flights** intending to use **upper airspace** (FL245+)
or flights to **ETOR**
|
| **SOBRA**
| only **Westbound flights** (including flights with destination in London TMA)
|
| **TABUM**
| only **Northbound flights** (except when entering British airspace)
|
| **UBENO**
| only **Southbound flights not entering upper airspace** (FL245-) or **Eastbound flights** |
### Ground Movement
##### Pushback
All parking positions on Ramp C are taxi-out. All parking positions on Ramps A and B require a pushback for all fixed wing aircraft except from stands 1 thru 8. However, **when traffic permits, taxi-out is available from all positions**.
##### Stand assignment
While concrete stand numbers are publicly available for Ramps A and B, most **pilots should be expected to not be aware of them**. Because of this, the automatic stand assignment only assigns the ramp instead of a specific position.
##### VIP spot
In front of the base ops office is a VIP spot for helicopters. This **blocks part of the ramp taxiway** and is **not a permanent parking position**. Any helicopters dropping off VIPs shall be guided from the runway to the VIP spot and afterwards to the final parking position. Likewise, any helicopters picking up VIPs shall be guided from their parking position to the VIP spot and afterwards to the runway. This may require 180° turns on the taxiway, traffic permitting.
# Tower
Wiesbaden Tower is responsible for all traffic on the runway and in the CTR of the airport.
### General
##### Operating direction
The operating direction at Wiesbaden shall match the operating direction in Frankfurt/Main.
##### Runway crossing
**Ground may delegate taxiway F to Tower**. If taxiway F is not delegated to Tower, runway crossings have to either be coordinated or aircraft have to switch to Tower for the crossing.
##### "Wiesbaden corner"
Part of the Frankfurt CTR can be delegated to Wiesbaden Tower; this area is called the "Wiesbaden corner". It allows operations in the Southern traffic circuit without individual coordination with Frankfurt Tower.
### IFR traffic
##### Outbound
All IFR departures require a **departure release from DFAN**. Wiesbaden Tower shall hand off all IFR departures to Langen Radar as soon as possible.
##### Inbound
Both runways have an RNAV and a TACAN approach and for runway 25, an ILS or LOC DME approach is additionally available.
### VFR traffic
##### Outbound
There are different outbound VFR routes with the same name. Which one the pilot has to fly depends on aircraft type and runway in use. Keep in mind that these routes are only published in the military AIP and pilots might not be aware of their names or restrictions; when in doubt, pilots shall be given the exact routing instead of the name.
The maximum speed for all outbound aircraft within 10 NM of the airport is 140 KIAS.
| **Departure**
| **Routing**
| **Remarks**
|
| **Route November**
(07 ops)
*Helicopters only*
| EDNA *(at 1000ft)* - RESTSTOP - NIEDERNHAUSEN
| one way at night
|
| **Route November** (07 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| EDNA *(at 1000ft)* - RESTSTOP - NIEDERNHAUSEN | one way at night
|
| **Route November**
(25 ops)
*Helicopters only*
| exit South pattern on base - EDNA *(at 1000ft)* - RESTSTOP - NIEDERNHAUSEN
| one way at night
|
| **Route November** standard pattern
(25 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| IGSTADT *(at 1400ft)* - RESTSTOP - NIEDERNHAUSEN
| one way at night
|
| **Route November** extended pattern
(25 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| RAILROAD *(at 2100ft)* - RESTSTOP - NIEDERNHAUSEN
| only on pilot request
**approval by DFAN mandatory**
**clearance to enter airspace D required**
|
| **Route Echo**
*Helicopters only*
| EDNA - WEILBACH - NOVEMBER
| **approval by Frankfurt Tower mandatory**
frequency change to Frankfurt Tower takes place prior WEILBACH
|
| **Route Apache**
(07 ops)
*Helicopters only*
| exit South pattern on downwind - WEILBACH *(at 1000ft)* - NOVEMBER
| **deconfliction route by ATC only**
**approval by Frankfurt Tower mandatory**
frequency change to Frankfurt Tower takes place abeam EDNA
|
| **Route Sierra**
*Helicopters only*
| exit South pattern at Southwest corner - BRIDGE - Ried VOR
| avoiding built up area |
| **Route Sierra**
(07 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| exit North pattern on base - BRIDGE - Ried VOR
| avoiding built up area
|
| **Route Sierra**
(25 ops)
*Fixed wing only* | BRIDGE - Ried VOR
| avoiding built up area
|
| **Route Whiskey**
*Helicopters only*
| WILLI *(at 1400ft)* - WANDA
| --
|
| **Route Whiskey**
(07 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| exit North pattern on base - WILLI *(at 1400ft)* - WANDA
| --
|
| **Route Whiskey**
(25 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| WILLI *(at 1400ft)* - WANDA
| --
|
##### Inbound
There are different inbound VFR routes with the same name. Which one the pilot has to fly depends on aircraft type and runway in use. Keep in mind that these routes are only published in the military AIP and pilots might not be aware of their names or restrictions; when in doubt, pilots shall be given the exact routing instead of the name.
The maximum speed for all inbound aircraft within 10 NM of the airport is 140 KIAS.
| **Arrival**
| **Routing**
| **Remarks**
|
| **Route November** (07 ops)
*Helicopters only*
| NIEDERNHAUSEN *(at or below 2100ft)* - RESTSTOP *(at or below 1400ft)* - EDNA *(at 1000ft)*
| one way at night
|
| **Route November** standard pattern
(07 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| NIEDERNHAUSEN *(at or below 2100ft)* - RESTSTOP *(at or below 1400ft)* - IGSTADT
| one way at night
|
| **Route November** extended pattern
(07 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| NIEDERNHAUSEN *(at or below 2100ft)* - RESTSTOP *(at or below 1400ft)* - RAILROAD
| only on pilot request
one way at night
|
| **Route November** (25 ops)
*Helicopters only*
| NIEDERNHAUSEN *(at or below 2100ft)* - RESTSTOP *(at or below 1400ft)* - EDNA *(at 1000ft)*
| one way at night
|
| **Route November**
(25 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| NIEDERNHAUSEN *(at or below 2100ft)* - RESTSTOP *(at or below 1400ft)* - EDNA
| one way at night
|
| **Route Echo**
*Helicopters only*
| NOVEMBER *(at 1400ft)* - WEILBACH - EDNA *(at 1000ft)*
| **approval by Frankfurt Tower mandatory**
frequency change to Wiesbaden Tower takes place between WEILBACH and EDNA
|
| **Route Apache**
(07 ops)
*Helicopters only*
| NOVEMBER *(at 1400ft)* - WEILBACH *(at 1400ft)* - enter South pattern on downwind
| **deconfliction route by ATC only**
**approval by Frankfurt Tower mandatory**
frequency change to Wiesbaden Tower takes place between WEILBACH and EDNA
|
| **Route Sierra**
*Helicopters only*
| Ried VOR *(at 1400ft)* - BRIDGE *(at 1400ft)* - enter South pattern on base
| avoiding built up area |
| **Route Sierra**
(07 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| Ried VOR *(at 1400ft)* - BRIDGE *(at 1400ft)* - enter extended right base
| avoiding built up area
|
| **Route Sierra**
(25 ops)
*Fixed wing only* | Ried VOR *(at 1400ft)* - BRIDGE *(at 1400ft)* - enter North pattern on crosswind
| avoiding built up area
|
| **Route Whiskey**
(07 ops)
*all aircraft*
| WANDA *(at 1400ft)* - WILLI *(at 1400ft)*
| --
|
| **Route Whiskey**
(25 ops)
*Helicopters only*
| WANDA *(at 1400ft)* - WILLI *(at 1400ft)* - enter South pattern on downwind
| --
|
| **Route Whiskey**
(25 ops)
*Fixed wing only*
| WANDA *(at 1400ft)* - WILLI *(at 1400ft)* - enter North pattern on downwind
| --
|
##### Traffic circuit
Wiesbaden has three published traffic patterns: the standard Northern one (pattern altitude 1400ft), the extended Northern one (pattern altitude 2100ft), and the Southern one (pattern altitude 1000ft).
The **Northern pattern is only available for fixed wing aircraft** but exceptions may be granted by Wiesbaden Tower.
**Only one of the two Northern patterns can be in use at any time**. If only propeller aircraft are in the North pattern, the first aircraft to enter the pattern decides the pattern in use; if both jet and propeller aircraft are in the North pattern, the first jet aircraft to enter the pattern decides the pattern in use. The **extended pattern can only be made available with approval by Langen Radar**. Aircraft in the extended pattern will enter airspace D above the CTR, but remain on the frequency of Wiesbaden Tower.
The **Southern pattern is only available for helicopters** but exceptions may be granted by Wiesbaden Tower. The crosswind (07 ops) or base (25 ops) leg is abeam taxiway C. A pattern altitude above 1000ft may be approved by Wiesbaden Tower on pilot request.
##### CTR crossings
CTR crossings must take place along the published VFR routes and will thus have to cross above the airfield.
# ETSB - Büchel Airbase
# Overview
Büchel is a Bundeswehr base in Büchel. The airfield was originally built by the French Army but transferred to Germany shortly after its completion. Today, the airport serves as a base for the Taktische Luftwaffengeschwader 33, although all of its aircraft are currently stationed at Nörvenich air base while Büchel's runway is undergoing construction work; once this construction work is completed, the Luftwaffe plans to station new F-35 fighter jets here as part of NATO's nuclear sharing concept.
As Büchel is a military airport, charts can't be found in the normal AIP. They are accessible through the MIL AIP, GEMIL FLIP VAD, and CENOR FLIP in the [milais](https://www.milais.org/publications.php "MILAIS Publications").
**Büchel is an unrestricted airport**. The Tower position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S2** rating or higher. The radar position can be staffed by all controllers with an **S3** rating or higher. Additionally, controllers should closely familiarize themselves with military procedures before staffing the airport.
Büchel's runway is currently **closed IRL** due to construction work on the runway. Due to this, the **parallel taxiway is used as a substitute runway** for VFR only; departing and arriving traffic has to pick up/cancel IFR after departure/before landing.
### Büchel ATC Stations
| **Station**
| **Station ID**
| **Login**
| **Frequency**
| **Remarks**
| **Endorsement**
|
| **Tower**
| TSBT
| ETSB\_TWR
| 131.460
| military station
| unrestricted: no course
|
| **Arrival**
| TSBA
| ETSB\_APP
| 130.155
| military station
| unrestricted: no course |
### Quickview
[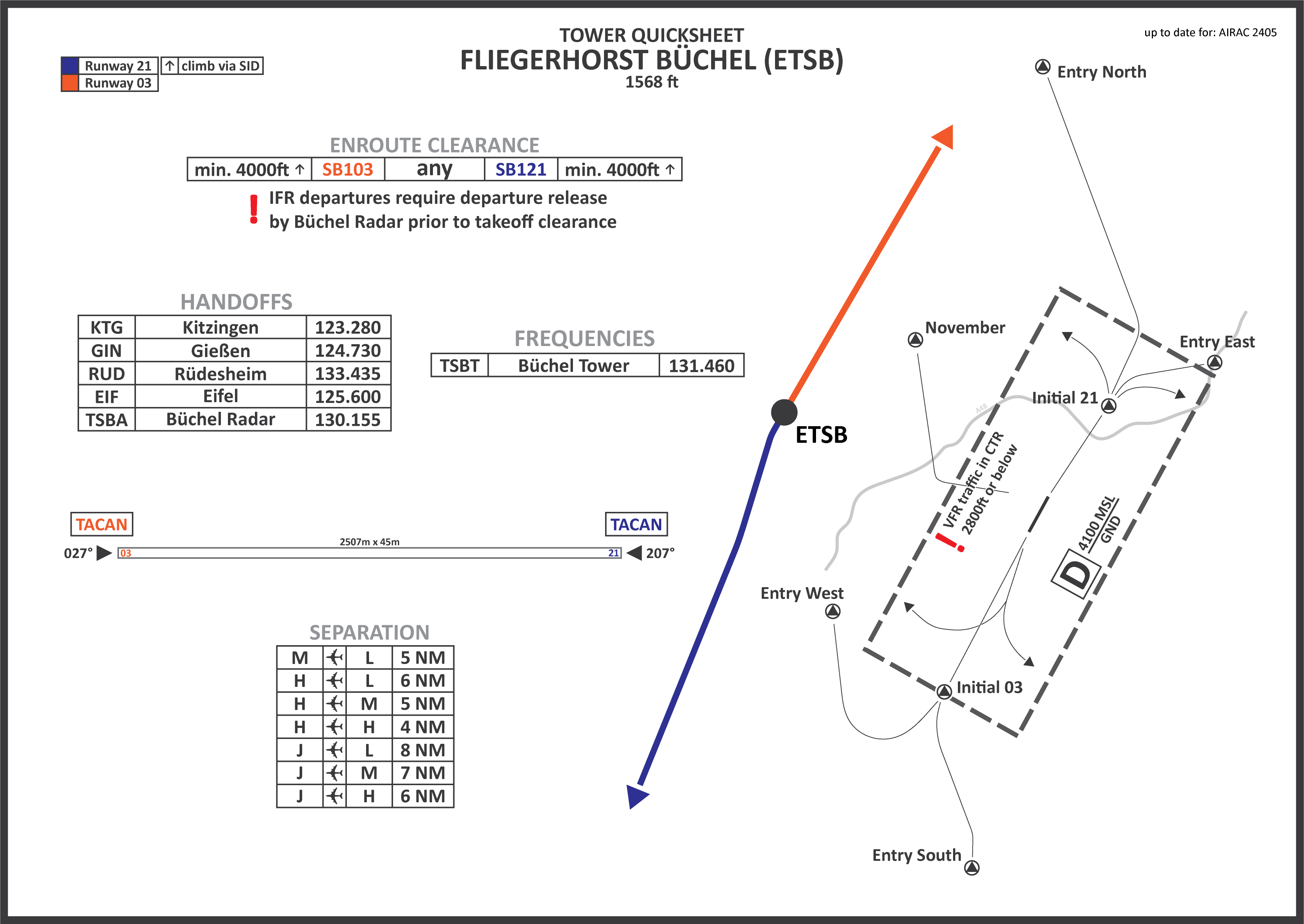](https://dms.vatsim-germany.org/s/4FCeEi8TZT879iJ "ETSB Quicksheet (VATGER DMS)")
*click on the image to open the printable quicksheet*
# Tower
Büchel Tower is responsible for all movements at the airport and within the CTR as well as all enroute and startup clearances.
### General
##### Enroute clearances
All enroute clearances must be **coordinated with Büchel Radar**. The clearance will be given by Büchel Radar to be **relayed to the pilot** by Büchel Tower. Usually, pilots are first given their startup and taxi clearance and the enroute clearance is coordinated while the aircraft is on its way to the runway to be **given at the holding point shortly before departure**. If Büchel Radar is offline, the enroute clearance has to be coordinated with the appropriate civilian radar controller.
Further information on clearances to be given can be found in the [ETSB Approach SOP](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/books/sops-fir-langen/page/approach-tzk "ETSB Approach SOP").
##### Approaches to Spangdahlem (ETAD)
Traffic approaching runway 22 at Spangdahlem Airbase will cross through the Southwestern corner of the Büchel CTR. These crossings are **automatically released** and Büchel Tower shall ensure separation to these aircraft and, if necessary, inform Spangdahlem GCA of any conflicting traffic.
### IFR traffic
##### Departures
A **departure release for all IFR departures** shall be obtained from Büchel Radar.
Departures shall be handed off to Büchel Radar as soon as possible.
##### Arrivals
For IFR arrivals on a PAR approach, a landing clearance shall be relayed to Büchel Radar.
### VFR traffic
##### Break direction
Overhead breaks shall only take place toward the East.
##### Circuit
Circuit operations shall primarily take place toward the East. Jet circuits are not permitted toward the West.
##### Reporting points
There are seven reporting points around the Büchel CTR, all of which are mandatory reporting points.
| **Reporting point**
| **Location**
| **Remark**
|
| **November**
| radio mast Hochkelberg | -- |
| **Entry North**
| radio mast Hellersberg | for military traffic during 21 operations only |
| **Entry East**
| rest stop Elztal | for military traffic during 21 operations only |
| **Entry South**
| bridge Hochmoselbrücke | for military traffic during 03 operations only |
| **Entry West**
| Holzmaar lake | for military traffic during 03 operations only |
| **Initial 03** | solar farm West of Hontheim | for military traffic during 03 operations only |
| **Initial 21** | town of Masburg | for military traffic during 21 operations only |
# Approach
Büchel Radar is responsible for all airborne traffic within the Büchel approach sector as well as coordinating all enroute clearances for IFR departures out of Büchel airport.
Büchel Radar shall **always inform the controller of EDGG sectors Eifel, Köln Arrival, and Taunus** when opening and closing the position.
### Airspace
The airspace controlled by Büchel Radar is class E which is lowered to 1000ft AGL in the majority of the area of responsibility with small sections of class E lowered to 1700ft AGL in the North and Northeast.
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2024-04/etsb.png)
##### Airspace boundary
Büchel Radar may use the entire vertical range of the sector. Langen Radar is responsible for maintaining full vertical separation to the sector border.
### Departure procedures
##### Enroute clearances
Enroute clearances must **always be coordinated with all concerned adjacent sectors**. Exact routings to the first fix in the flight plan must be adapted to the individual traffic situation but **usually a DCT to the first waypoint is the best solution**. The initial climb shall always be 4000ft. Initial flight levels beyond the upper boundary of the Büchel Radar sector must be coordinated with all concerned sectors. All IFR departures shall use the applicable OID for the departure runway.
The enroute clearance will be requested by Büchel Tower and has to be communicated to Büchel Tower once it has been coordinated. Büchel Tower will then relay the clearance to the pilot.
##### Transfer to civilian ATC or Spangdahlem GCA
Handoffs for departures shall always be **coordinated individually** (preferably while coordinating the enroute clearance) and then take place as agreed, but **usually a handoff at the sector border is the best solution**.
### Arrival procedures
##### Transfer from civilian ATC or Spangdahlem GCA
Handoffs for arrivals shall always be **coordinated individually** and then take place as agreed. Büchel Radar should, whenever possible, approach civilian ATC/Spangdahlem GCA with a proposal for the handoff ahead of time, but **usually a DCT to BUE at 4000ft with a full release is the best solution**.
##### Approach
Büchel only has a TACAN approach to both runways.
# ATIS Codes
### Default ATISmaker URL
> http://uniatis.net/atis.php?metar=$metar($atisairport)&arr=$arrrwy($atisairport)&dep=$deprwy($atisairport)&apptype=ILS&info=$atiscode
The above URL is designed for Euroscope versions with only one ATIS. For the newest Euroscope versions with four ATISes, the **letters A, B, C, or D need to be appended** to the $atisairport and $atiscode parameters (e.g. $atisairportA for the first ATIS).
### General ATIS Codes
Add the following code at the end of the ATISmakerURL to include the ATIS broadcast message. For **all airports except Frankfurt** the **departure frequency** has to be included in the ATIS!
| **CODE** | **Broadcast** |
|---|
| **&depfreq=123.123** | ATTENTION! DEPARTURE FREQUENCY FOR ALL DEPARTING AIRCRAFT IS 123.123 |
|---|
| **&lvp** | LOW VISIBILITY PROCEDURES IN OPERATION CAT II AND III AVAILABLE |
|---|
| **>o** *(do not use together with &lvp; at EDDF: DEP ATIS only)*
| LOW VISIBILITY PROCEDURES IN OPERATION CAT III AND GUIDED TAKE-OFF AVAILABLE FOR RUNWAY \[...\] |
|---|
### EDDF ATIS Codes
##### Manual Setup
| **CODE** | **Broadcast** |
|---|
| **&atistype=dep** | *sets the desired ATIS as departure ATIS **(mandatory!)*** |
|---|
| **&atistype=arr** | *sets the desired ATIS as arrival ATIS **(mandatory!)*** |
|---|
| **&acdm** *(DEP)* | ALL IFR DEPS REPORT TOBT AT VACDM.VATGER.DE BEFORE REQ ENROUTE CLEARANCE |
|---|
| **&alternate** *(ARR)* | EXPECT ILS \[...\]
|
|---|
| **&birds** | CAUTION FLOCK OF BIRDS IN VICINITY OF THE AERODROME |
|---|
| **&ilsz** *(ARR)*
| *replaces ILS Y with ILS Z* |
|---|
| **&indep** *(ARR)* | EXPECT INDEPENDENT PARALLEL ILS \[...\]
|
|---|
| **&night** *(DEP)* | *suppresses 18 not available message* |
|---|
| **&rnpx** *(ARR)* | EXPECT RNP X APCH RWY \[...\]
|
|---|
| **&southonly** *(DEP)* | ALL DEPARTING ACFT VIA MARUN, OBOKA AND TOBAK EXPECT SID WITH DESIGNATOR MIKE OR WHISKEY |
|---|
| **&tailwind18** *(DEP)*
| TAILWIND COMPONENT RWY 18 MORE THAN 10 KT PILOTS UNABLE TO ACCEPT SHALL ADVISE ATC UPON START-UP REQUEST |
|---|
| **&windshear07** | WINDSHEAR RUNWAY 07L 07C AND 07R |
|---|
| **&windshear18** | WINDSHEAR RUNWAY 18 |
|---|
| **&windshear25** | WINDSHEAR RUNWAY 25L 25C AND 25R |
|---|
| **&windshearall** | WINDSHEAR ALL RUNWAYS |
|---|
##### Automatic Setup
### EDDL ATIS Codes
##### Manual Codes
| **CODE** | **Broadcast** |
|---|
| **&acdm** | ALL IFR DEPS REPORT TOBT AT VACDM.VATGER.DE BEFORE REQ ENROUTE CLEARANCE |
|---|
| **&windshearall** | CAUTION WINDSHEAR ALL RWYS |
|---|
| **&const23l** | LANDING DISTANCE AVAILABLE RWY 23L 2400 METRES .. VACATE LATEST VIA TWY L8 |
|---|
| **&const23r** | LANDING DISTANCE AVAILABLE RWY 23R 2100 METRES .. IF ABLE VACATE VIA TWY K3 .. LATEST K4 .. RWY CLOSED WEST OF K4 |
|---|
### EDDK ATIS Codes
##### Manual Codes
| **CODE** | **Broadcast** |
|---|
| **&acdm** | ALL IFR DEPS REPORT TOBT AT VACDM.VATGER.DE BEFORE REQ ENROUTE CLEARANCE |
|---|
| **&cdo** | EXPECT CDO FOR ILS APCH |
|---|
| **&sra** | SRA APPROACH ON REQUEST |
|---|
| **&windshearall** | CAUTION WINDSHEAR ALL RWYS |
|---|
### EDDS ATIS Codes
##### Manual Setup
| **CODE** | **Broadcast** |
|---|
| **&acdm** | ALL IFR DEPS REPORT TOBT AT VACDM.VATGER.DE BEFORE REQ ENROUTE CLEARANCE |
|---|
| **&sra** | SRA APPROACH AVAILABLE ON REQUEST
|
|---|
### EDSB ATIS Codes
##### Automatic Setup
### EDFM ATIS Codes
##### Manual Setup
### EDFQ ATIS Setup
As EDFQ lacks its own certified METAR, automatic ATIS updates are currently not possible. However, an ATIS can still be generated manually using the following steps:
- replace the *$metar($atisairportA)* parameter in the ATIS maker URL with the latest [official EDFQ METAR](https://www.viessmann.family/de/was-wir-tun/real-estate/flugplatz-allendorf/informationen-fuer-piloten.html "EDFQ Weather Information (airport website)")
- replace the EDFQ ICAO in the METAR with *EDZZ*
- continue connecting the ATIS as usual
You will have to manually update the ATIS this way every time a new EDFQ METAR is published.
### EDLA ATIS Setup
As EDLA lacks its own certified METAR, automatic ATIS updates are currently not possible. However, an ATIS can still be generated manually using the following steps:
- replace the *$metar($atisairportA)* parameter in the ATIS maker URL with the latest EDLW METAR
- replace the EDLW ICAO in the METAR with *EDZZ*
- remove the *&apptype* and *&depfreq* parameters entirely
- continue connecting the ATIS as usual
You will have to manually update the ATIS this way every time a new EDLW METAR is published.
# ATC Coordinator Position
Coordinators supervise a specific group of controllers during high traffic operations or events. They are responsible for keeping an eye on all traffic in their area of responsibility and, if necessary, taking control measures to enable efficient traffic flow. Their key duties are
- supervising airport and frequency capacities,
- decide and coordinate flow management regulations,
- coordinating between controller groups, especially while primary controllers are busy.
A coordinator has the **responsibility to make own decisions which apply to all members of his/her controller group** based on weather, traffic flow and frequency load.
### General conditions
To observe the situation, Coordinators should login as CO\_DEL/TWR/APP/CTR without having a primary frequency set (expect for DEL/TWR). Additional plugins (e.g. Arrival Manager, Topsky features) can be used or may be mandatory during events.
Usually the Coordinators are seperate stations. If there are not enough controllers available for that, the station with the lowest workload should do the coordinator tasks. This station may change during the day and staffing. However, the primary frequency must always be the first task in this case.
Coordination shall always take place by voice (Teamspeak or VCCS). Only if one station is available by text only (e.g. for neightbouring countries) privat chat may be used.
### Delivery Coordinator Duties
With an increased number of flights on the network especially during events and online days the task of Delivery is getting more and more important and the workload is increasing immensely. To handle the outbound traffic the most efficient way it is recommended to work Delivery with two controllers, one operator and one coordinator.
**vACDM** should **not be used** during high traffic situations due to server issues.
**Operator:** The operator is responsible for all **voice communication** with the pilots on the frequency (enroute and startup clearance). He is responsible to set the clearance received flag and the startup state.
**Coordinator:** The coordinator has the following duties:
- Check and editing flightplans (routing, set SID, initial climb, Squawk etc.) and for the correct ICAO callsign
- Run **vSID** in auto mode (manual mode can be used as well if prefered)
- **Datalink** clearances (via Topsky). Enter the ATIS code you have transmitted to the pilot into the Euroscope Remarks to indicate, that a DCL clearance has been sent.
- **Text communication** (e.g. with textpilots on frequency chat and via private message prior clearance request)
- Coordination with other stations (e.g. Tower)
**Flightplan editing:** Additionally if there are any errors inside the flightplan that need to be corrected (e.g. the routing), the coordinator should clarify this issues with the pilot by private message prior clearance request, not on frequency! Only if the flightplan is checked, edited and corrected the squawk should be set. That indicates the operator that the clearance can be issued.
**Enroute Clearance:** Before issuing the enroute clearcance the operator should check the ES remarks and the flightplan checker (FPC) if there is still any problem with the flightplan, especially if the Squawk is already set. If the Squawk was accidentally set by the coordinator and no clearance should be issued, use 0000 as manual Squawk until the flightplan is corrected.
**Startup Approval:** Both controllers should have the [vSID startup counter](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/link/1235#bkmrk-startup-counter "vSID Controller Manual") open. Startup should only be issued when the amount of active startup approvals is below a certain level (see below). Startup will be issued on the "first come, first served" basis. To optimice the outbound flow minor deviations from this rule are possible. **Caution:** manuall confirming the SID (left click) will assign a Squawk.
**Request queue:** For the clearance and startup request queue the vSID plugin request function has to be used.
### Optimal decision making - Capacity
To make the right decisions it is important to know what the maximum capacity of the airport at all, runways and single sectors are.
However, it is highly recommended to keep in mind that human (especially controller) capacity is variable and therefore a huge factor in defining a movement cap for specific frequencies or runways.
| **Outbound EDDF** | **Inbound EDDF** |
| **RWY 18** | 40 / hr
every 2 min + 10 extra movement
| **staggered** | 35 - 40 / hr |
| **RWY 25C / 25L** | 25 / hr
every 3 min + 5 extra movement
| **parallel independent** | 50 - 60 / hr |
| **RWY 07C / 07R** | 40 / hr
every 2 min + 10 extra movement
| **single runway** | 25 - 30 / hr |
| **Sector FS**: 8 - 10 at the same time |
| **Sector FN**: 10 - 12 at the same time |
| **Airport**
| **Runway**
| **max. active Startups**
|
| **EDDF**
| 25
| 10 - 12
|
| 07 / 18
| 15
|
| **EDDK**
| ALL
| 12
|
| **EDDL
| one active runway
| 10
|
| two active runways
| 13
|
| **EDDS
| 07
| 8 - 10
|
| 25
| 10 - 12
|
With a **single runway** a maximum of 30 movements per hour (Inbounds and Outbounds) can be expectetd to handle. Depending on the overall situation (e.g. during LVO), the capacity need to be reduced.
### Controller groups
#### Tower/Delivery
It is highly recommended to split TWR/DEL coordinator positions into two separate ones whenever possible. DEL/TWR Coordinator is responsible to monitor the amount of outbound traffic.
TWR/DEL Coordinator should keep the following things in mind:
- It will take some time until you will see an effect of the regulations at the holding points, so you need to work and look in advance.
- During high outbound rushs the primary used runway for inbounds may be changed to have more space for the outbounds.
- Let the holdingpoint never run empty when regulating traffic.
- Especially during high traffic loads do not deviate from the default SID assignment. Exceptions are only if the outbounds that deviate from default will stay completely independent from each other. Otherwise the APP/CTR Controllers will have a highly increased workload!
### Approach/Center
It is highly recommended to split APP/CTR coordinator positions into two separate ones whenever possible.
- When using Holdings, CTR Coordinator is responsible for them and he should calculate times or amount of orbits.
- Coordinate when and how to exit the holdings.
- APP coordinator needs to decide when the APP stations can accept traffic again (final should never run empty!).
- APP coordinator is responsible to use all APP stations' capacity accordingly (e.g. FN/FF and FS/FU sectors regarding north and south arrivals).
"**EDGG Co**" Euroscope profile should be used. Change the Tag to "EDGG Co" to see inbound/outbound traffic to the active airports highlighted.
### Teamspeak Setup
Coordinators identify themselves with the Teamspeak function "Channel Commander". Continuous coordination within numerous Teamspeak channels can be distracting for active controllers. With the "Whisper" function they will be able to coordinate with all other channel commanders without leaving the channel or disturbing other controllers.
Tools (Extras) => Whisper Lists => Set Hotkey (e.g. "ALT" or ENDE") | Whisper to "Groups" | Group Whisper Type "Channel Commander" | Group Whisper Target "Complete Channel Family"
[](https://knowledgebase.vatsim-germany.org/uploads/images/gallery/2022-10/edff-teamspeak-whispern.PNG)*Teamspeak Whisper List Setup*