Visual separation
Visual separation refers to two possibilities of separation used in different cases. There is visual separation in the vicinity of aerodromes (relevant for the tower controller, depending on the situation possibly also for the approach controller) and there is the delegation of separation to the pilot during descent or climb (relevant for the approach controller).
Visual separation in the vicinity of aerodromes
TheIn specifiedthe vicinity of an aerodrome, the prescribed radar separation (not the wake turbulence separation or runway separation!) between two aircraft may be reduced inif:
1. the vicinity of the aerodrome if:
- adequate separation can be maintained by the tower controller, provided that
hetheycan seehave both aircraft in sight continuously andgivestraffic information is issued to at least one aircraft or
2. both pilots havesight ofeach other in sight and report that they can maintain adequateseparation,separation or- if one aircraft is following
the other,another, the pilot of thefollowingsucceeding aircraft reports thathetheycan seehave thefrontpreceding aircraft in sight and can maintain adequateseparation.
3.
The terms “vicinity of the aerodrome” and “adequate separation” are not defined in detail. Therefore, this procedure should be used sensibly. Examples are a swing-over in Frankfurt from the 25L to the 25C if a pilot is simultaneously approaching the 25R in parallel or the avoidance of a missed approach if there is a risk of falling below the minimum separation.
| G: DLH123, traffic, A320, 2 o'clock, report in sight and able for own separation |
| A: DLH123, traffic in sight and able |
| G: DLH123, cleared visual approach runway 25C, in case of missed approach, climb on runway track to 5.000 feet, maintain own separation to mentioned traffic |
Another regular use case for this type of visual separation is multiple consecutive departures in different directions.
Here's an example: GWI9086 turns directly north after departure from runway 23L, whereas SWR3BZ initially flies straight ahead. The departures thus turn away from each other quickly. In this configuration, the radar separation may be reduced if the TWR sees both aircraft according to point 1 and issues traffic information to the following departure. This means the takeoff roll of the following departure can already begin as soon as (reduced) runway separation is ensured. There is no prescribed minimum separation in the air.
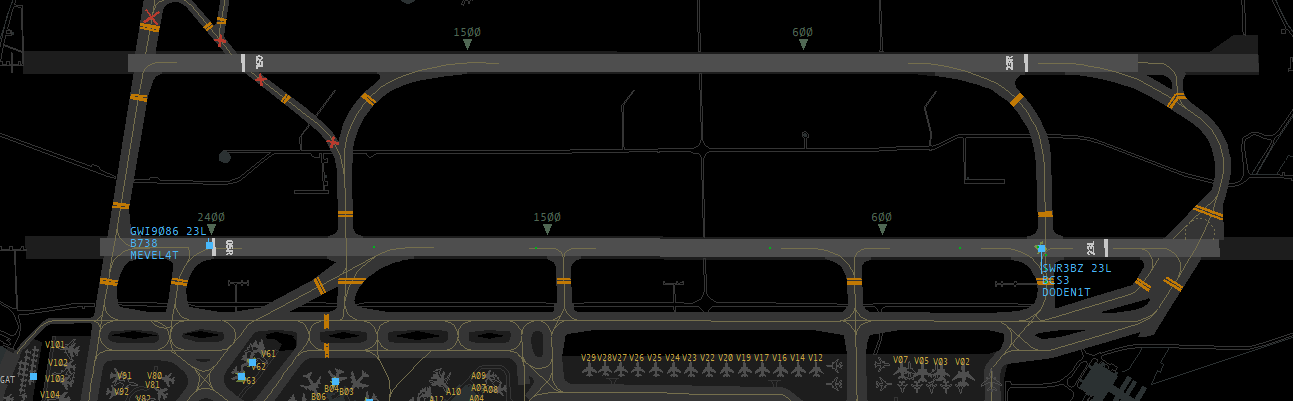 GWI9086 has just passed the 2400m marker, thus reduced runway separation exists and SWR3BZ can begin the takeoff roll.
GWI9086 has just passed the 2400m marker, thus reduced runway separation exists and SWR3BZ can begin the takeoff roll.
Since the TWR on Vatsim cannot actually look out the window, weather conditions under which this procedure can be applied are defined in the SOPs of the respective airport (e.g. only in VMC).
It is important that the following aircraft remains on the tower controller's frequency until 3 NM / 1000 feet are ensured. Therefore, the pilot must be told before departure to remain on the TWR frequency (except at airports where this is standard practice). As soon as the 3 NM / 1000 feet are ensured, the pilot can switch to the departure controller
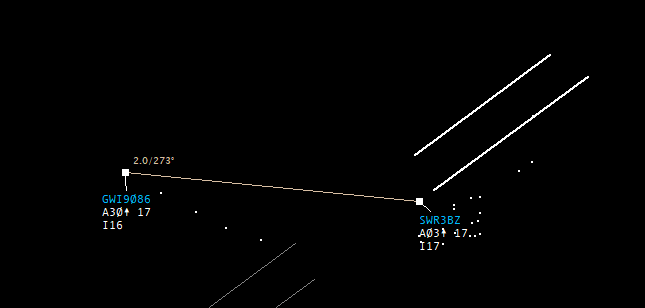
When SWR3BZ is airborne, the distance is initially < 3 NM, thus SWR3BZ must remain on the TWR frequency (although here it is more than 1000 feet, however it is not ensured that this will remain the case).
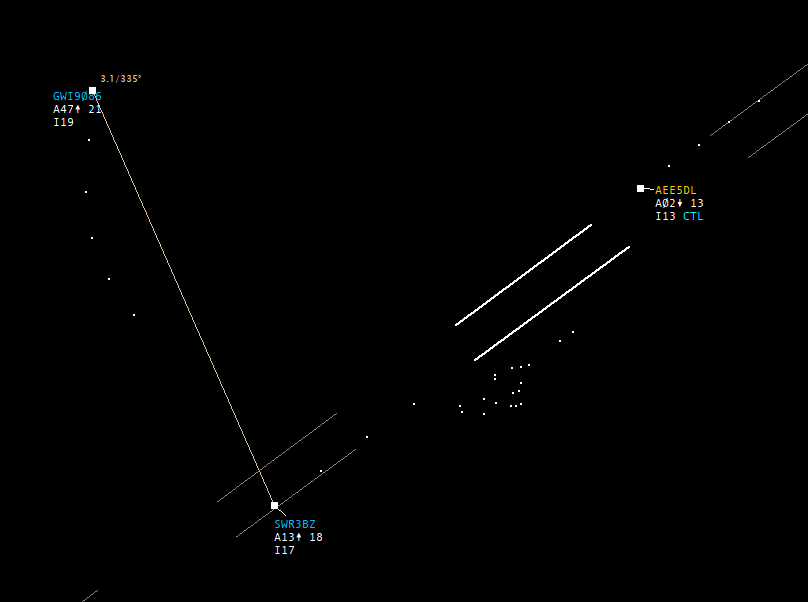
A short time later, due to the different departure routes, the 3 NM are ensured. Now SWR3BZ can be handed over to the radar controller.
| Phraseology example: Visual Separation between Departures |
| G: SWR3BZ, after departure remain on this frequency, preceding Boeing 737 on a diverging SID (alternatively e.g.: preceding Boeing 737 turning right 1 mile end of runway), wind..., runway 23L cleared for takeoff. |
| A: SWR3BZ, roger, cleared for takeoff runway 23L. |
Delegation of separation during climb or descent
Under certain conditions, the responsibility of maintaining separation between two flights requiring separation may be delegated to the pilot. The conditions are:
- Daytime
- Below FL100
- Airspace E or D
- VMC
- Only during climb or descent
- Both pilots involved agree to the procedure
| Funkbeispiel Own Separation - CLB/DES |
| G: DLH123, REPORT FLIGHT CONDITIONS AND LEVEL |
| A: DLH123, VMC, FL80 |
| G: DLH123, TRAFFIC IS PA42, 1 O'CLOCK 5 MILES SAME DIRECTION, 1000 FEET BELOW, REPORT IN SIGHT |
| A: DLH123, TRAFFIC IN SIGHT |
| G: DLH123, ADVISE ABLE TO MAINTAIN OWN SEPARATION UNTIL PASSING FL60 |
| A: DLH123, AFFIRM |
| G: DEHHH, TRAFFIC 7 O'CLOCK 5 MILES AIRBUS 320 HAS YOU IN SIGHT. MAY HE DESCEND THROUGH YOUR LEVEL MAINTAINING OWN SEPARATION |
| A2: DEHHH, AFFIRM |
| G: DLH123, DESCEND 5000 FEET QNH1013, MAINTAIN OWN SEPARATION AND VMC UNTIL PASSING FL60 |
| A: DLH123, DESCENDING 5000 FEET QNH1013, MAINTAINING OWN SEPARATION AND VMC UNTIL PASSING FL60 |
| G: DLH123, DEHHH, CLEAR OF TRAFFIC |
