Tower
Hamburg Tower is responsible for all arriving and departing traffic. The top level of the airspace D controlzone is 2500ft MSL. Above this altitude, airspace C covers this area around Hamburg within responsibility of Hamburg East/West Approach.
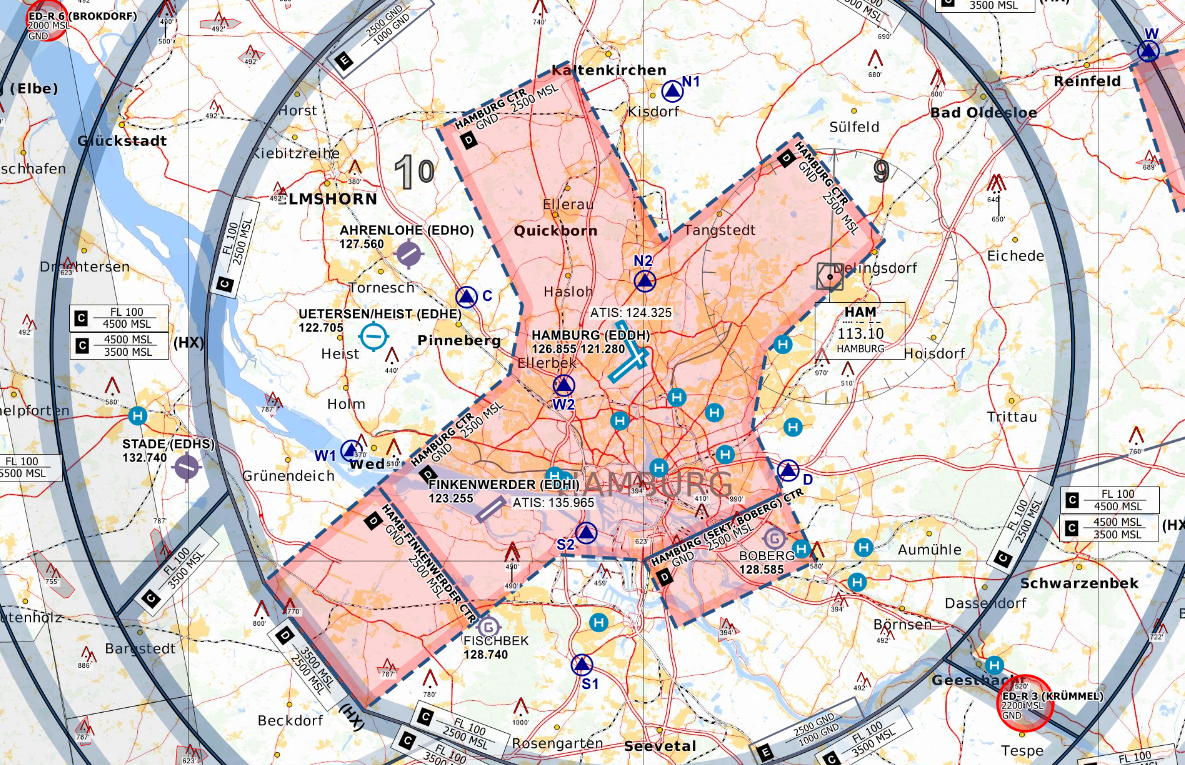 Controlzone of Hamburg Airport - © openflightmaps.org
Controlzone of Hamburg Airport - © openflightmaps.org
Finkenwerder: In the west side of the controlzone is the Airbus Airport Finkenwerder EDHI. Traffic to and from Finkenwerder can cause critical situations in Hamburg. The responsible radar controller will give information about traffic. It may be necessary to:
- clear VFR aircraft in the area
- hold back departures, in coordination with radar
Additionally, when EDHI_TWR is unstaffed the whole aerodrome or some procedures (e.g. VFR from EDDH for one touch and go in EDHI) can be delegated from radar to Hamburg Tower.
Hamburg CTR, Boberg Sector: only active at 33 arrivals or 15 departures
Ham-Finkenwerder CTR: only active with traffic in EDHI - airspace is in responsibility of Finkenwerder Tower (or Hamburg East Approach top-down)
Runways
Hamburg has a dependent crossing runway system with two runways.
Preferred Runway Config: 23 arrival and 33 departure is preferred and is used as long as possible (5kt tailwind component, pilot reports). All other runway configurations decrease your efficiency, increase target spacing for arrivals and causes more congestions on the ground.
Helper: EDDH Wind/Runway Chooser
Specialties
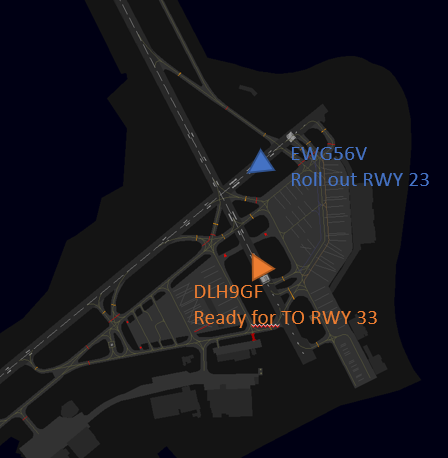
Visual example
blue = landing traffic RWY 23, orange = traffic ready for departure RWY 33
 |
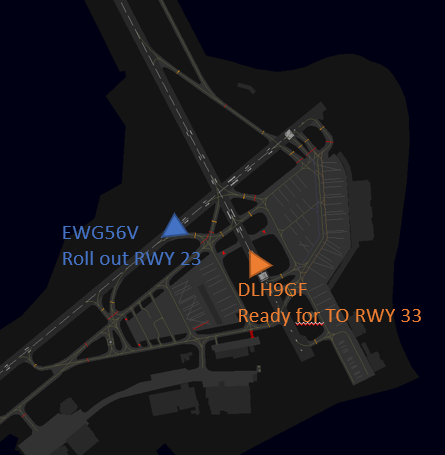 |
| Runway 33 blocked! | Runway 33 clear, a take-off clearance can be issued |
Crossing Runway Wake Turbulence Separation
Due to the position of the runway cross and the distinct system of separated landing and departure runways, there are only two situations which need to be watched for crossing wake turbulence separation:
- 05 or 15 departure with a go-around on the other runway. Departure needs to be delayed anyway due to missed approached procedure leading to HAM VOR!
- 33 light type departures before the runway cross. Prefer to assign intersection D9/A6 at the runway cross
Area of Responsibility
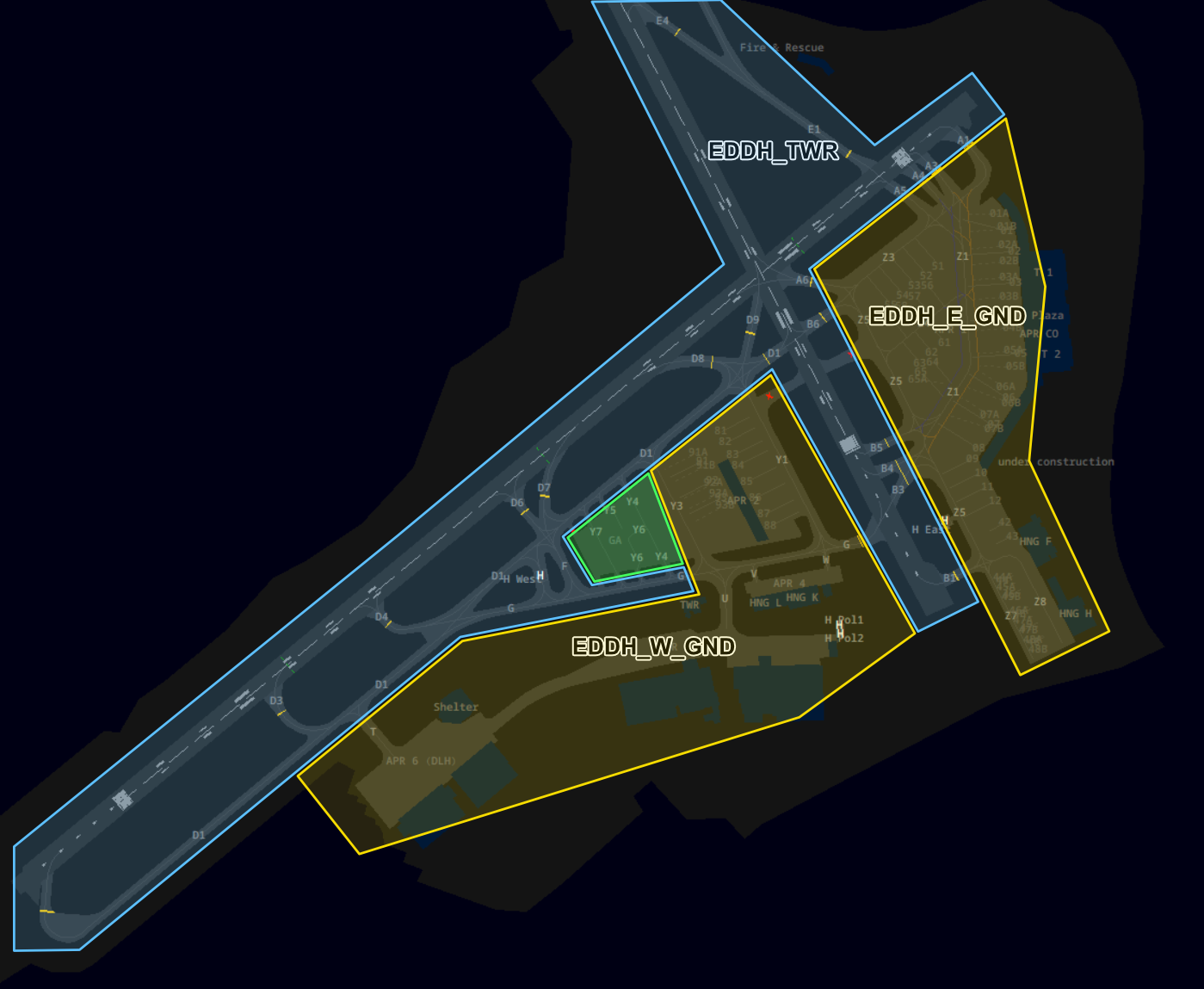 Additionally in Euroscope: Ground View > Functions > Maps > AoR
Additionally in Euroscope: Ground View > Functions > Maps > AoR
Movement at GA delegated to Tower (green area): Taxiing out of and into the general aviation parking area is delegated to tower to ensure a steady traffic flow. Parking positions are not assigned to arriving traffic. Outbound traffic should be handed off to tower when they report ready for pushback or taxi, whichever comes first.
Departures
Auto-Handoff: Hamburg has an auto-handoff to the departure frequency when passing 2000ft, as stated in the charts. A short "bye bye" at the end of the take-off clearance can help vPilots to get the hint.
Spacing: Departures shall be separated with a minimum of 3nm or wake turbulence separated, whichever is greater. When two aircrafts have the same SID the separation shall be increased to 5nm or wake turbulence separation whichever is greater. Different aircraft performances and climb speeds need to be taken into account.
Efficiency: Try to sequence departures with alternating SID directions, left/right in relation of the runway track. In case of two westbound departures (different SIDs) out of runway 33, more spacing (5nm) is preferred but not mandatory, as all aircrafts fly the same route until ELSOB.
As there are distinct landing and departure runways, use lineups constantly to issue take-off clearances as soon as possible.
Arrivals
Approaches: By default, the ILS Approach is used for all arrivals, except runway 33 or coordinated otherwise.
Runway 23 (very often): The target spacing is only 3nm on runway 23. In high traffic situations pilots need to vacate as soon as possible. Most of the time the phrase "taxi left via D1, hold short of runway 33" is used.
Runway 15 (regularly): The first exit is E4 to the left. Depending on the spacing on the final and planed parking position, long rollouts might be instructed to vacate left via D6 or right via D9.
Runway 05 (some times): Same as runway 23 pilots should vacate as soon as possible and be guided onto D1. In this case to have enough time for departures out of runway 33 before the next arrival is on short final.
Runway 33 (only at very strong winds): This RNP only approach is being avoided as long as possible as its path is directly above Hamburg city. All arriving traffic will taxi via E1 to hold short of runway 23 within the responsibility of the tower.
One of your primary objectives with arrivals is to keep the runways useable. Unfortunately some vPilots will hold before the holding line blocking the runway, unless you keep them rolling. Issue taxi instructions as soon as possible.
Handover to apron will take place as early as possible, at the latest when reaching the boundary of responsibility.
Missed Approaches
In case of an unplanned missed approach, the Tower controller shall inform Hamburg East Approach immediately. Traffic will be handed over to Hamburg East Approach after coordination.
The next departure is always subject to release, if not coordinated otherwise (Departure Release).
Efficiency
Reduced Runway Separation (RRS): Reduced Runway Separation can be applied on both runways for all categories.
Sequencing traffic: Keep up clearances and rolling instructions. A good sequence on default config (23/33) looks like:
- Landing Clearance runway 23
- Lineup runway 33
- Cross D1 traffic at runway 33 and send to East Apron
- Takeoff Clearance runway 33
- Taxi arrival on D1 hold short runway 33
VFR
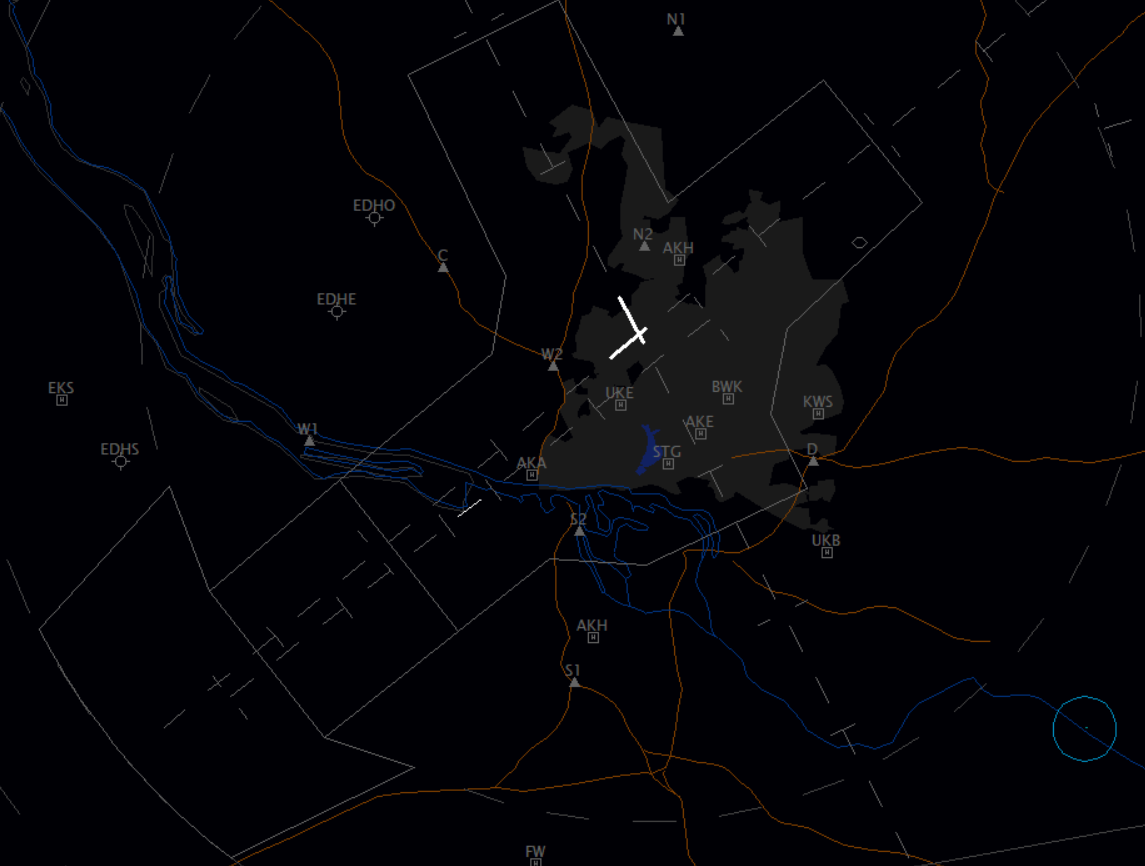
Hamburg offers several options for traffic under VFR. There are published holding patterns north and south of runway 05/23 and east of runway 15/33. (Caution: not every virtual pilot is familiar with these holdings)
| VRP | NAV |
|---|---|
| N1 | East abeam Kisdorf/Henstedt-Ulzburg |
| N2 | Large roundabout at federal street B432 |
| D | Highway junction A1 and A24 |
| S1 | Highway junction A7 and A261 |
| S2 | Bridge Köhlbrandt "Köhle" |
| W1 | Marina/Yachthafen Hamburg, River Elbe |
| W2 | Highway junction A7 and A23 |
| C | Highway exit A23 Pinneberg-Nord, Radio Tower |
VRPs W2 + N2: these reporting points are pretty close to the runways. Be careful and respect the current runway config. Possible landing, departing and go-around traffic.
Finkenwerder: Good coordination between tower and approach is needed in case of traffic at EDHI Finkenwerder.
VFR Departure Efficiency: Take into consideration where the traffic is leaving the CTR and avoid an unnecessary runway overfly after take-off. For example at 23/33: VFR leaving the CTR to the south can better be departed from runway 23 without blocking the departure sector or a runway overfly / crossing the final.
VFR Traffic Circuits: Try to use the traffic circuit of the landing runway without crossing the departure runway. This avoids most of the wake turbulence separations and departure delays.
Examples:
- traffic circuit 23 behind 33 departures
- right traffic circuit 05 behind 33 departures
- traffic circuit 15 behind 23 departures
VFR - Tower (EDDH_VFR_TWR)
Tower, East Apron, and Delivery need to be online before the VFR Tower can be staffed.
Usually only staffed at the Hamburg Harbor Festival and the Overload Real-life Event.
In reality the Hamburg VFR Tower is a station to provide precise traffic information using radar coverage and to organize the VFR traffic flow efficiently. Its area of responsibility includes all VFR flights in the area of the control zone, as well as entry/exit/through flights. Traffic circuits and runway clearances remain the responsibility of the normal EDDH_TWR.
In order to provide traffic information with exact and verified altitude information, the EDDH_VFR_TWR may assign squawks and delegate the squawk assignment for departing traffic from Hamburg to Apron/Tower. Departures are handed over to the radar tower after takeoff. Individual arrangements can be made for handovers of approaches to Hamburg but for certain runway configurations the Outer Alster is recommended as a visual reference point in the south of the airport.
The efficient handling of traffic can only be guaranteed through good cooperation and coordination between the tower and the radar tower.
Helicopters
Departures directly from the parking position are not permitted. All helicopter traffic needs to air-taxi from and to the helipad, except helicopters based at the police station.
Helipad West: Main arrival/departure point for helicopters in Hamburg.
Helipad East: Helipad East between B1 and B3 is not used that often or is closed via NOTAMS. Prefer using Helipad West.
Police helicopters: The police helicopters are based at Hamburg Airport east of apron 5 (H Pol1 / H Pol 2), Callsign "Libelle". These helipads are not reachable via air-taxi and can only be used for direct arrival/departures. Pilots will communicate directly with the tower.
Rescue helicopters: There are no rescue helicopters located at the airport but within the area of the tower control zone. In EuroScope the surounding hospitals with helicopter platforms are displayed as:
- AKA = Asklepios Klinik Altona
- AKE = Schön Klinik Eilbek (ehm. Asklepios Klinik Eilbek)
- AKH = Asklepios Klinik Nord (Heidberg)
- BWK = Bundeswehrkrankenhaus - Station of CHX29 (ehm. SAR71 = CS/MEDEVAC+REG)
- KWS = Kath. Kinderkrankenhaus Wilhelmstift
- STG = Asklepios Klinik St. Georg
- UKB = BG Unfallklinikum Boberg - Station of CHX50 (Hansa)
- UKE = Universitätsklinikum Eppendorf
Low Visibility Operations (LVO)
When the weather condition requires low visibility operations the use shall be announced in the ATIS. At runway 23 the CAT II / CAT III needs to be used.
use &lvp in the ATIS maker URL or "LOW VIS OPS" flag in the NOTAM menu of vATIS
During low visibility operations, the departure and arrival spacing is increased. Delays may be issued earlier than in normal conditions. Additionally, under low visibility operations runway 33 or 23 shall be used for departures and 23 for arrivals.